Ultrasonic waves, or sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper limit of human hearing, have a wide range of applications in various fields. These include medicine, engineering, and biology, to name a few.
One common application of ultrasonic waves is in medicine, where they are used for diagnostic imaging and therapy. Ultrasonic waves can be used to create images of the inside of the body, known as ultrasound. This is a non-invasive and painless procedure that is widely used to examine the uterus and ovaries during pregnancy, as well as to visualize the heart, blood vessels, and internal organs. In addition to imaging, ultrasonic waves can also be used for therapeutic purposes, such as breaking up kidney stones or treating tissue damage.
Another application of ultrasonic waves is in engineering, where they are used for non-destructive testing (NDT). NDT is the process of evaluating the properties of a material, component, or system without damaging it. Ultrasonic waves are used to detect internal flaws or defects in materials, such as welds, metals, and composites. They can also be used to measure the thickness of materials, such as metal plates or pipes, and to determine the presence of corrosion or cracks.
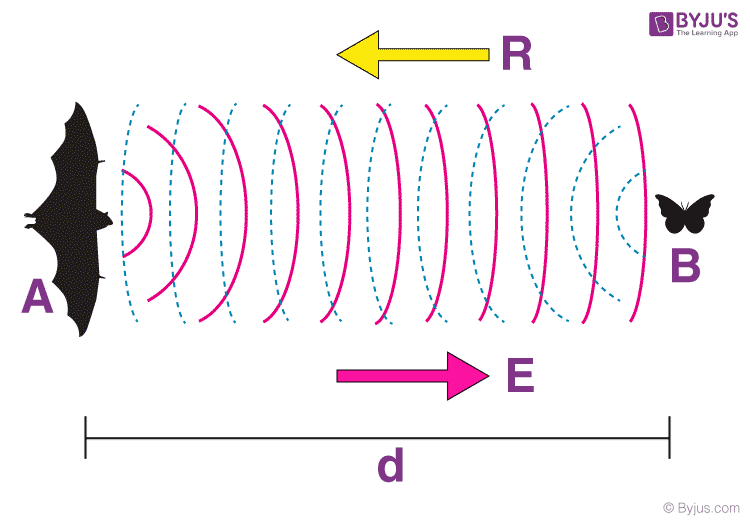
In biology, ultrasonic waves are used to study animal behavior and communication. For example, bats and dolphins use ultrasonic waves for echolocation, which is the ability to locate objects by emitting sound waves and detecting the echoes. Scientists also use ultrasonic waves to study the behavior and communication of birds, whales, and other animals.
Overall, the application of ultrasonic waves is diverse and has a significant impact on various fields. From diagnostic imaging in medicine to non-destructive testing in engineering and the study of animal behavior in biology, ultrasonic waves have proven to be a valuable tool in understanding and improving the world around us.