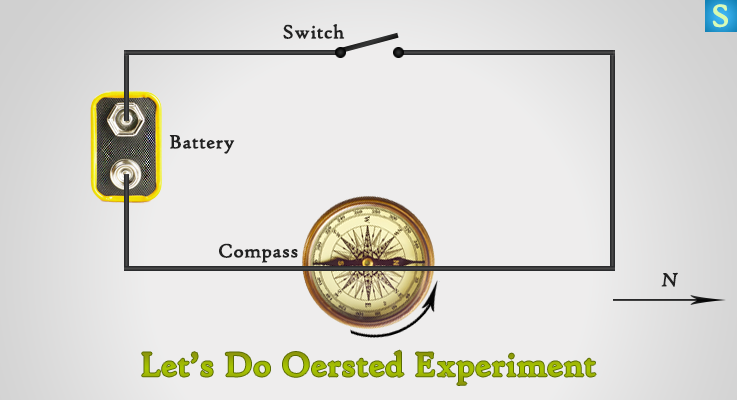
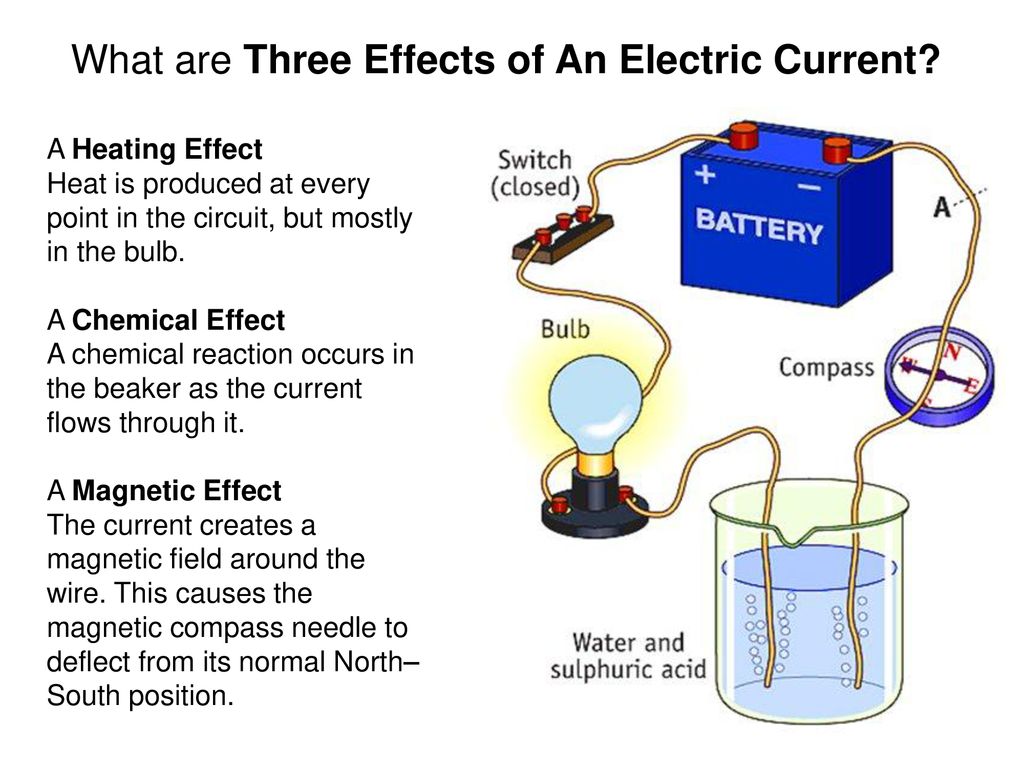
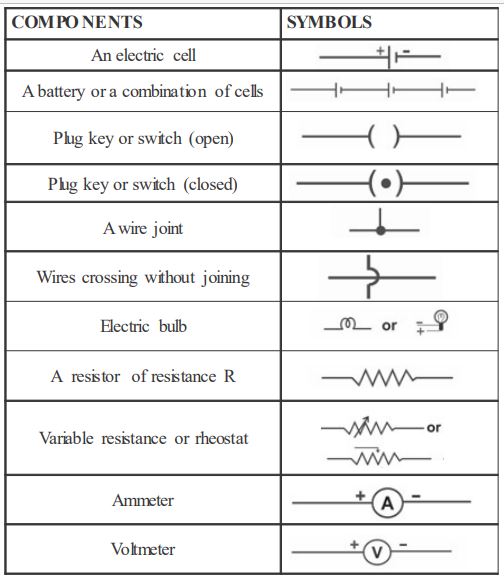
An electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. It is an essential aspect of how electricity is used and transmitted in our modern world. There are several effects of an electric current that are important to understand, including its ability to produce heat, magnetism, and chemical reactions.
One of the most noticeable effects of an electric current is the production of heat. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it can cause the conductor to heat up. This is because the movement of the electric charges within the conductor creates a form of resistance, which can cause the conductor to become hot. This effect can be useful in a variety of applications, such as in electric heaters or in soldering irons. However, it can also be dangerous if the conductor becomes too hot, as it can cause fires or other accidents.
Another effect of an electric current is the production of magnetism. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field around the conductor. This is because the movement of the electric charges creates a magnetic force, which can attract or repel other magnetic materials. This effect is used in a variety of applications, such as in electric motors and generators, which use the magnetic force produced by an electric current to create mechanical energy.
Finally, an electric current can also produce chemical reactions. For example, an electric current can be used to break down water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, a process known as electrolysis. This effect is used in a variety of applications, such as in the production of hydrogen fuel for vehicles. An electric current can also be used to produce chemical reactions in other materials, such as in the electroplating process, where a metal is deposited onto another surface using an electric current.
In conclusion, an electric current has a variety of effects that are important to understand and utilize in our modern world. It can produce heat, magnetism, and chemical reactions, which are used in a variety of applications, from electric heaters to hydrogen fuel cells. Understanding these effects is essential for the safe and effective use of electricity.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/electric-shock-causes-effects-and-treatment-options-5209616_final-7cd6292742174d4393350d10a669566f.gif)