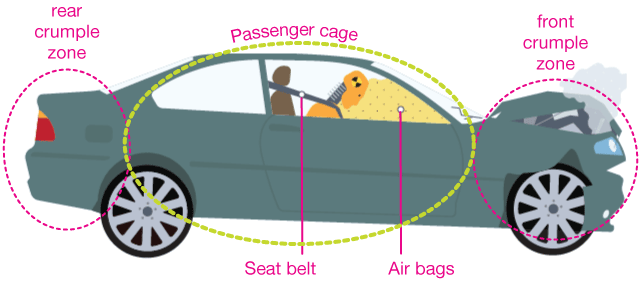
Airbags are safety devices that are designed to protect drivers and passengers in the event of a car crash. They are activated by sensors that detect the sudden deceleration that occurs during a collision, and are deployed within a fraction of a second. The airbag inflates rapidly, filling up the space between the driver or passenger and the steering wheel, dashboard, or door, in order to cushion the impact and reduce the likelihood of serious injury.
The physics behind airbags is based on the principles of acceleration and deceleration. When a vehicle is in motion, it has a certain amount of kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. During a collision, this kinetic energy is transferred to the objects within the vehicle, including the driver and passengers. If the kinetic energy is not properly dissipated, it can cause serious injury or death.
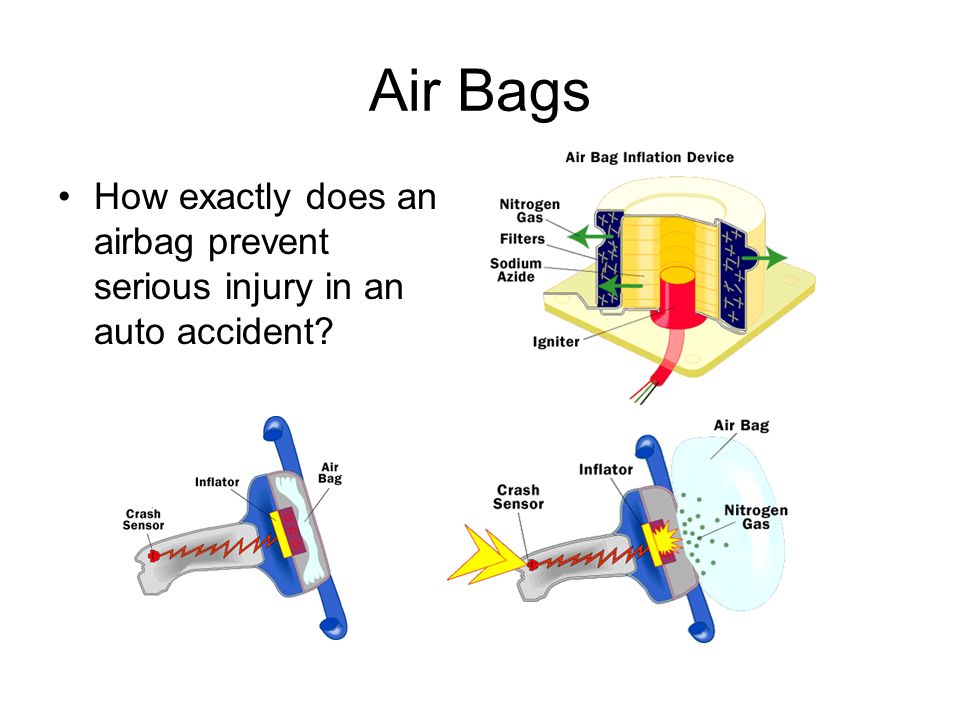
Airbags work by using the energy of the collision to inflate a bag made of a strong, flexible material, such as nylon. The bag is stored in a compact form within the vehicle, and is connected to a gas generator or inflator. When the sensors detect a collision, they trigger the gas generator, which rapidly inflates the bag. The bag expands outward, filling the space between the driver or passenger and the dashboard, steering wheel, or door.
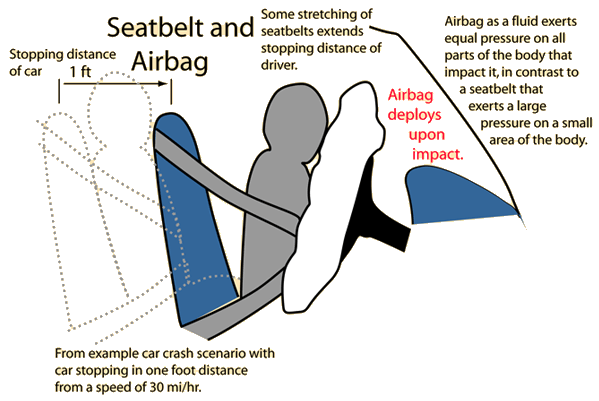
As the bag inflates, it absorbs some of the kinetic energy of the collision, reducing the force of the impact on the driver or passenger. The bag also creates a cushioning effect, which helps to reduce the likelihood of serious injury.
There are several factors that influence the effectiveness of an airbag. One of the most important is the size and position of the bag. In order to be effective, the bag must be large enough to fill the space between the driver or passenger and the dashboard, steering wheel, or door. It must also be positioned in the correct location in order to properly protect the driver or passenger.
Other factors that can affect the performance of an airbag include the type and strength of the material used to make the bag, the speed and angle of the collision, and the size and weight of the driver or passenger.
In conclusion, airbags are an important safety feature that can help to reduce the likelihood of serious injury in the event of a car crash. They work by using the energy of the collision to inflate a strong, flexible bag, which absorbs some of the kinetic energy of the impact and creates a cushioning effect. The effectiveness of an airbag is influenced by a number of factors, including the size and position of the bag, the strength of the material used, and the speed and angle of the collision.