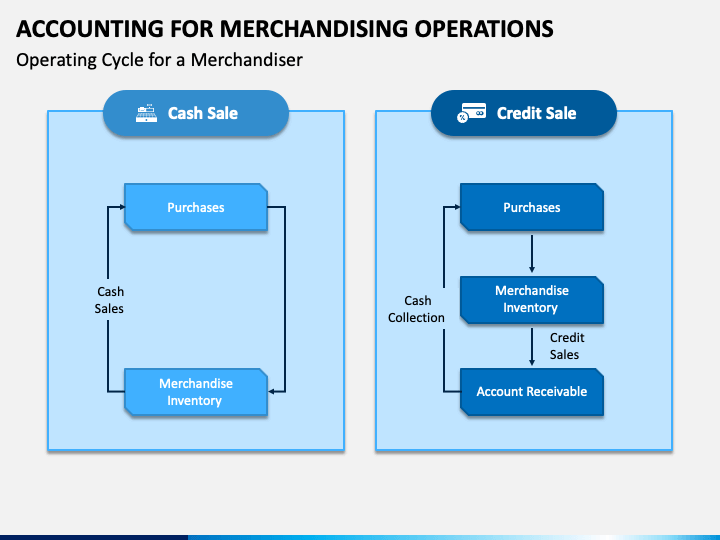
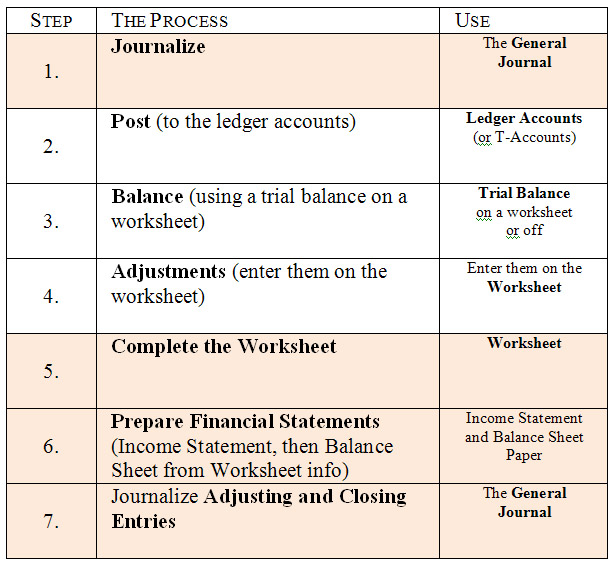
Accounting for merchandising operations involves the systematic recording, classification, and analysis of financial transactions related to the sale of goods. These transactions may include the purchase of inventory, the sale of goods to customers, and the returns and allowances made to customers. Proper accounting for merchandising operations is essential for businesses to accurately track their financial performance and make informed decisions about their operations.
There are several key concepts that must be understood in order to effectively account for merchandising operations. The first is the concept of inventory. Inventory refers to the goods that a business has available for sale to its customers. The cost of inventory includes the purchase price of the goods, as well as any additional costs associated with acquiring them, such as transportation and handling fees.
Another important concept in accounting for merchandising operations is the cost of goods sold (COGS). This represents the cost of the goods that were sold during a given period, and is calculated by subtracting the ending inventory balance from the beginning inventory balance, and adding any purchases made during the period. COGS is an important metric for businesses to track, as it represents the direct cost of generating revenue and can help to inform pricing and profitability decisions.
In addition to tracking inventory and COGS, businesses must also properly account for any returns and allowances made to customers. Returns and allowances may be made for a variety of reasons, such as defective goods or errors in the original sale. These transactions must be properly recorded in the business's financial records in order to accurately reflect the financial performance of the business.
Effective accounting for merchandising operations is essential for businesses to accurately track their financial performance and make informed decisions about their operations. By understanding key concepts such as inventory, COGS, and returns and allowances, businesses can accurately record and analyze the financial transactions related to their sale of goods, helping them to make informed decisions about their operations and achieve their financial goals.