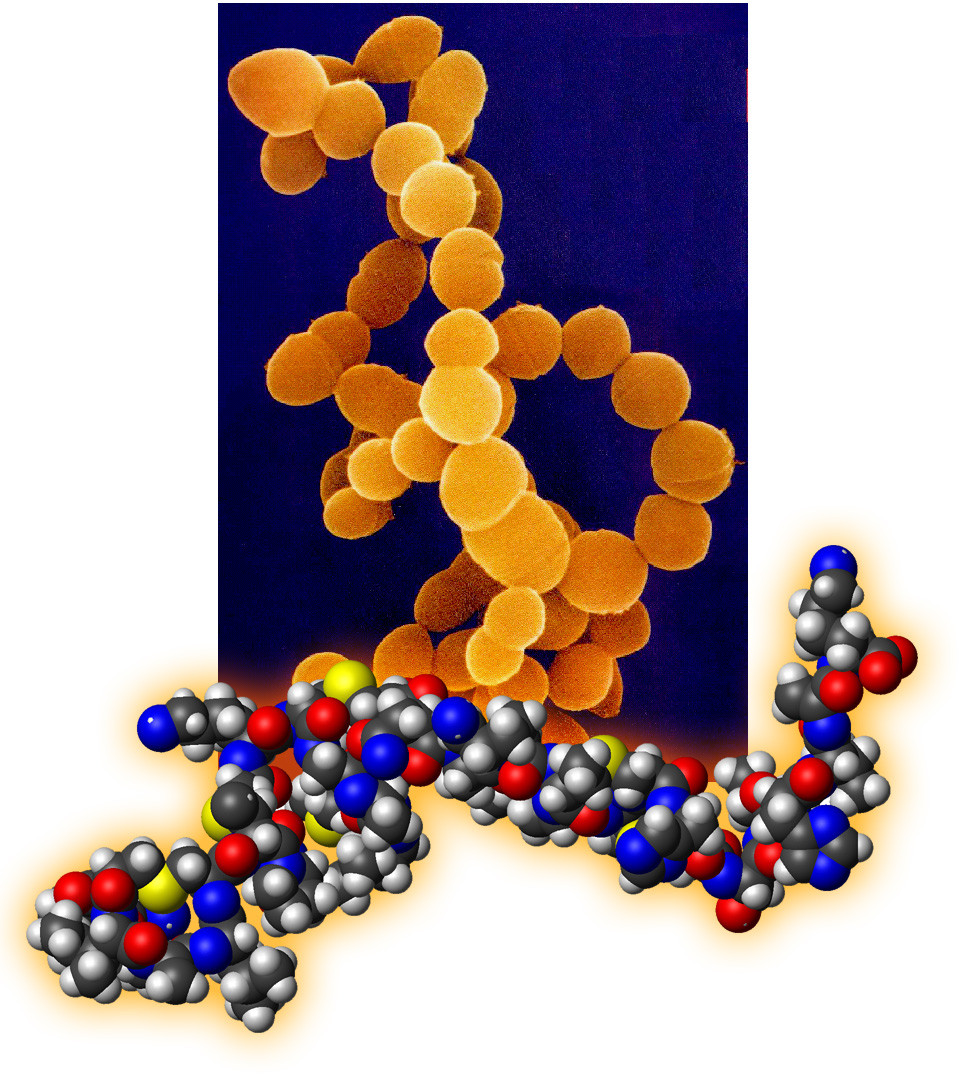
Bacillus lactis, also known as Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis, is a gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium that is widely used in the production of fermented dairy products. It is a member of the Lactobacillus family, which is known for its ability to produce lactic acid through the fermentation of carbohydrates.
B. lactis is found naturally in the intestinal tracts of humans and animals, as well as in the environment. It is a common starter culture in the production of fermented dairy products such as yogurt, cheese, and kefir. In these products, B. lactis converts lactose (a sugar found in milk) into lactic acid, which gives the products their characteristic tart flavor and helps to preserve them.
B. lactis has several beneficial properties that make it an attractive ingredient in fermented foods. It is a probiotic, meaning that it can contribute to the health of the digestive system by helping to balance the microflora in the gut. It has been shown to have a positive effect on gastrointestinal health, including reducing the risk of diarrhea and constipation and improving the absorption of nutrients. In addition, B. lactis has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, which can help to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria in the digestive system.
B. lactis is also used as a starter culture in the production of fermented vegetables such as sauerkraut and pickles. In these products, B. lactis ferments the sugars in the vegetables, producing lactic acid and other compounds that give the vegetables their characteristic flavor and texture.
Despite its widespread use and beneficial properties, B. lactis is not without its potential drawbacks. Some people may be allergic to it or may have sensitivities to fermented dairy products. In addition, overconsumption of fermented dairy products may lead to an excess of lactic acid in the body, which can have negative effects on bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
In conclusion, Bacillus lactis is a widely used bacterium in the production of fermented dairy products and vegetables. It has several beneficial properties, including its role as a probiotic and its antimicrobial properties. However, it is important to consume fermented products containing B. lactis in moderation, as overconsumption may have negative effects on health.
List of clinically important bacteria
Azonban akad néhány faj, mint például a A legtöbb baktériumfaj gömb vagy pálcika alakú. Oxygen-containing derivatives of terpenes such as alcohols, aldehydes, or ketones are referred to as terpenoids. Terpenes used for chiral pool synthesis. Mol Microbiol 23 3 , 423—9. In addition, many health benefits of Kimchi have been reported such as antioxidant, antimutagenic, anticarcinogenic, and antihypertensive activities. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.
ラクトバチルス アシドフィルス

Monoterpenes have two isoprene units, sesquiterpenes have three, and diterpenes have four. Az egyik ilyen eljárás a Bizonyos élőlények kimutatására a Gram-festés helyett más módszereket alkalmaznak, például a Nocardia egyedeinek kimutatására elterjedt a saválló , így a sejtek a háttérhez képest sötétebb színt vesznek fel. A Probiotic use is ineffective for acute pancreatitis and Crohn disease. However, only recently, there is emerging literature that an overgrowth of fungus in the small intestine of non-immunocompromised subjects may cause unexplained GI symptoms. Tapai pulut and Tapai ubi Tapai pulut is fermented rice produced in Malaysia. Lee, GI Lee, in Encyclopedia of Food Safety, 2014 Fermented Vegetable Products Kimchi is a unique fermented vegetable product with a long tradition in Korea. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
Examples of Bacteria: Types and Infections

Philippine Fermented Food: Principles and Technology. Further, it has been found that LAB isolated from kimchi block the adherence of Helicobacter pylori to a human gastric epithelial cell line and inhibit the growth of H. Am J Health Syst Pharm 59 Suppl 1, S13—9. Because menthol is the major component of this formula, peppermint oil, especially enteric-coated capsules, may offer similar results. Chapter 116: Infection and Inflammation of the Pediatric Genitourinary Tract. Tanasupawat, in Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology Second Edition , 2014 Vegetable, Fruit, and Cereal Fermentation Kimchi Kimchi is a traditional Korean fermented vegetable.
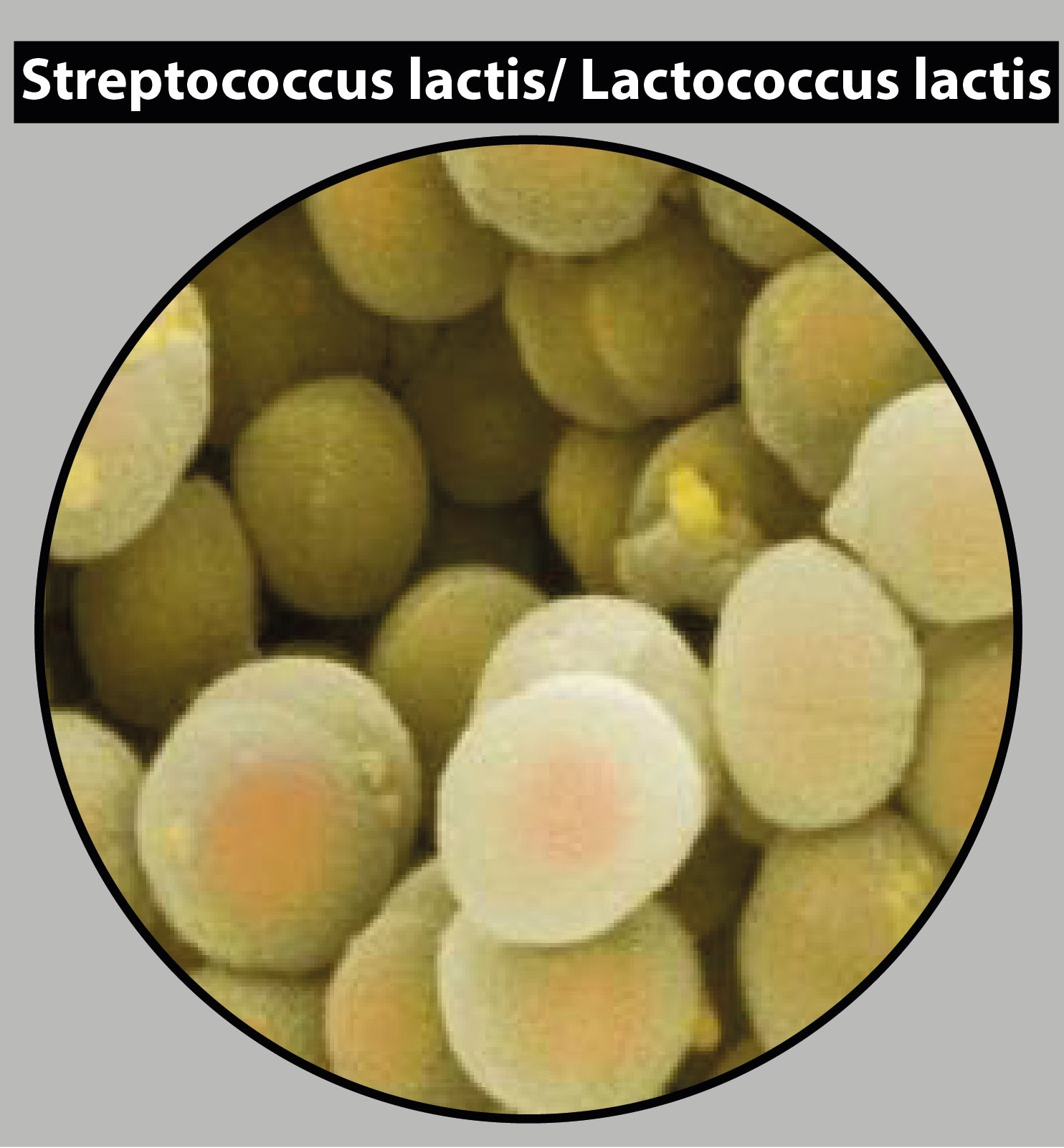
Lactococcus lactis
Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 78 3 , 435—63. Aktivitas antagonistik kultur starter yogurt dan kefir terhadap bakteri Staphylococcus aureus selama proses penyimpanan dingin Tesis Skripsi. They are divided into the following classes by the number of five carbon isoprene units they contain: hemiterpenes C5 , monoterpenes C10 , sesquiterpenes C15 , diterpenes C20 , sesterterpenes C25 , triterpenes C30 , and carotenoids C40. A Probiotic use may reduce the incidence of Clostridium difficile—associated diarrhea. Slimy biofilm-forming lactobacilli Type species: Heterofermentative, thermophilic, vancomycin resistant with two exceptions, Limosilactobacillus species are vertebrate host adapted and generally form exopolysaccharides from sucrose to support biofilm formation in the upper intestine of animals. Although probiotics appear to be effective for hepatic encephalopathy, there is insufficient patient-oriented evidence of their effectiveness for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.