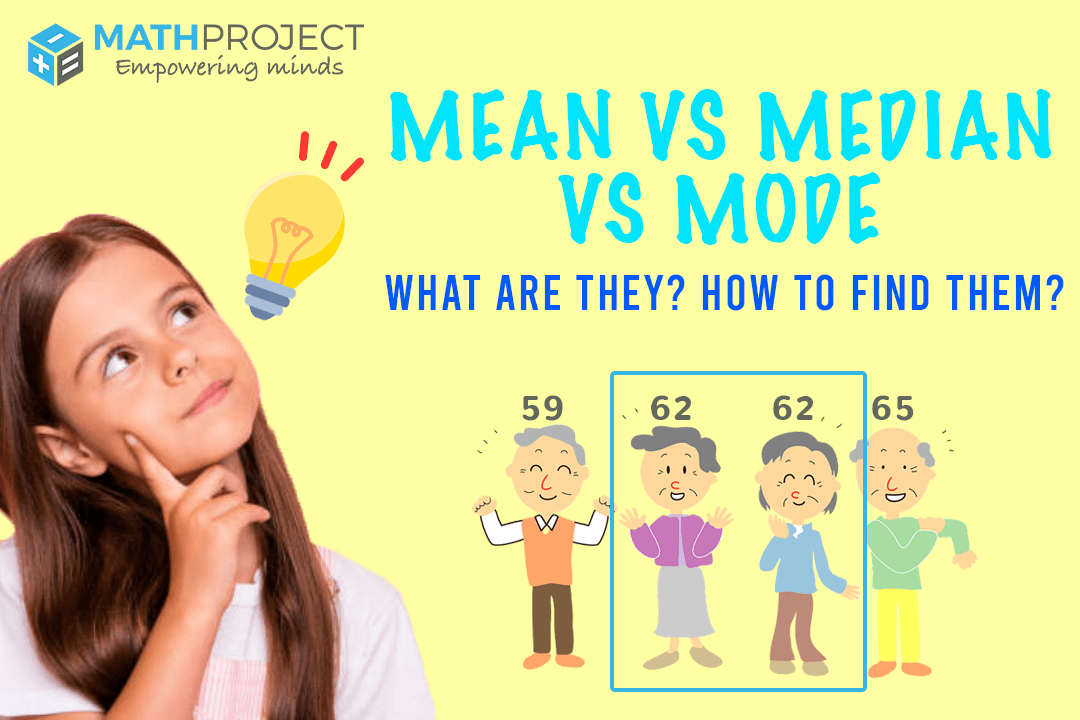
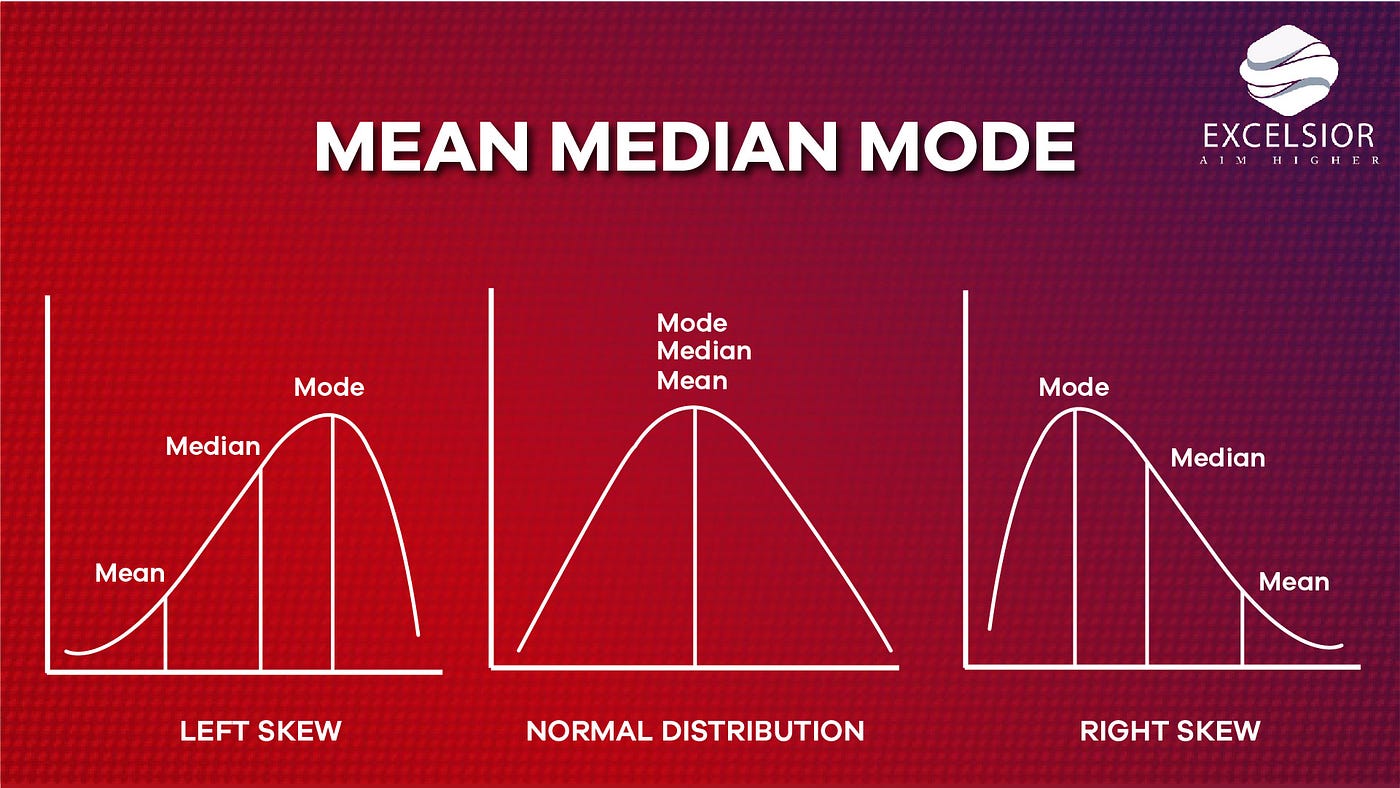
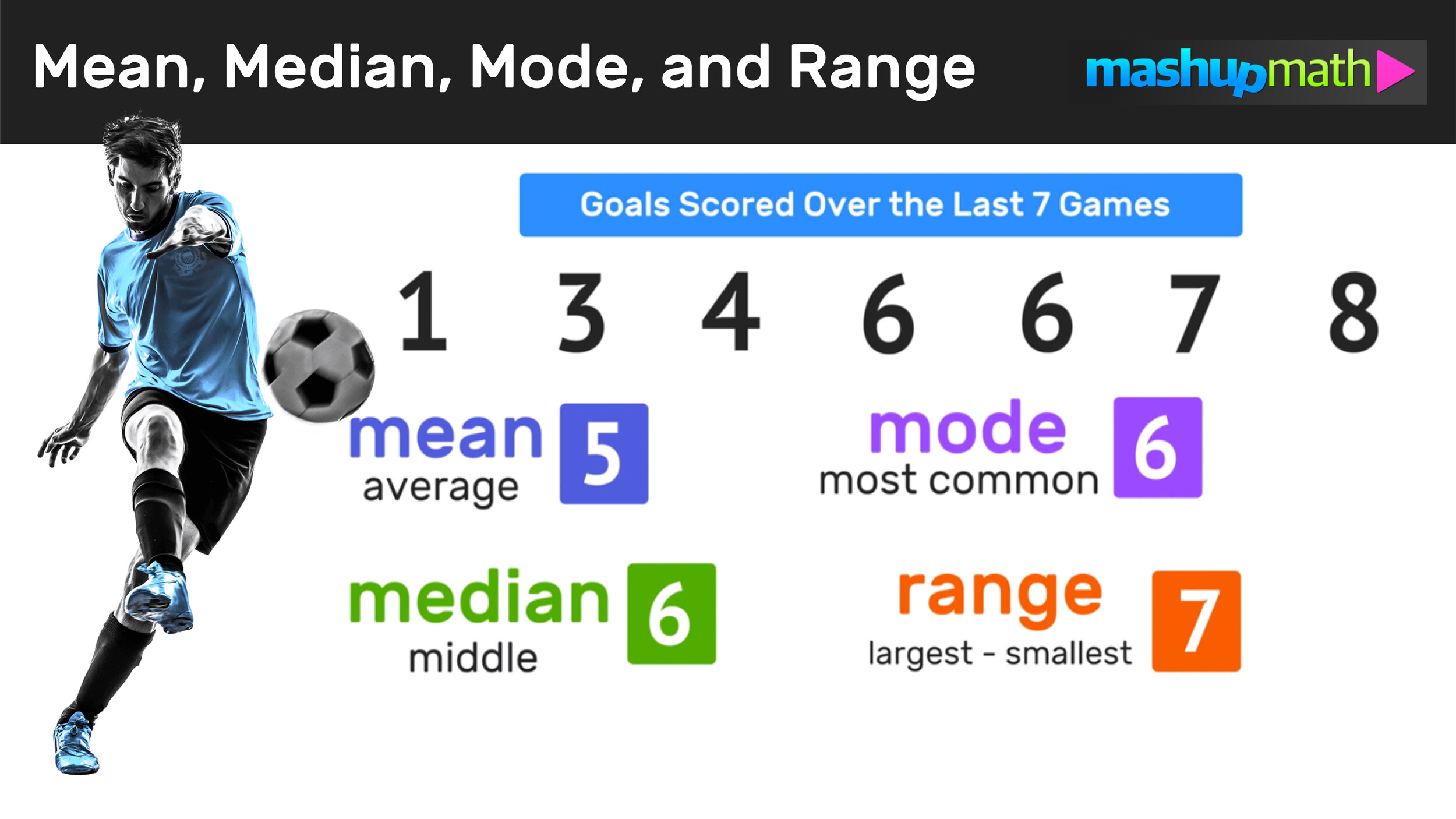
The mean, median, and mode are all statistical measures that can be used to describe the characteristics of a dataset. These measures are often used in various fields, such as business, economics, and science, to help summarize and interpret data.
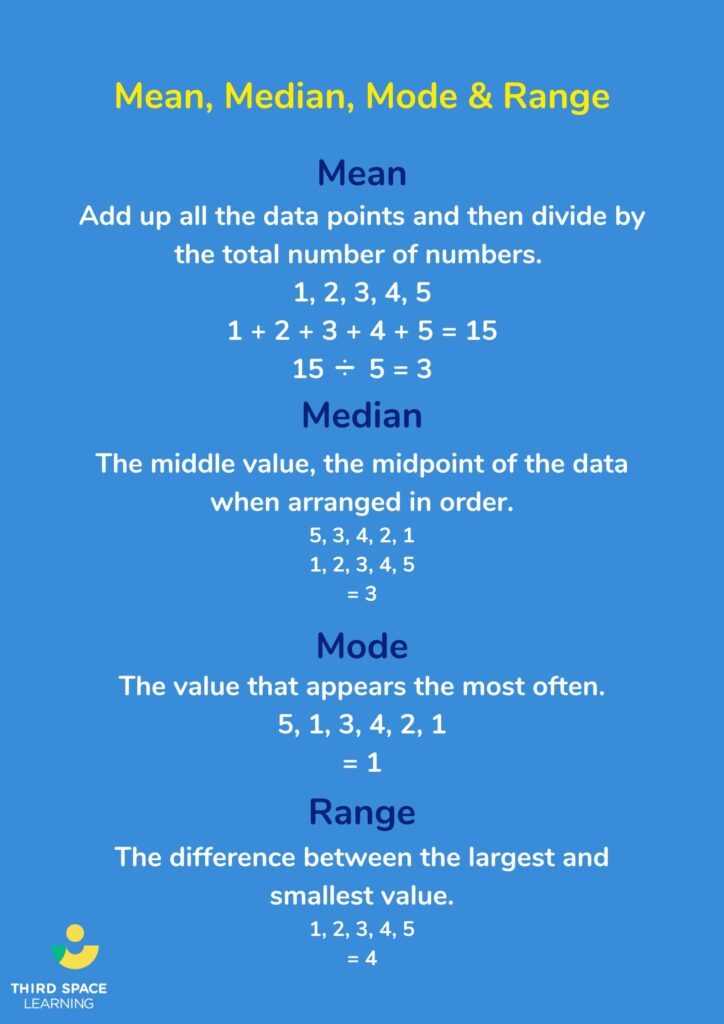
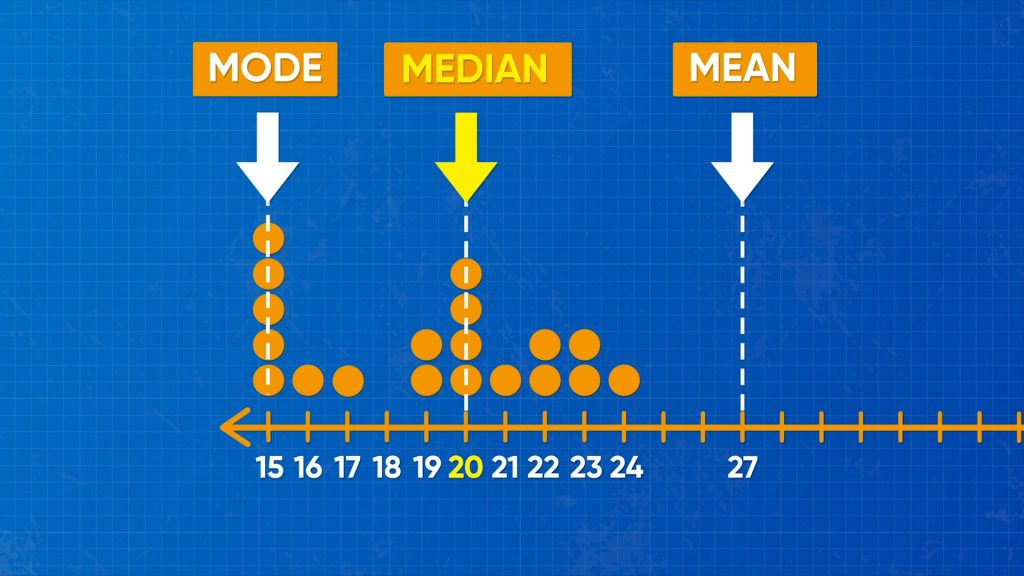
The mean, also known as the average, is calculated by summing all the values in a dataset and dividing the result by the total number of values. It is a useful measure for understanding the overall trend or central tendency of a dataset. For example, if a company wants to know the average salary of its employees, it can calculate the mean salary of all its employees.
The median is the middle value in a dataset when the values are arranged in numerical order. It is useful for understanding the distribution of values in a dataset, particularly when the dataset contains outliers or extreme values that might distort the mean. For example, if a school wants to understand the academic performance of its students, it can calculate the median grade of all its students.
The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a dataset. It is useful for understanding which values are most common in a dataset. For example, if a retailer wants to understand the most popular product in its store, it can calculate the mode of the products sold.
In practice, the mean, median, and mode are often used together to provide a more complete picture of a dataset. For example, a business might use the mean to understand the overall trend of its sales, the median to understand the distribution of its sales, and the mode to understand the most popular products.
In conclusion, the mean, median, and mode are important statistical measures that are widely used in various fields to help summarize and interpret data. These measures provide valuable insights into the characteristics of a dataset and can help inform decision-making and problem-solving in many contexts.