Assumptions of absolute advantage theory. What are the assumptions of absolute advantage theory? 2022-12-16
Assumptions of absolute advantage theory
Rating:
9,2/10
1336
reviews
The theory of absolute advantage is a fundamental concept in international trade economics. It was first introduced by economist Adam Smith in the 18th century, and it remains an important theory in the field today.
The basic premise of the theory is that countries have different comparative advantages in producing certain goods or services due to their unique resources, technology, and labor skills. According to the theory, countries should specialize in the production of goods or services in which they have an absolute advantage, and then trade with other countries for the goods or services in which they do not have an absolute advantage.
There are several key assumptions underlying the theory of absolute advantage. These include:
Countries have different resources: The theory assumes that countries have different resources, such as land, labor, and capital, which can be used to produce different goods or services. For example, a country with a lot of fertile land might have a comparative advantage in producing agricultural products, while a country with a highly skilled workforce might have a comparative advantage in producing high-tech products.
Countries have different technologies: The theory also assumes that countries have different technologies, which can be used to produce goods or services more efficiently. For example, a country with advanced manufacturing technologies might have an absolute advantage in producing automobiles, while a country with more primitive technologies might have an absolute advantage in producing textiles.
Countries have different labor skills: The theory assumes that countries have different labor skills, which can affect the efficiency of production. For example, a country with a highly educated workforce might have a comparative advantage in producing high-tech products, while a country with a less educated workforce might have a comparative advantage in producing low-tech products.
Trade is beneficial: The theory assumes that trade is beneficial for all countries involved. According to the theory, countries that specialize in the production of goods or services in which they have an absolute advantage will be able to produce these goods or services more efficiently, leading to lower prices and higher profits. At the same time, other countries will be able to access these goods or services at a lower cost, leading to increased consumer welfare.
In summary, the theory of absolute advantage is based on the assumptions that countries have different resources, technologies, and labor skills, and that trade is beneficial for all countries involved. This theory has been widely accepted by economists as a fundamental principle of international trade and has had a significant impact on the way that countries interact with one another in the global economy.
Limitations of Theory of Absolute Advantage

To illustrate, let there be two countries A and B having absolute differences in costs in producing a commodity each X and Y respectively at an absolute lower cost of production than the other. It refers to the capability to manufacture a particular commodity or better quality than a competitor. However, the theory of comparative advantage does not fully explain why nations benefit from trade. By specializing in the production of goods in which each has an absolute advantage, both countries benefit by engaging in trade. India can get more wine with its labor by specializing in wool and trading the wool for Spanish wine, while Spain can benefit by trading wine for wool. What is Adam Smith's Absolute Advantage Theory? Smith mentioned they base on natural and acquired man-made advantages.
Next
What is the Assumption of absolute cost advantage?

Therefore, France enjoys a comparative advantage in the production of wine. This theory is based on Opportunity cost becomes a crucial explanation because we are dealing with scarce resources. The benefits to nations from trading are the same as to individuals: trade permits specialization, which allows resources to be used more productively. The US also enjoys another absolute cost advantage in the entertainment and media sector. Each country focuses on the products it can produce at the lowest unit cost compared to other countries. I think this article has given you a full understanding of the absolute advantage theory.
Next
The Theory of Absolute Advantage

The benefit of comparative advantage is the ability to produce a good or service for a lower opportunity cost. Assumptions of the Theory of Absolute Advantage Both Smith's theory of absolute advantage, and Ricardo's theory of comparative advantage, rely on certain assumptions and simplifications in order to explain the benefits of trade. Hence both countries can get the benefits of trade by specializing in the least cost item. This is another theory of trade which states countries gravitate towards trading with similar countries with close geographical proximity. Likewise, Indonesia produces more affordable shoes because it has a lower opportunity cost than Malaysia. And then, international trade facilitates them to get other goods which are less efficiently produced domestically. Countries with an absolute advantage can decide to specialize in producing and selling a specific good or service and use the generated funds to purchase goods and services from other countries.
Next
1 Theory of Absolute Advantage The Scottish economist Adam Smith developed the

A country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good if it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost relative to another country. Many results from the formal model are contrary to simple logic. Comparative advantage drives countries to specialize in the production of the goods for which they have the lowest opportunity cost, which leads to increased productivity. However, in reality, utilization of the proportion of labour depends on the type of commodity being produced. But the Ricardo theory neglects this independent factor of production. Suppose to specialize in the production of Wheat, the U. Every country should specialize in the production of that commodity which it can produce more cheaply than others and exchange it for the commodities which cost less in other countries.
Next
Theory of Absolute Advantage

Similarly, the UK has the least cost advantage for specializing textiles. Similarly, another country would also have a similar advantage when it has a cost advantage for another product. Comments on this entry are closed. Similar Posts: Assumptions Underlying the Theory of Absolute Advantage The idea of absolute advantage rests on a number of assumptions on the part of Adam Smith. Absolute advantage and comparative advantage are two important concepts in economics and international trade. The theory of absolute advantage? A country has an absolute advantage economically over another, in a particular good, when it can produce that good at a lower cost.
Next
Absolute Advantage: Definition, Benefits, and Example

While this theory may thoughtful, it is not always true and accurate because some of these assumptions are false in practice. Compare this to developed countries with regular power supply, this gives them an advantage over the developing nations. For example The USA and UK produce two goods, such as soya and textile. The natural advantage refers to natural resources such as climate, land, soil, and locations, etc. Consider the table below which records the number of hours it takes to refine 1 barrel of crude oil by the United Kingdom UK and Singapore. The concept of absolute advantage has been used throughout history to justify the privileges of certain countries or businesses. According to Smith, countries should specialize in the production of goods for which they have an absolute cost advantage and then trade these goods for those produced by other countries.
Next
Adam Smith's Theory of Absolute Cost Advantage [Made Easy]

The third is the capital investment level, including infrastructure. The country with absolute cost advantage gains, with little or no gains for the other. Critical Review of Absolute Cost Advantage Theory Although this theory talks about and gives various ways to flourish in international trades, it can also be criticized in many ways. Comparative advantage suggests that countries will engage in trade with one another, exporting the goods that they have a relative advantage in. Money from sales to buy other goods — which are inefficient if produced domestically — from other countries. Intra-versus Inter industry trade : According to the absolute advantage theory, there is an exchange of one type of good with another type of good between two countries.
Next
Absolute Advantage Definition

More crucially, these theories both assume that a country's absolute advantage is constant, and scales equally. Absolute advantage is achieved through low-cost production. Furthermore, Smith explained in this theory that under the conditions of free trade and perfect competition, trade takes place between nations that have an absolute cost advantage in the manufacture of specific items. This gives the company an absolute edge over other companies in How can absolute cost advantage be achieved? The logic behind absolute advantage is quite intuitive. In contrast, other countries are poor in these resources. Therefore, the USA has the cost-efficiency in producing soya than the UK. In addition, non-tariff barriers such as consumption and environmental safety requirements still exist.
Next
Absolute Advantage: Examples, Assumptions, Criticism

He added, let the market forces determine the volume, pattern, composition, and direction of trades. Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations, Book IV, Ch. Observing that impact, Smith said the trade limits proposed by traders would limit world Therefore, he advised promoting free trade among nations. Indonesia buys clothes from Malaysia, and Malaysia buys shoes from Indonesia. First, this theory assumes only two products and two countries.
Next
What is absolute advantage? examples and theory
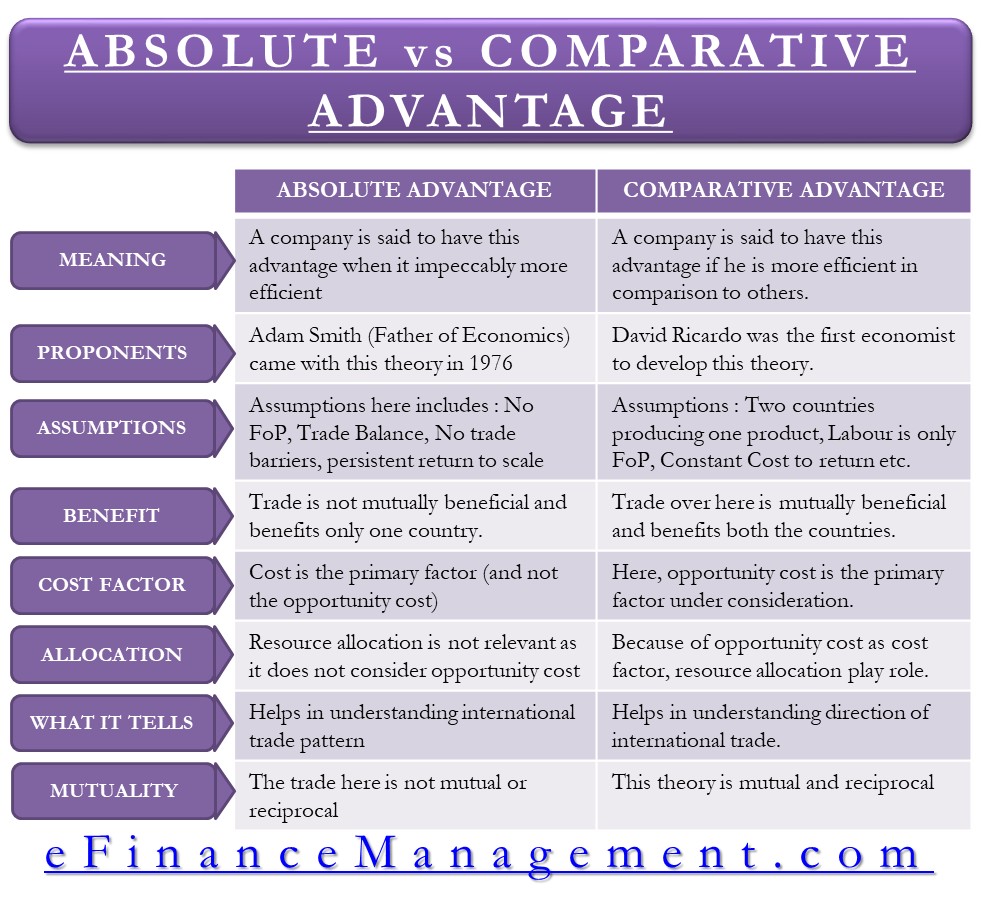
Conclusion Despite weaknesses, The Ricardian theory of comparative advantage has remained significant over the years. The benefits to nations from trading are the same as to individuals: trade permits specialization, which allows resources to be used more productively. The time of production is reduced and the cost of production such as paying wages or salaries to the workers would be reduced. It is believed that a nation that neglects this theory may have to pay a heavy price in terms of potential rate of growth and living standards. Absolute advantage refers to situations wherein one firm or nation can produce a given product of better quality, more quickly, and for higher profits than can another firm or nation.
Next









