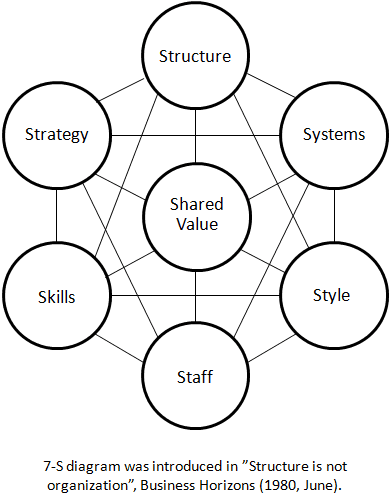
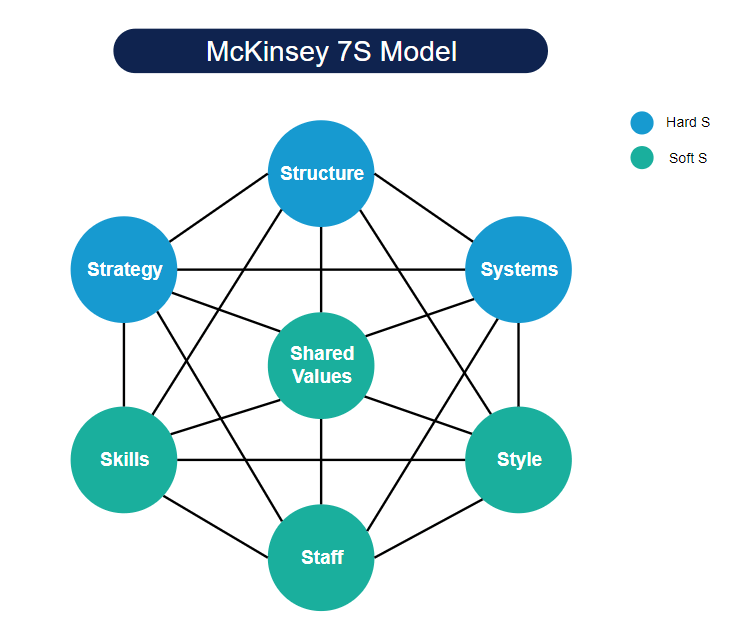
The 7s model, also known as the McKinsey 7s model, is a framework for organizational design and effectiveness. It was developed by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman, two consultants at McKinsey & Company, in the 1980s. The model suggests that there are seven interdependent factors that need to be aligned in order to ensure that an organization is functioning effectively. These seven factors are: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills.
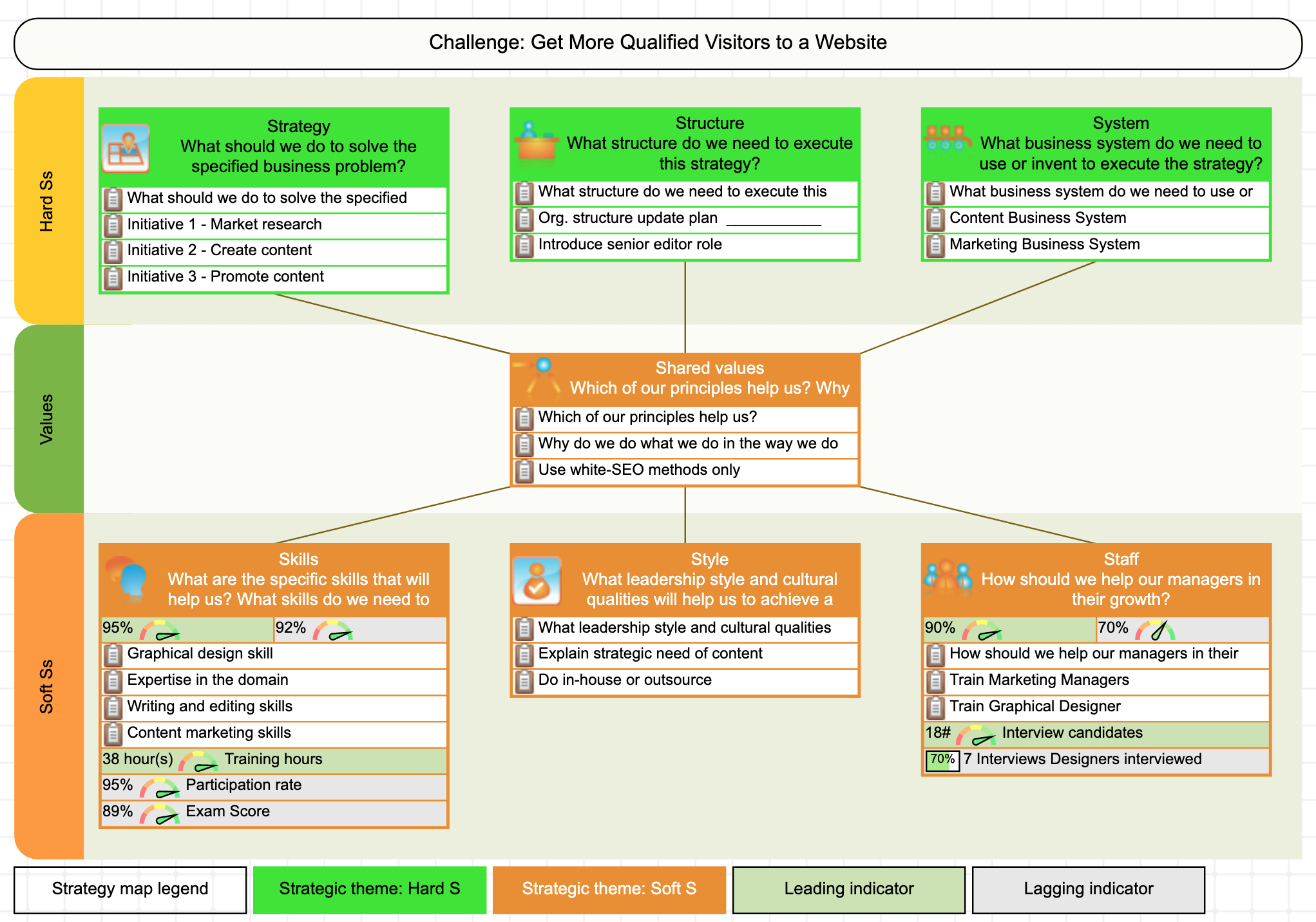
The first factor, strategy, refers to the long-term plan or direction of an organization. This includes the goals and objectives that the organization has set for itself, as well as the specific actions it will take to achieve those goals. For example, a company might have a strategy of expanding into new markets by acquiring smaller competitors.
The second factor, structure, refers to the way in which an organization is organized and the way that tasks and responsibilities are divided among its members. This includes the formal hierarchy of an organization, as well as the informal networks and relationships that exist within it. For example, a company might have a hierarchical structure with clear lines of authority, or it might have a more decentralized structure with greater autonomy for individual teams.
The third factor, systems, refers to the processes and procedures that an organization uses to get things done. This includes everything from the systems for communication and decision-making, to the systems for tracking and measuring performance. For example, a company might have a system in place for reviewing and approving new projects, or a system for tracking customer satisfaction.
The fourth factor, shared values, refers to the values and beliefs that are shared by the members of an organization. These values serve as a guiding force for the organization and help to shape its culture and behavior. For example, a company might have a strong commitment to sustainability, or a focus on innovation and creativity.
The fifth factor, style, refers to the leadership style of an organization and how it influences the behavior of its members. This includes the way that leaders communicate and interact with their subordinates, as well as the way that they make decisions and solve problems. For example, a company might have a more directive leadership style, with leaders making decisions for their subordinates, or it might have a more participative style, with leaders seeking input and collaboration from their team members.
The sixth factor, staff, refers to the people who work for an organization and the roles and responsibilities that they have. This includes not just the technical skills and expertise that they bring to the organization, but also their attitudes and behaviors. For example, a company might have a staff that is highly skilled in their specific areas of expertise, but also has a strong commitment to teamwork and collaboration.
Finally, the seventh factor, skills, refers to the specific skills and capabilities that an organization has developed over time. These skills can be technical, such as expertise in a particular industry or technology, or they can be more general, such as strong problem-solving or communication skills. For example, a company might have developed a strong expertise in data analytics, or it might have a track record of successful project management.
Overall, the 7s model is a useful tool for analyzing and improving the effectiveness of an organization. By considering each of the seven factors and ensuring that they are aligned, organizations can identify areas for improvement and take steps to become more efficient and effective.