The BCG matrix, also known as the Boston Consulting Group matrix, is a tool used by businesses to assess the performance and potential growth of their product lines or business units. It is based on the idea that a company's products can be classified into four categories: dogs, stars, question marks, and cash cows.
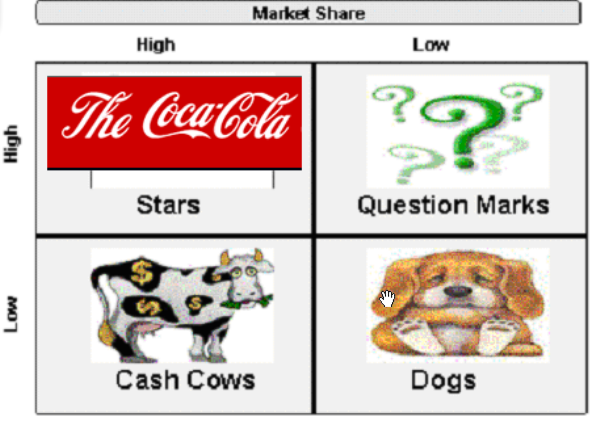
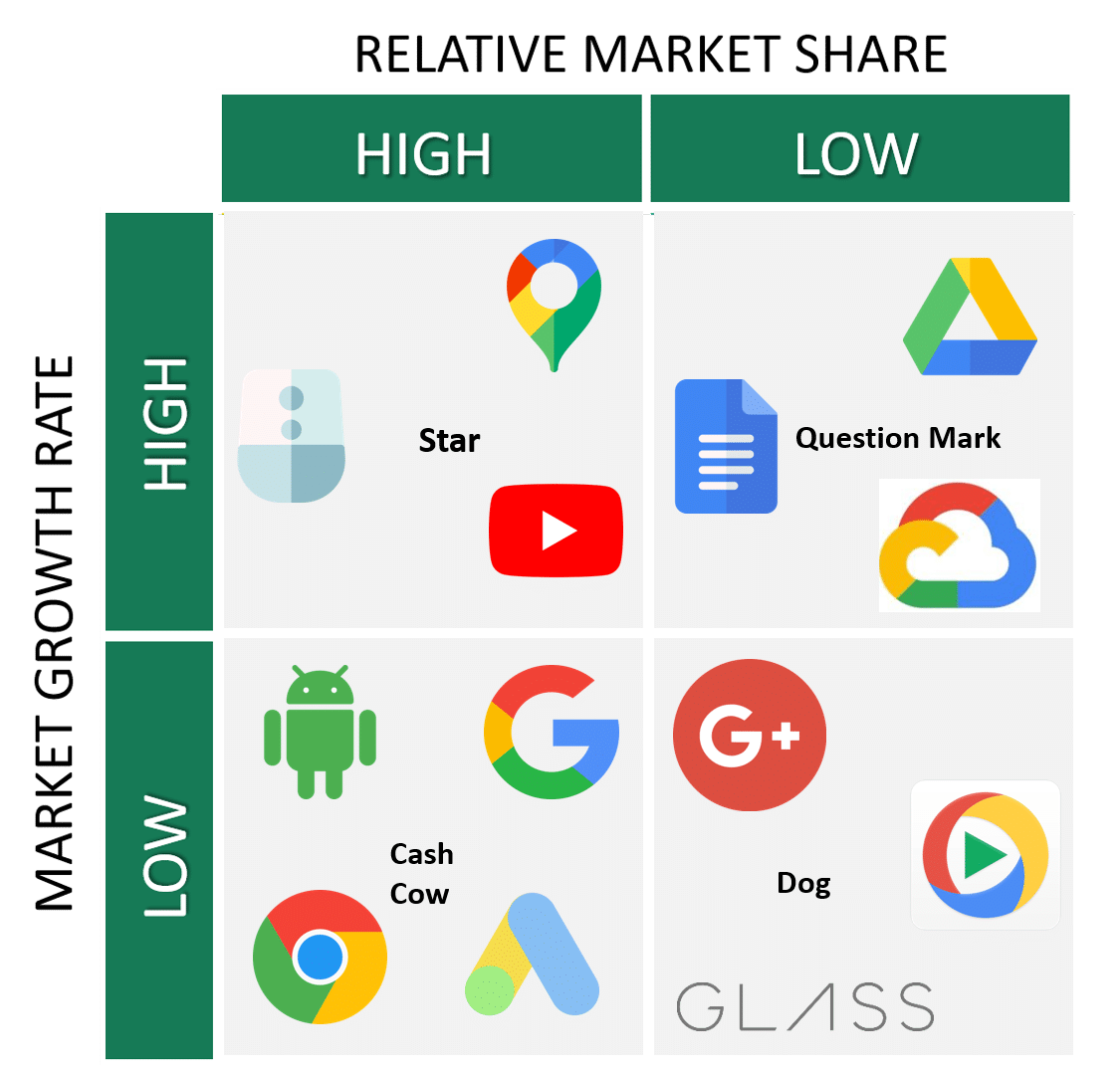
The BCG matrix is a two-dimensional graph, with market growth rate on the y-axis and relative market share on the x-axis. Products or business units are plotted on the graph based on their performance in these two categories.
A product or business unit that has a high market share in a low-growth market is classified as a cash cow. These products or units generate a steady stream of cash for the company and are important for maintaining the company's financial stability.
A product or business unit that has a low market share in a high-growth market is classified as a question mark. These products or units have the potential for significant growth, but also carry a high level of risk because they are not yet established in the market. The company will need to invest heavily in these products or units in order to capture market share and drive growth.
A product or business unit that has a high market share in a high-growth market is classified as a star. These products or units are the drivers of the company's growth and generate a significant portion of its profits. The company will need to continue investing in these products or units in order to maintain their market leadership and drive further growth.
Finally, a product or business unit that has a low market share in a low-growth market is classified as a dog. These products or units do not have much potential for growth and may even be a drain on the company's resources. The company may consider divesting these products or units in order to focus on more promising opportunities.
An example of how the BCG matrix can be applied to a specific company is by looking at Coca-Cola, one of the world's most well-known and successful brands. Coca-Cola is a global company that produces a wide range of nonalcoholic beverages, including carbonated sodas, juices, sports drinks, and teas.
Using the BCG matrix, we can classify some of Coca-Cola's products into the four categories. For example, Coca-Cola's flagship product, Coca-Cola Classic, is a star. It has a high market share in the carbonated soft drink market and is a well-established brand with a loyal customer base. The company will need to continue investing in this product in order to maintain its market leadership and drive further growth.
On the other hand, Coca-Cola's juice products, such as Minute Maid and Simply, may be classified as question marks. While the juice market is growing, these products have relatively low market share compared to other players in the industry. The company will need to invest heavily in these products in order to capture market share and drive growth.
Coca-Cola's sports drink, Powerade, may be classified as a cash cow. While the sports drink market is growing, Powerade has a strong market share and generates a steady stream of cash for the company. However, the company will need to be careful not to let this product become a dog by failing to innovate and keep up with changing consumer preferences.
Overall, the BCG matrix is a useful tool for businesses to assess the performance and potential growth of their product lines or business units. By understanding where each product or unit falls on the matrix, a company can make informed decisions about how to allocate its resources and drive growth.