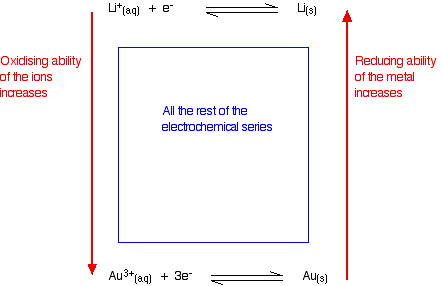
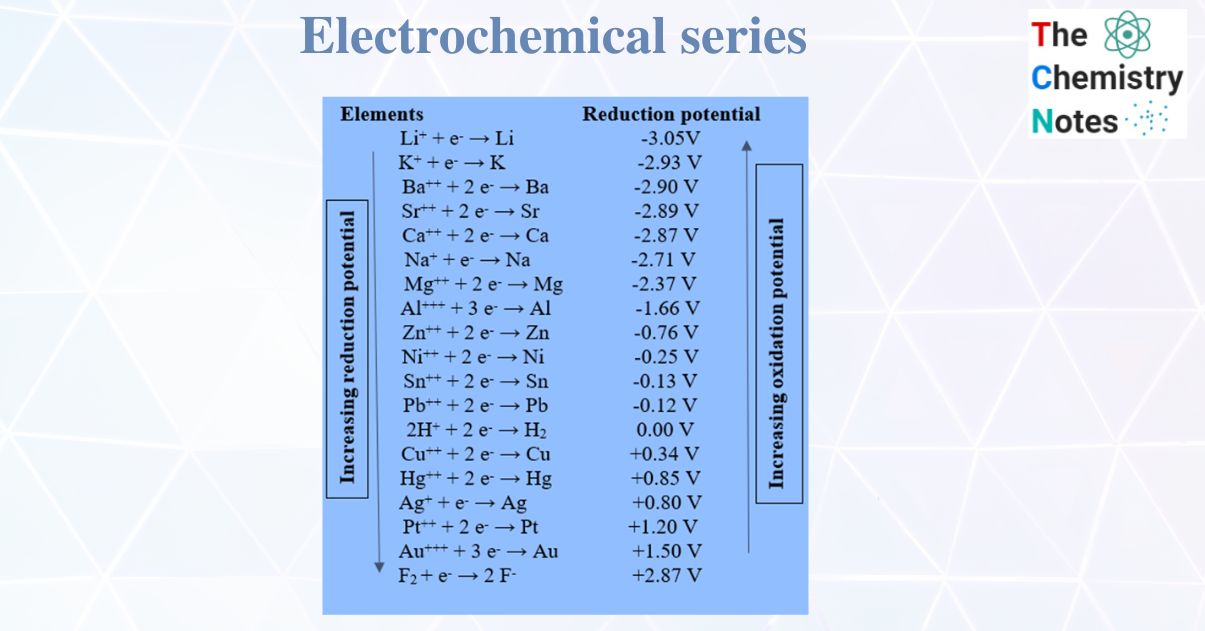
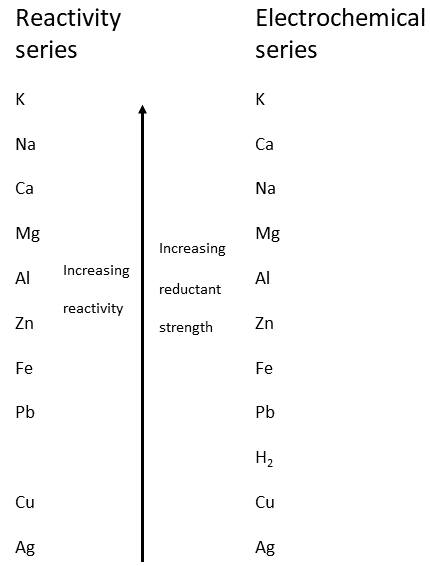
The electrochemical series is a list of elements arranged in order of their standard reduction potentials. It is a useful tool for predicting the feasibility of a redox reaction, as well as the direction of electron flow in a galvanic cell.
One common application of the electrochemical series is in the design of galvanic cells, which are devices that use a chemical reaction to generate an electrical current. By arranging the anode and cathode of a galvanic cell based on the relative positions of their constituent elements in the electrochemical series, it is possible to predict the direction of electron flow and the potential difference between the two electrodes.
For example, consider a galvanic cell consisting of a zinc anode and a copper cathode. Since zinc has a more negative reduction potential than copper, it is more likely to be oxidized, releasing electrons to the cathode. This creates a flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode, which can be harnessed to do work, such as powering an electrical circuit.
Another application of the electrochemical series is in the prediction of the feasibility of redox reactions. When two elements are placed in contact with each other, a redox reaction may occur if the reduction potential of one element is more positive than the other. If the difference in reduction potentials is large enough, the reaction will be highly exothermic and proceed spontaneously. If the difference is small, however, the reaction may not occur at all, or may require the input of energy to drive it forward.
One practical example of this is the use of the electrochemical series to predict the corrosion of metals. Corrosion occurs when a metal is oxidized by its surroundings, and the rate at which it occurs is determined by the relative positions of the metal and its oxidizing agents in the electrochemical series. If a metal is located lower in the series than the species that can oxidize it, it will be prone to corrosion. Conversely, if it is higher in the series, it will be more resistant to corrosion.
In summary, the electrochemical series is a valuable tool for predicting the direction of electron flow in a galvanic cell, as well as the feasibility of redox reactions. It is widely used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, electrochemistry, and materials science, to understand and predict the behavior of different elements and their reactions with one another.