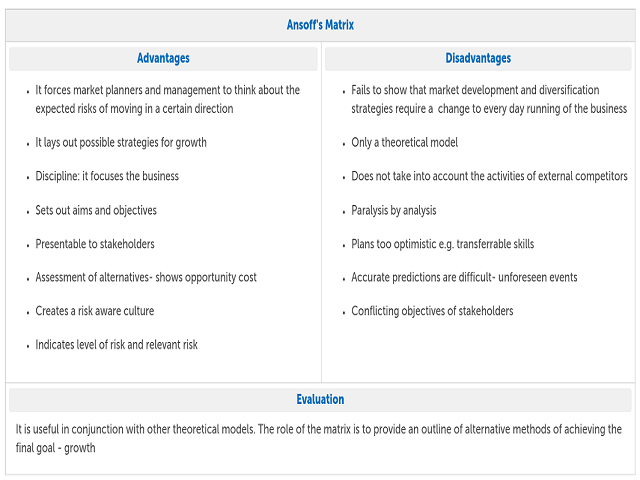
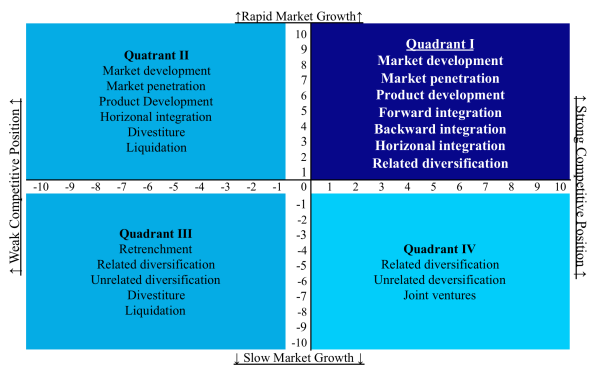
The Ansoff Matrix is a tool used in strategic planning to analyze and evaluate a company's potential growth opportunities. It was developed by Igor Ansoff, a Russian-American mathematician and business strategist. The Ansoff Matrix consists of four quadrants that represent different growth strategies a company can pursue. These strategies are market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification.
In the case of Cadbury, a British multinational confectionery company, the Ansoff Matrix can be used to identify potential growth opportunities.
Market Penetration
One growth strategy that Cadbury could pursue is market penetration. This strategy involves increasing the sales of existing products in the same market. Cadbury could achieve this by increasing its marketing and promotional efforts, or by lowering its prices to increase market share. For example, Cadbury could focus on increasing the sales of its chocolate bars in the UK market by promoting its products through targeted advertising campaigns and offering discounts to customers.
Market Development
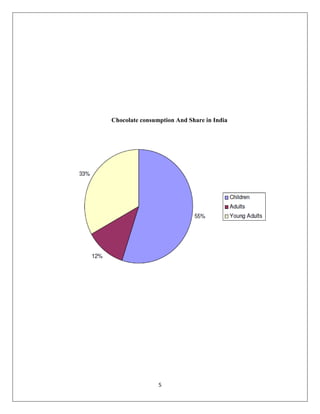
Another growth strategy that Cadbury could consider is market development. This strategy involves expanding into new markets with existing products. Cadbury could achieve this by entering new geographical markets or by targeting new customer segments. For example, Cadbury could expand into emerging markets such as China and India, where demand for confectionery products is high. Cadbury could also target new customer segments, such as health-conscious consumers, by introducing a line of healthier chocolate products.
Product Development
A third growth strategy that Cadbury could pursue is product development. This strategy involves introducing new products to the same market. Cadbury could achieve this by innovating and introducing new flavors of its chocolate products, or by introducing new categories of products altogether. For example, Cadbury could introduce a line of premium chocolate products, or launch a range of chocolate-covered snacks.
Diversification
The final growth strategy that Cadbury could consider is diversification. This strategy involves entering new markets with new products. Cadbury could achieve this by acquiring other companies or entering into partnerships with them. For example, Cadbury could acquire a company that produces non-chocolate confectionery products, such as gummy bears or hard candy, and expand its product range to include these products.
In conclusion, the Ansoff Matrix is a useful tool for strategic planning and can help a company like Cadbury identify potential growth opportunities. By considering the different growth strategies of market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification, Cadbury can evaluate which strategies are most suitable for its business and make informed decisions about its growth.
The Ansoff Matrix, also known as the Ansoff Product-Market Growth Matrix, is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations understand the risks and potential rewards of various growth strategies. It was developed by Igor Ansoff, a Russian-American mathematician and business manager, in the 1950s.
Cadbury, a leading global confectionery company, has used the Ansoff Matrix to guide its growth and expansion over the years. The company was founded in 1824 and has a long history of introducing new products and entering new markets.
One way Cadbury has used the Ansoff Matrix is through product development. The company has a strong focus on innovation and regularly introduces new products to its existing product line. For example, Cadbury recently launched a range of plant-based chocolate bars made with cocoa, almond milk, and cocoa butter. This strategy of introducing new products to its existing market is known as the "market penetration" growth strategy, which is represented in the Ansoff Matrix as the lower left quadrant.
Another way Cadbury has used the Ansoff Matrix is by entering new markets. The company has a global presence, with operations in over 50 countries and a strong brand recognition worldwide. In recent years, Cadbury has expanded into emerging markets such as India and China, where it has introduced new products that are specifically tailored to local tastes and preferences. This strategy of entering new markets with existing products is known as the "market development" growth strategy, which is represented in the Ansoff Matrix as the lower right quadrant.
In addition to product development and market expansion, Cadbury has also used the Ansoff Matrix to explore the possibility of diversification. This involves entering new markets with new products, which is known as the "diversification" growth strategy and is represented in the Ansoff Matrix as the upper right quadrant. Cadbury has diversified its product line to include non-chocolate confectionery items such as gum and candy, as well as snack bars and beverages.
Overall, the Ansoff Matrix has been an effective tool for Cadbury in its efforts to grow and expand. By considering the risks and rewards of different growth strategies, the company has been able to successfully enter new markets and introduce new products, leading to long-term success and profitability.
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations assess the risks and potential rewards of various growth strategies. It is named after its creator, Russian-American mathematician and management consultant Igor Ansoff. The matrix identifies four main types of growth strategies: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. These strategies can be applied to any organization, including Cadbury, the British multinational confectionery company.
Market penetration refers to the strategy of increasing sales of existing products to existing markets. Cadbury could use this strategy by increasing its advertising and marketing efforts, offering promotions and discounts, or expanding its distribution channels to reach more customers. This strategy carries relatively low risk, as the company is already operating in familiar markets and selling proven products. However, it may be difficult to achieve significant growth through market penetration alone, as the market may be saturated or competitors may also be vying for market share.
Product development involves introducing new products to existing markets. This strategy carries somewhat higher risk than market penetration, as the company is introducing an untested product to its existing customer base. Cadbury could use this strategy by developing new flavors or variations of its existing products, or by introducing entirely new product lines. For example, the company could develop a line of vegan or low-sugar chocolates to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
Market development involves expanding the market for existing products by entering new geographic regions or target demographics. This strategy carries higher risk than market penetration or product development, as the company is entering unfamiliar markets with products that may not be well-known or well-received. Cadbury could use this strategy by exporting its products to new countries, or by targeting new customer segments such as children or older adults.
Diversification is the strategy of entering entirely new markets with new products. This strategy carries the highest risk of the four, as the company is completely venturing into unknown territory with untested products. However, it also has the potential for the highest rewards if successful. Cadbury could use this strategy by entering entirely new industries, such as the health food or beverage sectors.
Overall, the Ansoff Matrix is a useful tool for Cadbury and other organizations to assess the risks and potential rewards of different growth strategies. By carefully considering the options available and the risks and rewards associated with each, the company can make informed decisions about how to pursue growth and achieve long-term success.