A plant with the genotype aabbcc is a plant that has a specific set of genetic traits. Genotypes refer to the genetic makeup of an organism, and they can be represented by a series of letters or other symbols. In this case, the genotype aabbcc refers to a plant that has two copies of the "a" allele, two copies of the "b" allele, and two copies of the "c" allele.
There are a few things that we can infer about this plant based on its genotype. First, it is likely that the "a" and "b" alleles are dominant over the "c" allele. This means that if the plant has any traits associated with the "a" or "b" alleles, they will be expressed in the plant's phenotype (the observable physical traits of the plant). The "c" allele, on the other hand, may be recessive, meaning that it will only be expressed if the plant has two copies of it (one from each parent).
It is also possible that the "a", "b", and "c" alleles are all codominant, meaning that they all contribute to the plant's phenotype in some way. In this case, the plant would have a unique set of traits that is a combination of all three alleles.
Overall, a plant with the genotype aabbcc is likely to have a specific set of genetic traits that are influenced by the "a", "b", and "c" alleles. These traits could include things like the color of the plant's flowers, the shape of its leaves, or the size of its fruit. Understanding the genotype of a plant can help us predict what it will look like and how it will behave, and this knowledge can be useful for plant breeders and horticulturalists.
Given a parent plant with the genotype AaBbcc is mated with a plant with genotype AaBbcc,...

What are the most likely genotypes for the two blue budgies? To determine the genotype of a purple flowering plant of unknown genotype, you would cross. If an allele is dominant, it means that it will always be expressed phenotypically even if only inherited from one parent. Last Update: October 15, 2022 This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. If a person with achondroplasia mates with a person who does not have achondroplasia, what percentage of their children would be expected to have achondroplasia? What happened to the yellow pod characteristic in the F1 cross? How do you find the number of gametes produced? In the case of wheat kernel color, there is a range of color from red to pink to white depending on which alleles of the genes involved are dominant and which are recessive. The phenotypic ratio of the resulting offspring is 9:3:3:1. What is an F1 gamete? It is homozygous at two loci.
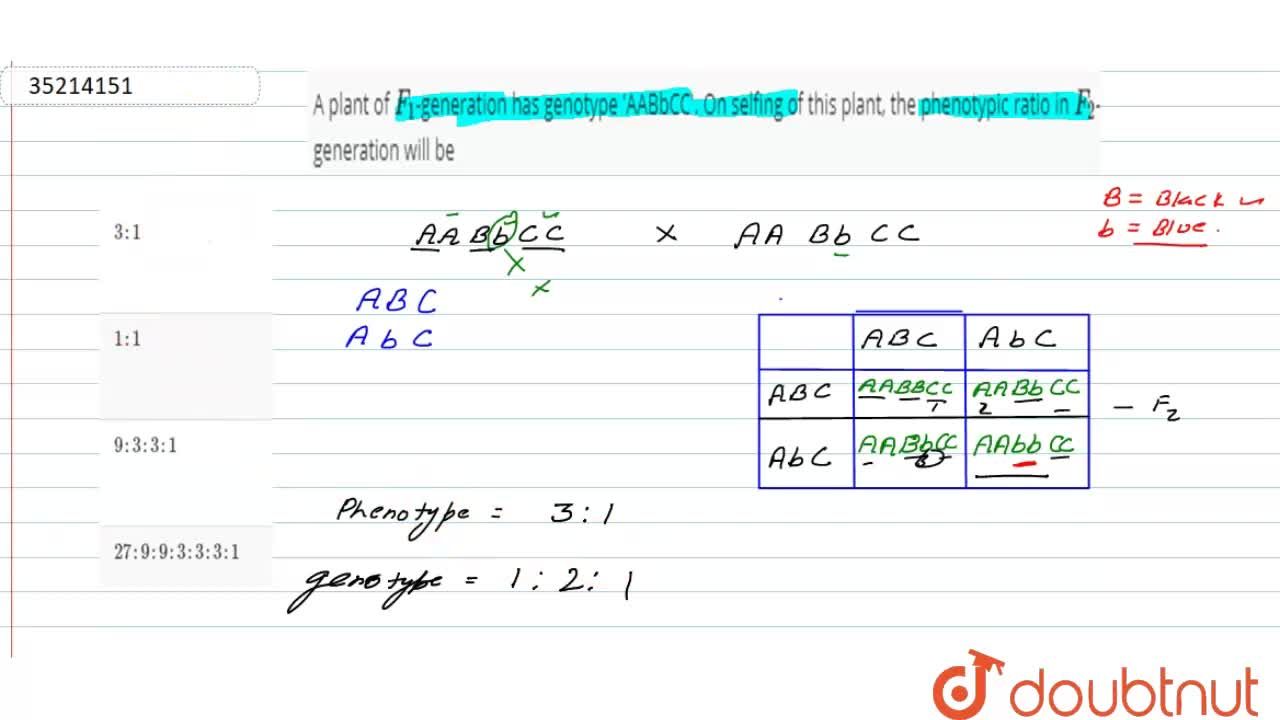
A plant of F 1 generation with genotype \"AABbCC\", on selfing of this plant, what is the phenotypic ratio in F 2 generation?
Now, we have got a complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested! It is important to understand though that many genes do not strictly follow Mendelian rules. Given a parent plant with the genotype AaBbcc is mated with a plant with genotype AaBbcc, what is the probability of an F1 offspring with the genotype aaBBCC? What role do the non-kinetochore microtubules play during mitosis? You have one tree that produces big yellow apples and another tree that produces small red apples. The plant with the genotype AaBbCc is a triploid plant. . Two EE individuals can only have EE offspring, so that probability is 1. Phenotypically AABBCC and AABbCC are same.
Chapter 14 Questions Flashcards by 💜 Languages
Cite this page as follows: "When an organism of genotype AaBbCc produces gametes, what proportion will be Abc, AbC, ABC, abc, abC, aBc. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns? The homozygous dominant genotype causes death, so individuals who have this condition are all heterozygotes. So the phenotypic ratio in F, generation will be 3 : 1. Twenty-five percent of their offspring exhibit hypophosphatemia. What are the genotypes of the parents? Philadelphia: USA, Saunders College Publishing.
Which of the following is true about a plant with the genotype AABbcc?

Which of the following phenotypes is possible for the father? How do you find the genotype of a Trihybrid cross? Full Answer: When Aabb is crossed with aaBb, the genotypic ratio of its offspring is 1:1:1:1. The Rh phenotype is recorded by stating "positive" or "negative" after the individuals ABO blood type. On selfing a plant of f1 generation? Multifactorial characters are influenced by environmental influences, so they are not strictly governed by Mendel's theory. Thus, t does not express itself in the heterozygous condition, that is when the Dominant T allele is present tallness. What can you say about the alleles for the parental traits? An example of a polygenic genotype is AABbcc in which there are three genes involved that together effect what the trait looks like. Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes, Y for pigment on the outside of the feather, and B for pigment on the inside of the feather. In this case, the dominant allele is the trait that will be seen.
When an organism of genotype AaBbCc produces gametes, what proportion will be Abc, AbC, ABC, abc, abC, aBc. Assuming there is incomplete dominance...
Homozygous recessive nn cacti have no spines at all. In order to talk about incomplete dominance and the chances of a particular type of phenotype, we have to talk about the actual offspring produced. If true-breeding red-flowered, long radishes long radishes are crossed with true-breeding white oval radishes, the F1 will be expected to exhibit which of the following phenotypes? The F1 generation results from the cross-pollination of two parent P plants, and it contains all purple flowers. Green pods G are dominant over yellow pods g and tall stems T are dominant over dwarf stems t. What would the genotypic ratio be if I crossed AABB and AABB? For instance, AA or aa would occur.
On selfing a plant of f1 generation? Explained by FAQ Blog

Table 2: Generation Data Produced by Monohybrid Crosses Possible Offspring Possible Offspring Genotype Genotypes Phenotypes Ratio 2:2 YG, Yg Yellow green, yellow red. In the parental P generation, one parent has green pods and dwarf stems and the second parent has yellow pods and tall. Thus, a total of four types of gametes are produced. Biology of Plants, 4th edition. For instance, his work led to the discovery of the concepts of dominance and recessiveness and the heterozygous and homozygous condition. .







