The monsoon season is a time of year when a region experiences a dramatic shift in weather patterns, marked by an increase in rainfall and often accompanied by strong winds. This seasonal weather phenomenon occurs in many parts of the world, but is most famously associated with South and Southeast Asia, where it plays a crucial role in the region's agriculture and economy.
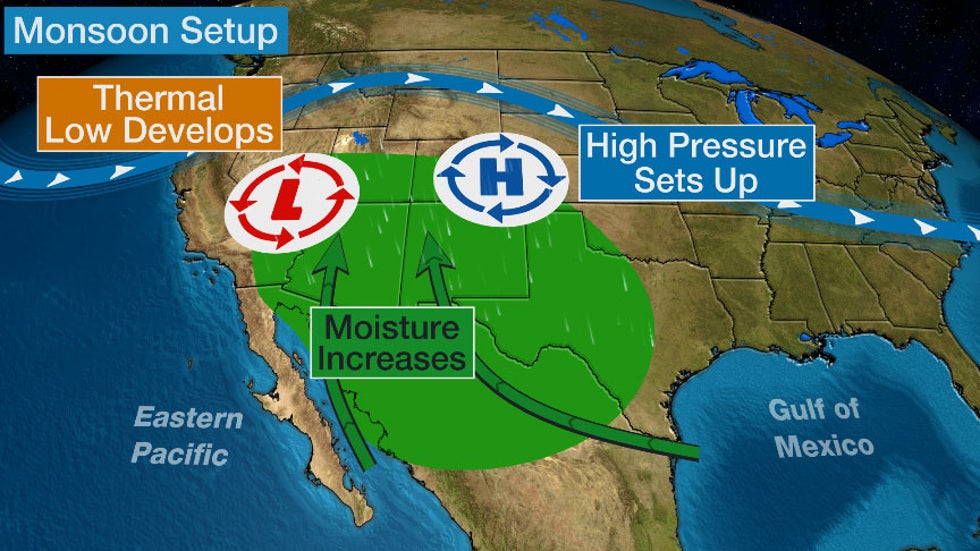
The monsoon season is caused by the shifting position of the Earth in relation to the sun, which causes changes in the temperature and pressure of the air. During the summer months, the sun's rays are more direct and the land heats up more quickly than the ocean. This causes the air above the land to rise and cool, creating low pressure. At the same time, the ocean remains cooler, causing the air above it to be denser and create high pressure.
As the land and ocean temperatures continue to diverge, the pressure difference between the two becomes more pronounced, leading to the formation of wind patterns that bring moist air from the ocean onto the land. This moist air then rises and cools, causing the water vapor it contains to condense and fall as rain.
The monsoon season is vital for the agriculture of many countries in South and Southeast Asia, as it provides the necessary water for crops to grow. In these regions, the monsoon season is often the only source of water for irrigation, and a good monsoon can mean the difference between a bountiful harvest and a year of drought.
However, the monsoon season can also bring negative consequences, such as floods and landslides. These natural disasters can cause significant damage to infrastructure and disrupt daily life for the people living in affected areas.
Despite the challenges it can bring, the monsoon season is an important part of life in many parts of the world. It brings much-needed rain to parched lands and supports the agriculture that is essential to the economies of many countries. Understanding the science behind the monsoon season and being prepared for its potential impacts can help communities and governments mitigate the negative effects and take advantage of the benefits it brings.



/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/KKF4MGIEBRETXBVFPBB3ALFNVY.png)



