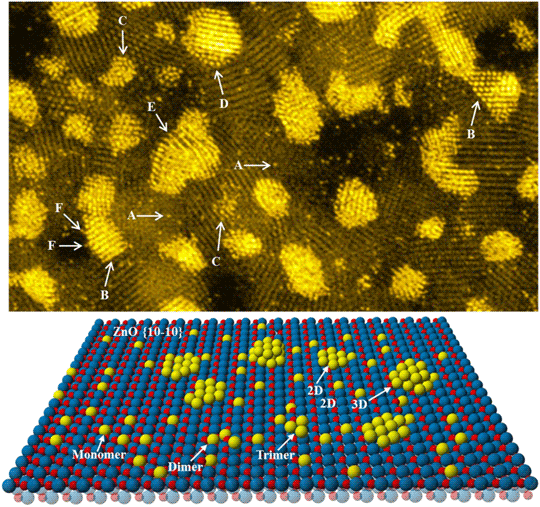
Bio 156 Lab Practical 2 is a lab course that focuses on the identification and understanding of various plant and animal specimens. This lab practical is typically taken by students who are enrolled in a biology program, and it covers a wide range of topics, including plant anatomy, animal physiology, and ecological principles.
In this lab practical, students will have the opportunity to work with a variety of specimens, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. They will learn how to properly identify these specimens, as well as how to classify them according to their characteristics and features. Students will also learn about the various functions and adaptations of these specimens, and how they interact with their environments.
One of the key skills that students will develop in this lab practical is the ability to observe and analyze biological specimens. This involves looking at the various structures and features of the specimens, such as their size, shape, and color, and using this information to draw conclusions about their biology and ecology. Students will also learn how to use various tools and techniques, such as microscopes, to study the specimens in greater detail.
In addition to observing and analyzing specimens, students will also have the opportunity to conduct experiments and make observations in the field. This may involve collecting specimens from local ecosystems, such as forests or wetlands, and studying their behavior and interactions in their natural habitats.
Overall, Bio 156 Lab Practical 2 is a valuable course for students who are interested in learning more about the biology of plants and animals. Through hands-on experiences and observation, students will gain a deeper understanding of the diversity of life on earth and the ways in which different species interact with each other and their environments. This knowledge will be useful for students who are considering careers in the field of biology or related fields, as well as for those who simply have a general interest in the natural world.
Biology Lab Practical #2 Flashcards
Bigot, whose son was one of Pasteur's students, sought for his advice on the problems of making beetroot alcohol and souring. In Prophase II, a new spindle. Translated by Elborg Forster. Explain the buret protein assay chemical reaction 8. Decourt, Les vérités indésirables, Paris, 1989, p.
Lab Practical 2 Flashcards & Quizzes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/important-lab-safety-rules-608156_final_CORRECTED-11865d88ddfc4b048118c918acec72a7.png)
Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences in French. Translated by Forster, Elborg. The Life of Pasteur. I also learned from those experiments how to determine. Bulletin of the History of Medicine. Finally, in 1964 Pasteur's grandson and last surviving male descendant, Pasteur Vallery-Radot, donated the papers to the In 1995, the centennial of the death of Louis Pasteur, a historian of science The Private Science of Louis Pasteur, and declared that Pasteur had given several misleading accounts and played deceptions in his most important discoveries. .
Nick Cross's BIO156: BIO 156 CROSS CHICKEN LEG LAB

However, Béchamp was on the losing side, as the Pasteur thought that Anthrax vaccine Pasteur publicly claimed his success in developing the anthrax vaccine in 1881. Report accidents immediately to instructor. In February 1854, to have time to carry out work that could earn him the title of correspondent of the Institute, he got three months' paid leave with the help of a medical certificate of convenience. Anthrax In the 1870s, he applied this immunization method to Louis Pasteur in his laboratory, painting by On 12 July 1880, Henri Bouley read before the French Academy of Sciences a report from But Pasteur found that anthrax bacillus was not easily weakened by culturing in air as it formed spores — unlike chicken cholera bacillus. This pertains to the bones rubbing together which causes damage and pain.
AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals

In 1870, he concluded that the corpuscles were the cause of pébrine it is now known that the cause is a Spontaneous generation Following his fermentation experiments, Pasteur demonstrated that the skin of grapes was the natural source of yeasts, and that sterilized grapes and grape juice never fermented. New York: William Wood and Company. When the fruiting bodies. Thus, if they cannot break lactose down, they cannot use glucose for energy and the lactose gets trashed LAB 6 CHROMOSOMES AND KARYOTYPES Objectives 1. Use a microvolume spectrophotometer to quantify a sample of DNA 4. . In fact, Pasteur's vaccine against chicken cholera was not regular in its effects and was a failure.
BIO156 Lab Assignment #blog.sigma-systems.com
» Émile Duclaux, Pasteur, Histoire d'un esprit, pp. Because of his study in germs, Pasteur encouraged doctors to sanitize their hands and equipment before surgery. Add 5 drops of safranin, wait 20 seconds, rinse with tap water B. A biologist more than a chemist, a spiritual more than a religious man, Pasteur was held back only by the lack of more powerful technical means and therefore had to limit himself to identifying germs and explaining their generation. Read lab exercise before lab. Vaccinations: a History: From Lady Montagu to Jenner and genetic engineering. Béchamp noted that Pasteur did not bring any novel idea or experiments.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/important-lab-safety-rules-608156_final_CORRECTED-11865d88ddfc4b048118c918acec72a7.png)