The animal kingdom is a diverse and fascinating group of organisms that includes everything from small invertebrates to large mammals. Classification, or the organization of living things into groups based on shared characteristics, is a crucial tool for understanding the animal kingdom and studying the relationships between different species. In this essay, we will explore the classification of animals and how scientists use it to understand the natural world.
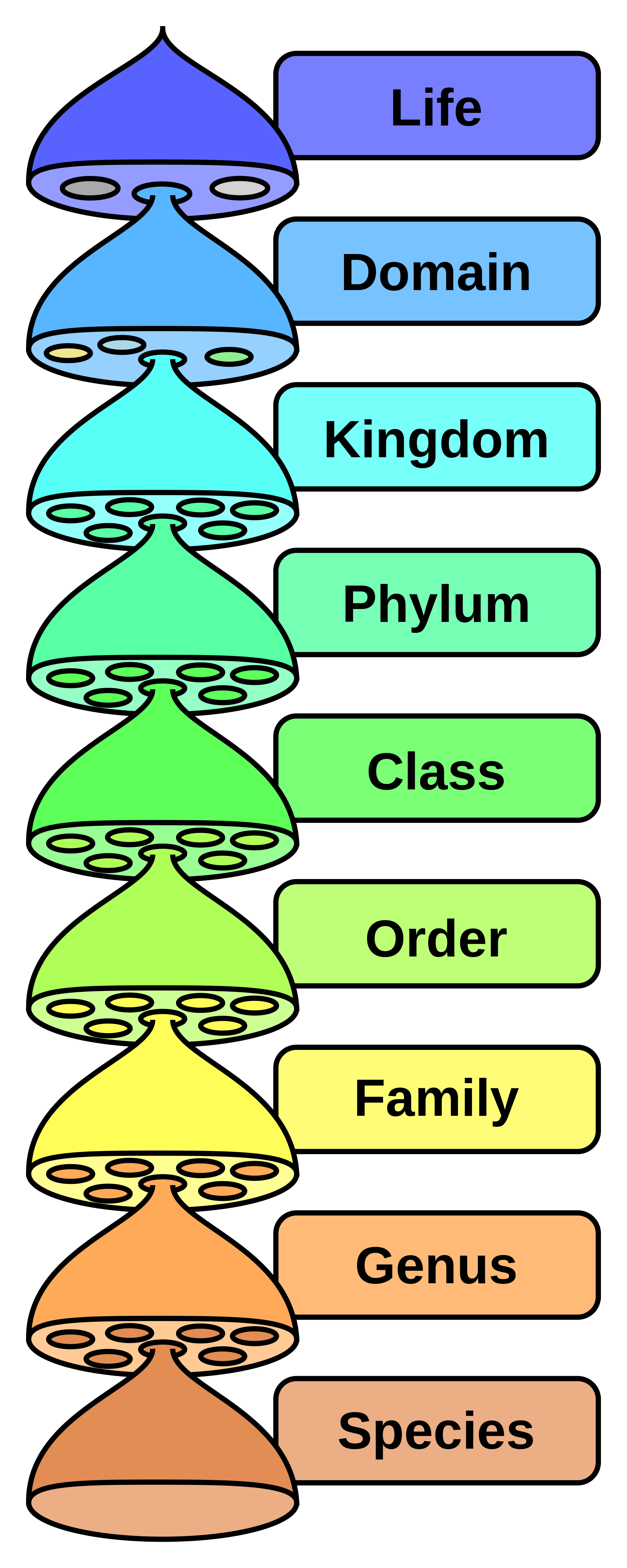
One of the earliest and most influential systems of animal classification was proposed by the 18th-century naturalist Carl Linnaeus. His system, known as the Linnaean taxonomy, is based on the idea of grouping organisms by their shared physical and biological characteristics. According to Linnaeus, all animals are classified into one of six major categories, known as taxa: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, and genus.
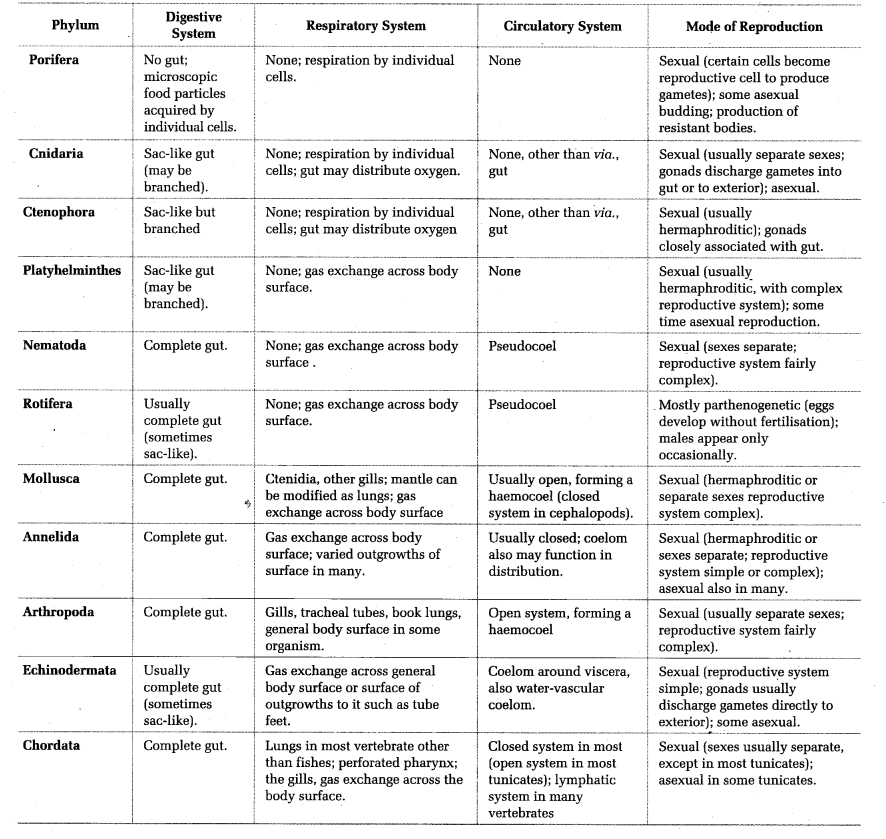
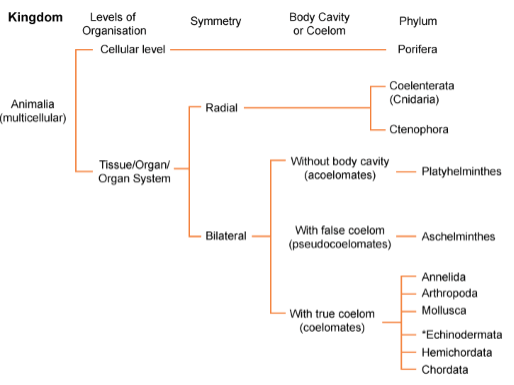
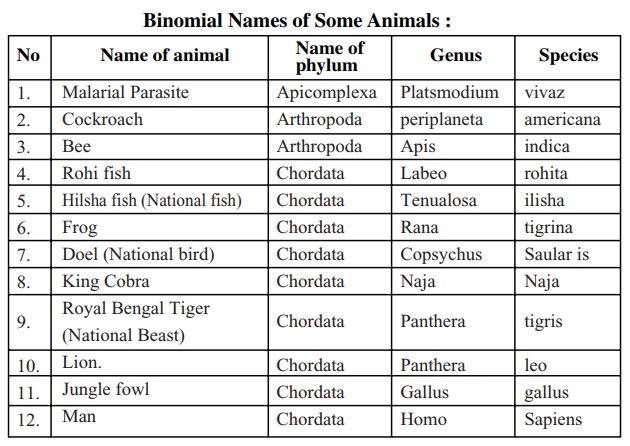
The highest level of classification in the animal kingdom is the kingdom, which is divided into two main categories: animals (Animalia) and plants (Plantae). Within the animal kingdom, animals are further divided into smaller groups based on their physical and biological characteristics, such as their body structure, mode of reproduction, and mode of nutrition. For example, animals that have a segmented body, such as worms and insects, belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
The next level of classification is the class, which is further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. For example, the class Mammalia, which includes all mammals, is characterized by the presence of mammary glands and the ability to regulate body temperature. Within the class Mammalia, animals are further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as the presence of fur, the number of toes, and the shape of their teeth.
The next level of classification is the order, which is further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. For example, the order Carnivora, which includes all carnivorous mammals, is characterized by the presence of sharp teeth and claws. Within the order Carnivora, animals are further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as the shape of their skulls and the number of teeth.
The next level of classification is the family, which is further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. For example, the family Canidae, which includes all dogs, is characterized by the presence of long muzzles and retractable claws. Within the family Canidae, animals are further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as the size and shape of their ears.
The final level of classification is the genus, which is further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. For example, the genus Canis, which includes all wolves, is characterized by the presence of long muzzles and bushy tails. Within the genus Canis, animals are further divided into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as the size and shape of their ears.
Classification is an essential tool for understanding the animal kingdom and studying the relationships between different species. By organizing animals into groups based on shared characteristics, scientists can better understand the evolution and natural history of different species and how they are related to one another.