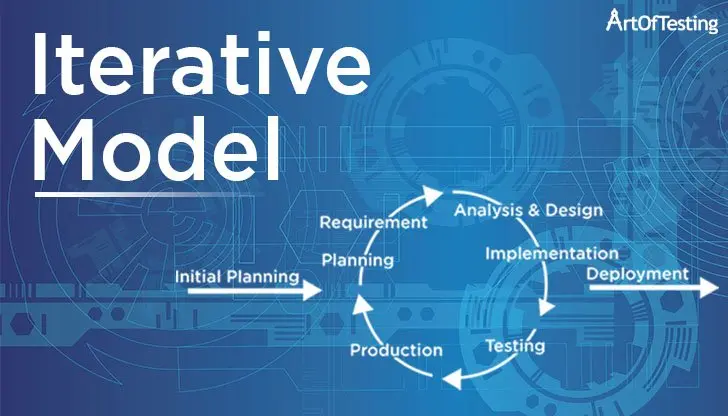
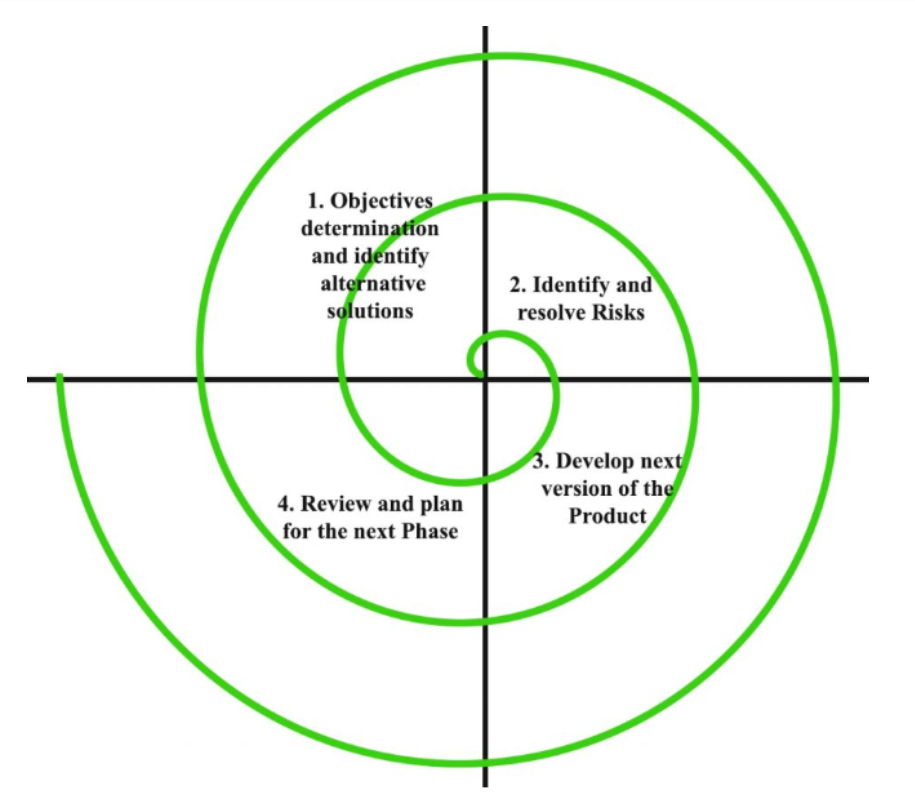
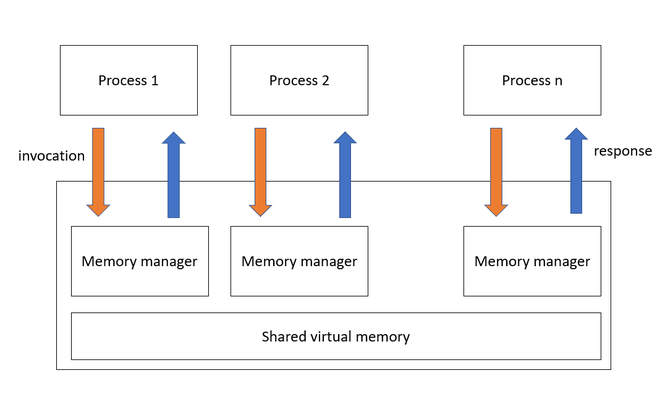
Computer models are mathematical representations of real-world systems or processes that can be used to analyze and predict the behavior of those systems or processes. They are a valuable tool in many fields, including engineering, biology, economics, and meteorology, and offer a number of advantages over traditional methods of analysis and prediction.
One of the main advantages of computer models is their ability to simulate complex systems and processes that would be difficult or impossible to analyze using traditional methods. For example, a computer model can simulate the flow of air over the surface of an aircraft wing, taking into account factors such as the shape of the wing, the angle of attack, and the temperature and humidity of the air. This can help engineers design more efficient and effective aircraft, as they can use the model to explore different design options and predict the performance of each option before building a physical prototype.
Another advantage of computer models is their speed and efficiency. Traditional methods of analysis and prediction, such as experiments and physical simulations, can be time-consuming and costly. In contrast, computer models can analyze and predict the behavior of a system or process in a matter of seconds or minutes, and they can do so at a much lower cost. This makes them an attractive option for researchers and practitioners who need to make quick decisions or need to analyze a large number of scenarios.
Computer models also have the advantage of being flexible and adaptable. They can be modified and updated as new data becomes available or as the system or process being analyzed changes. This allows researchers and practitioners to refine their models and improve their accuracy over time.
In addition, computer models can be used to explore a wide range of scenarios and conditions that may be difficult or impossible to replicate in the real world. For example, a meteorologist can use a computer model to simulate the effects of different atmospheric conditions on the path of a hurricane, or an economist can use a model to predict the impact of different policy decisions on the economy.
Overall, computer models offer a number of advantages over traditional methods of analysis and prediction. They are able to simulate complex systems and processes, they are fast and efficient, they are flexible and adaptable, and they can explore a wide range of scenarios and conditions. As a result, they are an invaluable tool for researchers and practitioners in a variety of fields.