Ancient Chinese mathematics made significant contributions to the development of mathematics as a whole. Some of the most notable achievements of ancient Chinese mathematics include the development of the decimal system, the use of negative numbers, and the solution of complex mathematical problems using algebraic methods.
One of the most significant achievements of ancient Chinese mathematics was the development of the decimal system. Prior to the development of the decimal system, the Chinese used a system of counting based on the number 10, with the numbers 1 through 9 represented by various symbols and the number 10 represented by a circle. This system was first used during the Shang Dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and became more widespread during the Zhou Dynasty (c. 1046–256 BCE). The decimal system allowed the Chinese to more easily perform calculations and to express larger numbers.
Another significant achievement of ancient Chinese mathematics was the use of negative numbers. Negative numbers were first used in China during the Han Dynasty (202 BCE – 220 CE). The Chinese used negative numbers to represent debts and to solve equations with negative solutions. This was a major advancement in mathematics, as negative numbers had not been used in this way before.
In addition to the development of the decimal system and the use of negative numbers, ancient Chinese mathematicians also made significant contributions to the field of algebra. One of the most notable achievements in this regard was the solution of complex mathematical problems using algebraic methods. The Chinese were able to solve problems involving simultaneous equations, quadratic equations, and higher-order equations using these methods.
Overall, ancient Chinese mathematics made important contributions to the development of mathematics as a whole. The development of the decimal system, the use of negative numbers, and the solution of complex mathematical problems using algebraic methods were all significant achievements that helped to lay the foundations for modern mathematics.
Chinese mathematics

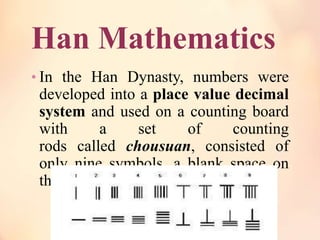
The oldest decimal multiplication table uncovered from archaeological excavations were compiled around the 4th century BC. This was largely because there was no concept or symbol of zero, and it had the effect of limiting the usefulness of the written number in Chinese. The most important mathematical innovation of the Eastern Zhou dynasty would be the counting board and counting rods. In fact, our ancients succeeded in calculating certain physical quantities, with the help of quite simple mathematics and with great ingenuity, that people today cannot even imagine. The digits added merged left to right with carries where needed. Around 5 AD, the astronomer Liu Xin approximated pi as 3.
The Historical Development of Chinese Mathematics

Very little is really known about his life. This was an impressive feat for the time, especially considering that the device Counting rods he used for recording intermediate results were merely a pile of wooden sticks laid out in certain patterns. Zhang Heng left , Zu Chongzhi centre , Yi Xing right After resigning from the imperial service in 464 AD, Zu Chongzhi devoted himself to the study of mathematics in the spirit of Liu Hui. Lun 1999 : "Nine Chapters of Mathematical Art", Oxford University Press, pp. This invention is described and attributed to Zhang in quotations by Hsu Chen and Li Shan, referencing his book Lou Shui Chuan Hun Thien I Chieh Apparatus for Rotating an Armillary Sphere by Clepsydra Water. In the 3rd century, Liu Hui made the calculation more accurate with his π algorithm, which allowed him to obtain the value 3. Shang numerals Mathematics of the Western Zhou Numerology was another form of divination developed in the early phases of Chinese civilization.
Ancient Chinese Mathematics

A History of Mathematics. The earliest evidence of counting occurred in mountains of Africa were notched bones and scored pieces of wood and stone were discovered. In a word, few educators can search the rich historical materials of Chinese mathematics for inspiration and apply it to mathematics education. Admittedly, some works, like Zhong Guo Gu Suan Jie Qu Interesting Computation Cases in Ancient China by Yu Zuquan and Shu Xue Liaozhai Mathematical Stories by Wang Shuhe are very impressive, but they cannot be used in classroom teaching because of their limited function in rigorous exams. It was therefore a decimal place value system, very similar to the one we use today - indeed it was the first such number system, adopted by the Chinese over a thousand years before it was adopted in the West - and it made even quite complex calculations very quick and easy.
Chinese Mathematics Education System and Mathematics Education Tradition
In doing so, the Han emperors adopted Confucianism as state philosophy with certain Legalist characteristics. Today, of course, we recognize that negative numbers do exist, as anyone who has overdrawn their bank account knows. And the last phase ranges from the 1,750B. The Greek astronomer Eratosthenes 276—194 BC invented the first armillary sphere in 255 BC. Tang took control of the Xia kingdom. He was the man who forged the Chinese identity, but simultaneously regarded as a ruthless tyrant.
Mathematics

Some claim that the ideas of decimal notation and zero originated in China, spreading to the West during these periods, but this may never be known for certain. Includes "Chinese remainder problem" or "problem of the Master Sun": find n so that upon division by 3 you get a remainder of 2, upon division by 5 you get a remainder of 3, and upon division by 7 you get a remainder of 2. Culturally, Vietnamese is much closer to Chinese than to any South East Asian. This practice matured during the Zhou dynasty 1046 — 256 BC , and has survived to the present day. Osaka Journal of Mathematics Education, 30, 35—39.
Ancient Achievements In Mathematics
Advances in the diagnostic isolation of Chlamydia, including TRIC agent, from the eye, genital tract, and rectum. Wrote Xugu suanjing Continuation of Ancient Mathematics of 22 problems. Cite this chapter Qin, D. . The Mojing can be considered a treasure-trove of scientific thought native to China. In fact, even dating the first Chinese civilization is difficult; various accounts place the first Chinese empire between about 2700 b.







