Acid-base balance refers to the regulation of the pH of the body's fluids, including blood, extracellular fluid, and intracellular fluid. The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, with lower pH indicating a higher concentration of H+ and a more acidic solution, and higher pH indicating a lower concentration of H+ and a more basic or alkaline solution. The pH of the body's fluids is tightly regulated, as pH imbalances can have serious consequences for the body's functions.
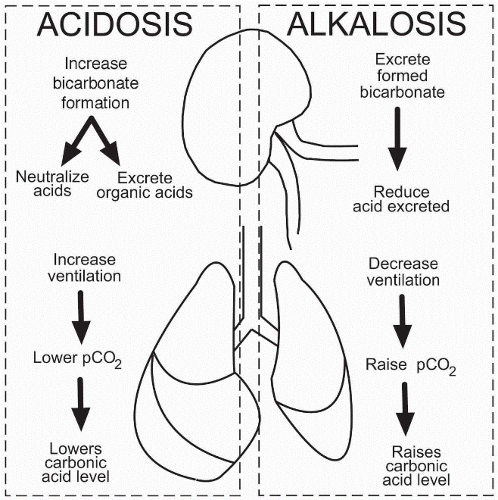
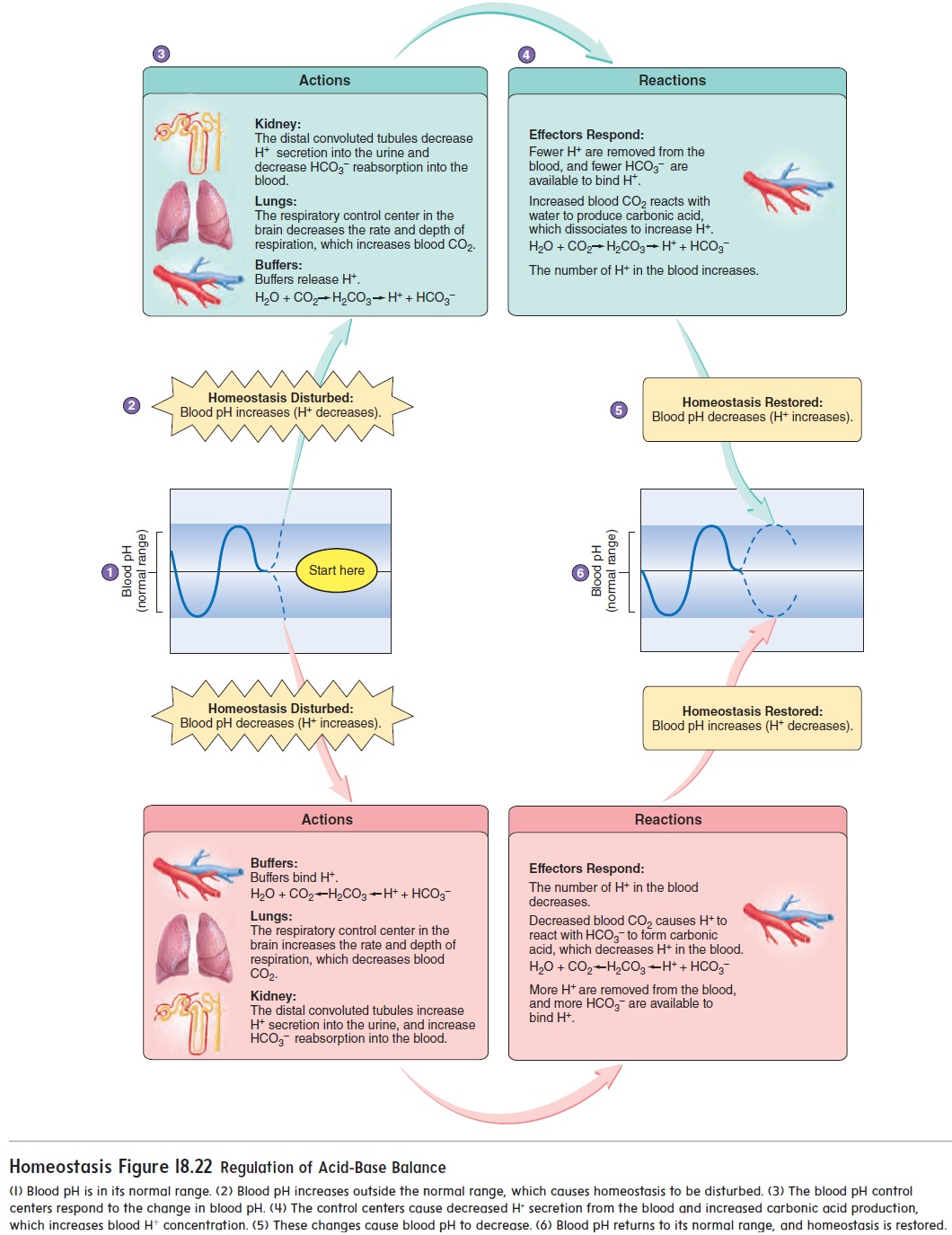
The body has several mechanisms in place to maintain acid-base balance. One important mechanism is the respiratory system, which helps to regulate the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the body. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, and when it is exhaled through the lungs, it helps to regulate the pH of the body's fluids. When the body is producing too much acid, the respiratory system increases the rate of CO2 excretion, which helps to decrease the concentration of H+ ions and raise the pH. Conversely, when the body is producing too little acid, the respiratory system decreases the rate of CO2 excretion, which helps to increase the concentration of H+ ions and lower the pH.
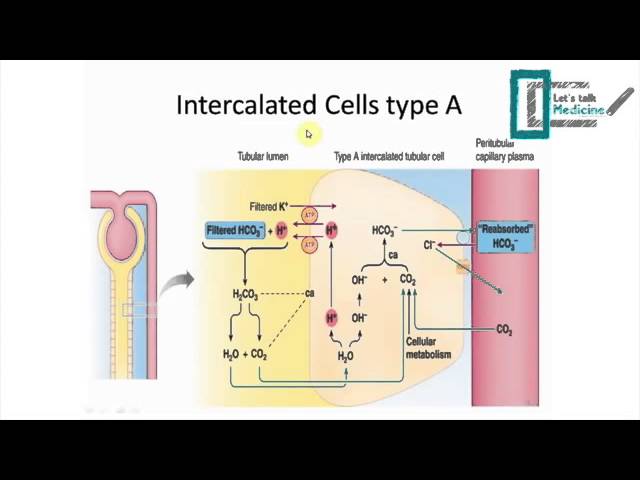
The kidneys also play a crucial role in maintaining acid-base balance. The kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood and removing excess acids or bases. They do this through the process of acid-base homeostasis, which involves the reabsorption and excretion of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). When the body is producing too much acid, the kidneys excrete more H+ ions and reabsorb more HCO3- ions, which helps to neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH. Conversely, when the body is producing too little acid, the kidneys excrete more HCO3- ions and reabsorb more H+ ions, which helps to neutralize the excess base and lower the pH.
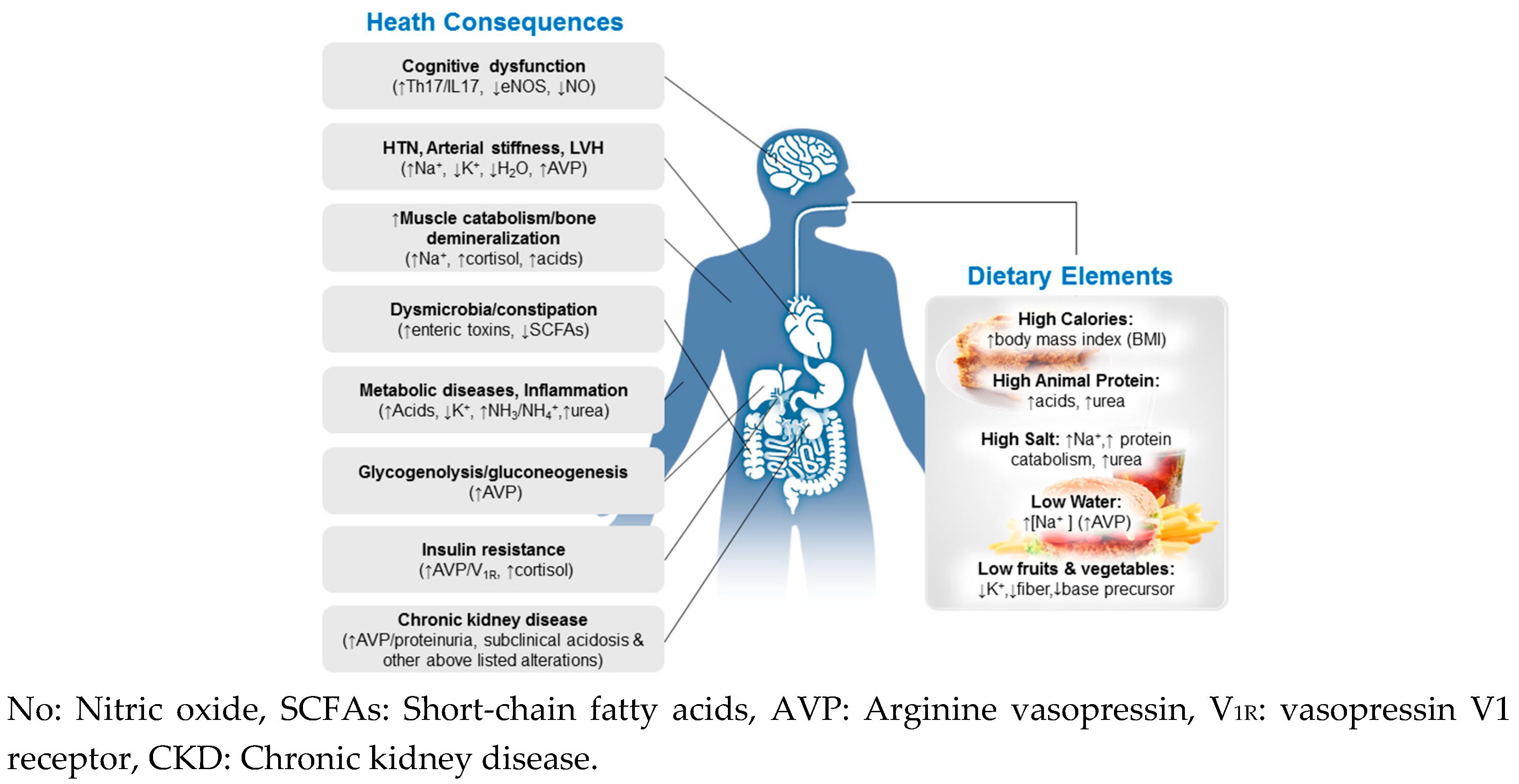
There are several factors that can affect acid-base balance in the body. One important factor is diet, as certain foods and beverages can affect the pH of the body's fluids. For example, a diet high in protein and dairy products can increase the production of acid in the body, while a diet high in fruits and vegetables can help to neutralize acid and raise the pH. Other factors that can affect acid-base balance include exercise, stress, illness, and medications.
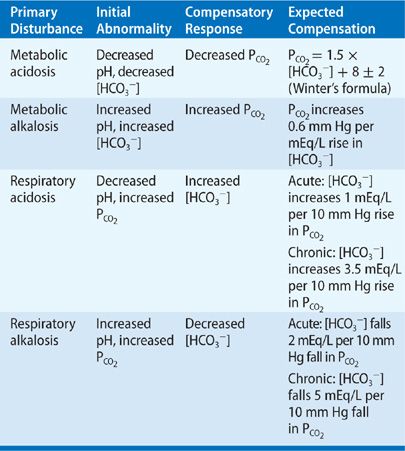
Acid-base imbalances can have serious consequences for the body's functions. Acidosis, which is characterized by an excess of acid in the body, can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, confusion, and shortness of breath. Alkalosis, which is characterized by an excess of base in the body, can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and muscle twitching. It is important to maintain proper acid-base balance in the body in order to support optimal health and well-being.