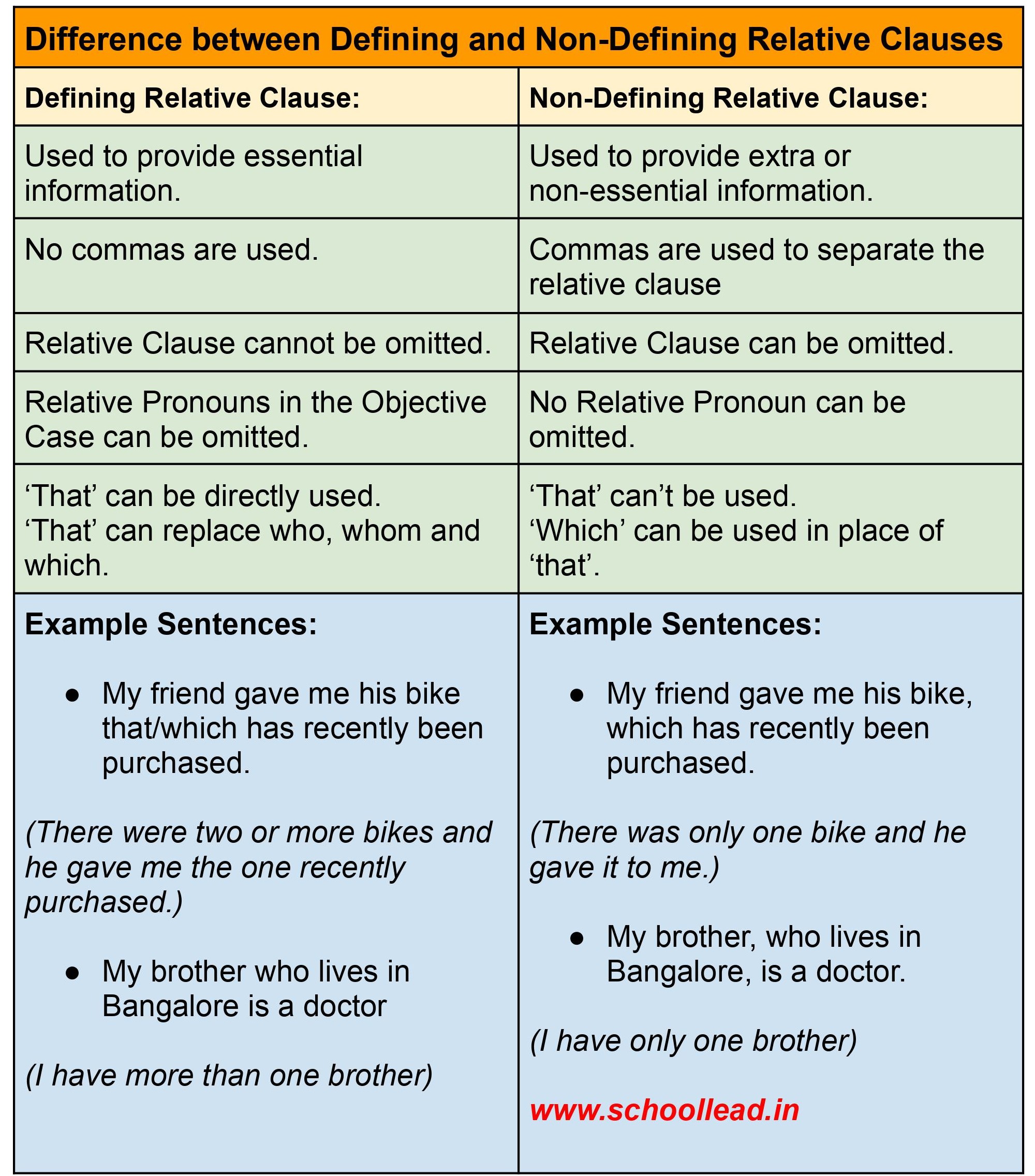
An adjective clause is a type of subordinate clause that functions as an adjective in a sentence. It provides additional information about a noun or pronoun in the main clause of the sentence. Adjective clauses are also known as relative clauses because they begin with a relative pronoun, such as who, whom, whose, that, or which.
Here are some examples of adjective clauses and their functions in a sentence:
- The man who is standing over there is my uncle.
- In this sentence, the adjective clause "who is standing over there" provides additional information about the noun "man," specifying which man is being referred to.
- The book which I read last night was really interesting.
- In this sentence, the adjective clause "which I read last night" provides additional information about the noun "book," specifying which book is being referred to.
- The people whom I met at the party were all very friendly.
- In this sentence, the adjective clause "whom I met at the party" provides additional information about the noun "people," specifying which people are being referred to.
- The woman whose car was stolen is very upset.
- In this sentence, the adjective clause "whose car was stolen" provides additional information about the noun "woman," specifying which woman is being referred to.
- The dog that I saw in the park was playing fetch with its owner.
- In this sentence, the adjective clause "that I saw in the park" provides additional information about the noun "dog," specifying which dog is being referred to.
It is important to note that adjective clauses must be essential to the meaning of the sentence and cannot be removed without changing the overall meaning. Non-essential adjective clauses, on the other hand, can be removed without changing the overall meaning of the sentence. These types of adjective clauses are usually set off with commas.
For example:
- The man, who was wearing a hat, waved at me as he walked by. (non-essential adjective clause)
- The woman whose car was stolen was very upset. (essential adjective clause)
In the first sentence, the adjective clause "who was wearing a hat" is non-essential because it does not provide crucial information about the noun "man." The sentence still makes sense without it. In the second sentence, however, the adjective clause "whose car was stolen" is essential because it specifies which woman is being referred to. Without this clause, the sentence would not make sense.
In summary, an adjective clause is a subordinate clause that provides additional information about a noun or pronoun in the main clause of a sentence. It is introduced by a relative pronoun and must be essential to the overall meaning of the sentence. Adjective clauses can also be non-essential, in which case they are set off with commas.