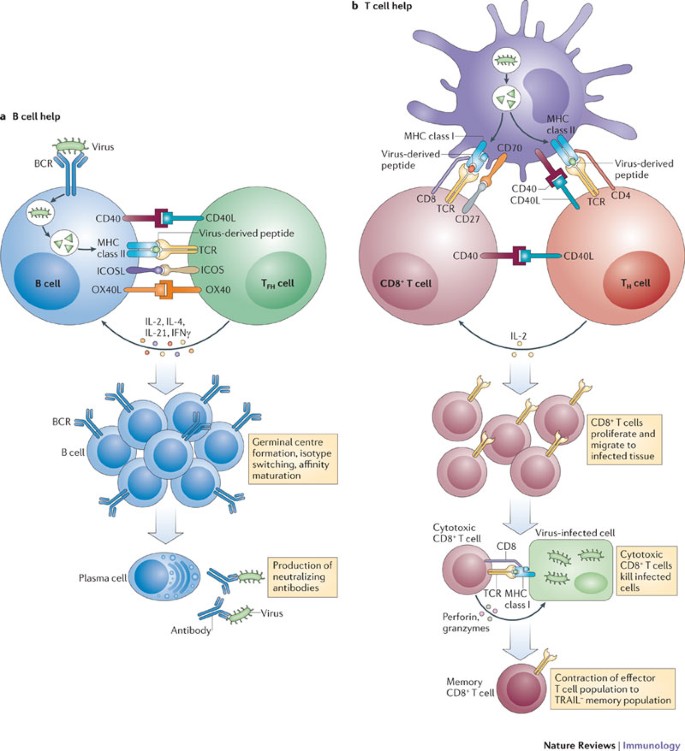
B and T cells, also known as B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, are two types of white blood cells that play a crucial role in the immune system. They are responsible for protecting the body against infections and diseases by identifying and eliminating harmful pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses.
B cells are produced in the bone marrow and are responsible for producing antibodies, which are proteins that recognize and neutralize foreign substances in the body. When a B cell encounters a pathogen, it will produce large amounts of antibodies and release them into the bloodstream. These antibodies will bind to the pathogen, marking it for destruction by other immune cells.
T cells, on the other hand, are produced in the thymus gland and are responsible for directly attacking infected cells. T cells can be divided into two main types: CD4+ T cells, also known as T helper cells, and CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T cells. T helper cells help to coordinate the immune response by releasing chemicals called cytokines, which stimulate the activity of other immune cells. Cytotoxic T cells, on the other hand, directly attack and destroy infected cells by releasing toxic substances called perforins and granzymes.
Both B and T cells are important for maintaining the body's immune defense against infections and diseases. However, they work in different ways and have different roles in the immune system. B cells produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens, while T cells directly attack infected cells. Together, they form a strong defense against potential threats to the body's health.
It is worth noting that B and T cells also play a role in autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body. In these cases, B and T cells may mistakenly recognize the body's own cells as foreign and attack them, leading to inflammation and damage to healthy tissues.
In conclusion, B and T cells are two types of white blood cells that play a crucial role in the immune system by protecting the body against infections and diseases. B cells produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens, while T cells directly attack infected cells. Together, they form a strong defense against potential threats to the body's health.