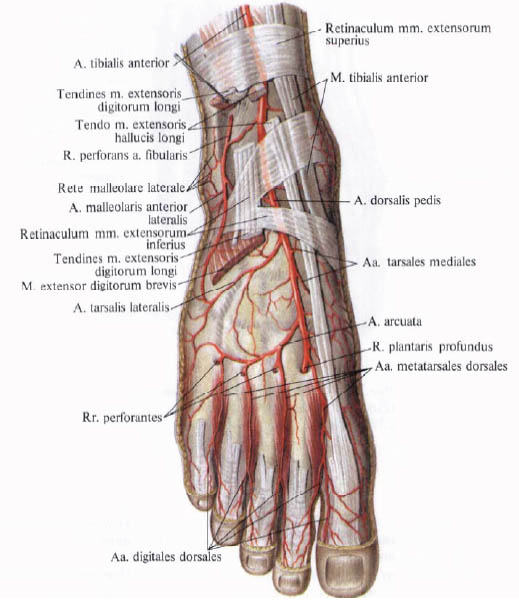
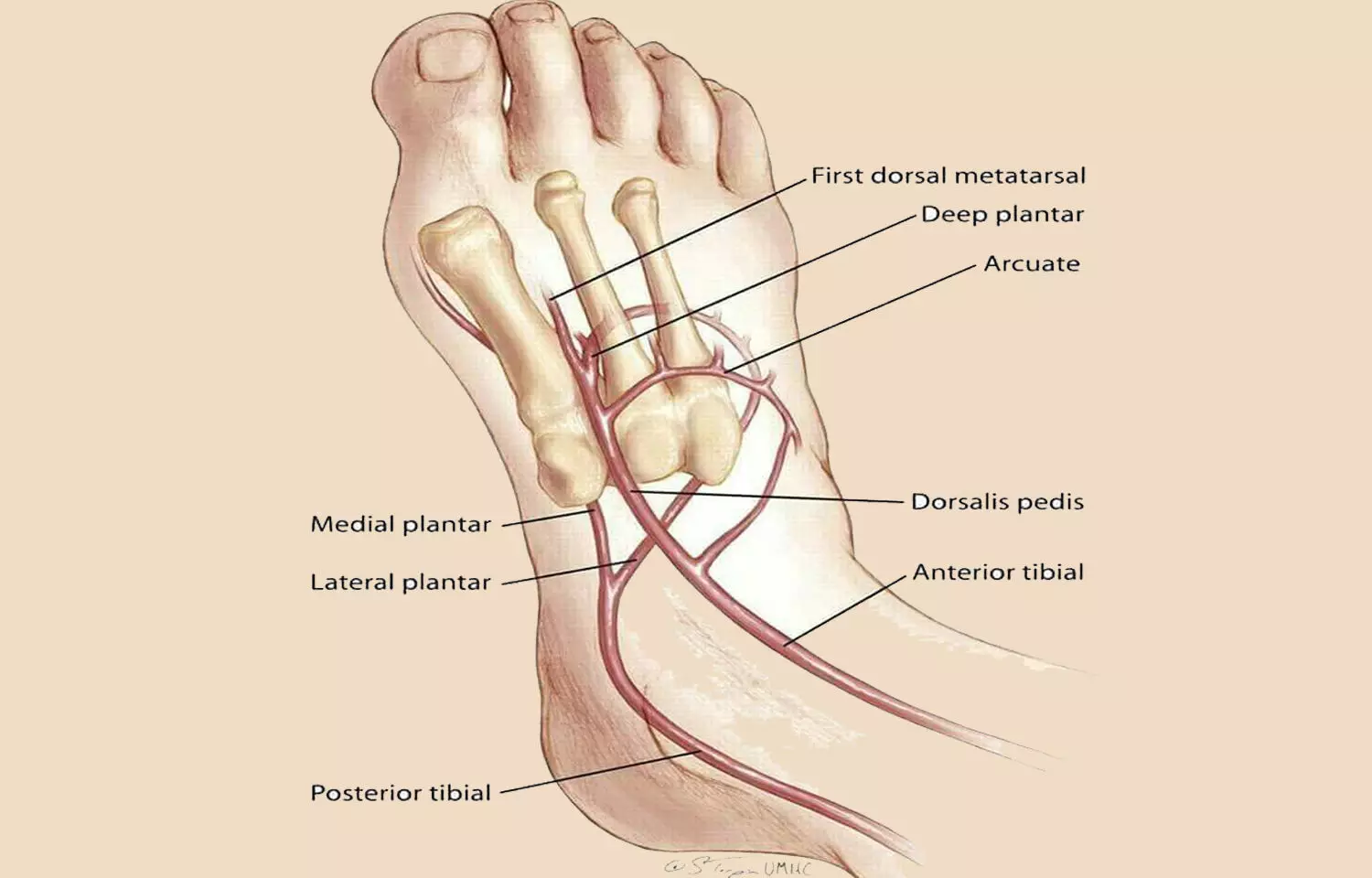
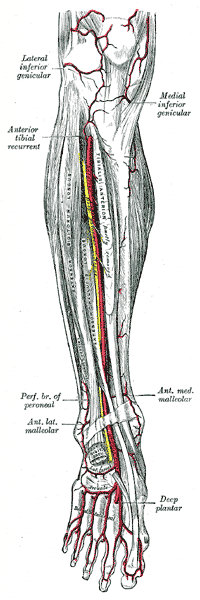
The arteria dorsalis pedis, also known as the posterior tibial artery, is a crucial vessel that supplies blood to the lower leg and foot. It is a continuation of the popliteal artery, which is located in the posterior aspect of the knee. The arteria dorsalis pedis begins at the level of the ankle and extends distally to the toes, running along the medial aspect of the foot and ankle.
As the arteria dorsalis pedis travels down the leg, it gives off several branches that supply blood to the muscles and skin of the lower leg and foot. The plantar artery is a significant branch of the arteria dorsalis pedis that supplies blood to the sole of the foot. Other branches include the medial and lateral tarsal arteries, which supply blood to the bones and muscles of the foot, and the digital arteries, which supply blood to the toes.
The arteria dorsalis pedis plays a vital role in maintaining the circulation of blood in the lower leg and foot. When this artery becomes blocked or damaged, it can lead to a variety of problems, including pain, swelling, and tissue death. Some common causes of arterial damage include peripheral artery disease, trauma, and arterial thrombosis.
To diagnose problems with the arteria dorsalis pedis, a healthcare provider may use a variety of techniques, including physical examination, ultrasound, and angiography. Treatment options may include medications to improve blood flow, surgery to repair or bypass the damaged artery, or lifestyle changes to manage risk factors such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Overall, the arteria dorsalis pedis is a critical vessel that is essential for maintaining proper circulation in the lower leg and foot. Proper care and attention to this artery can help prevent problems and ensure optimal health and function of the lower extremities.