A biomolecule is a type of molecule that is found in living organisms and plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the organism. These molecules can be classified into four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
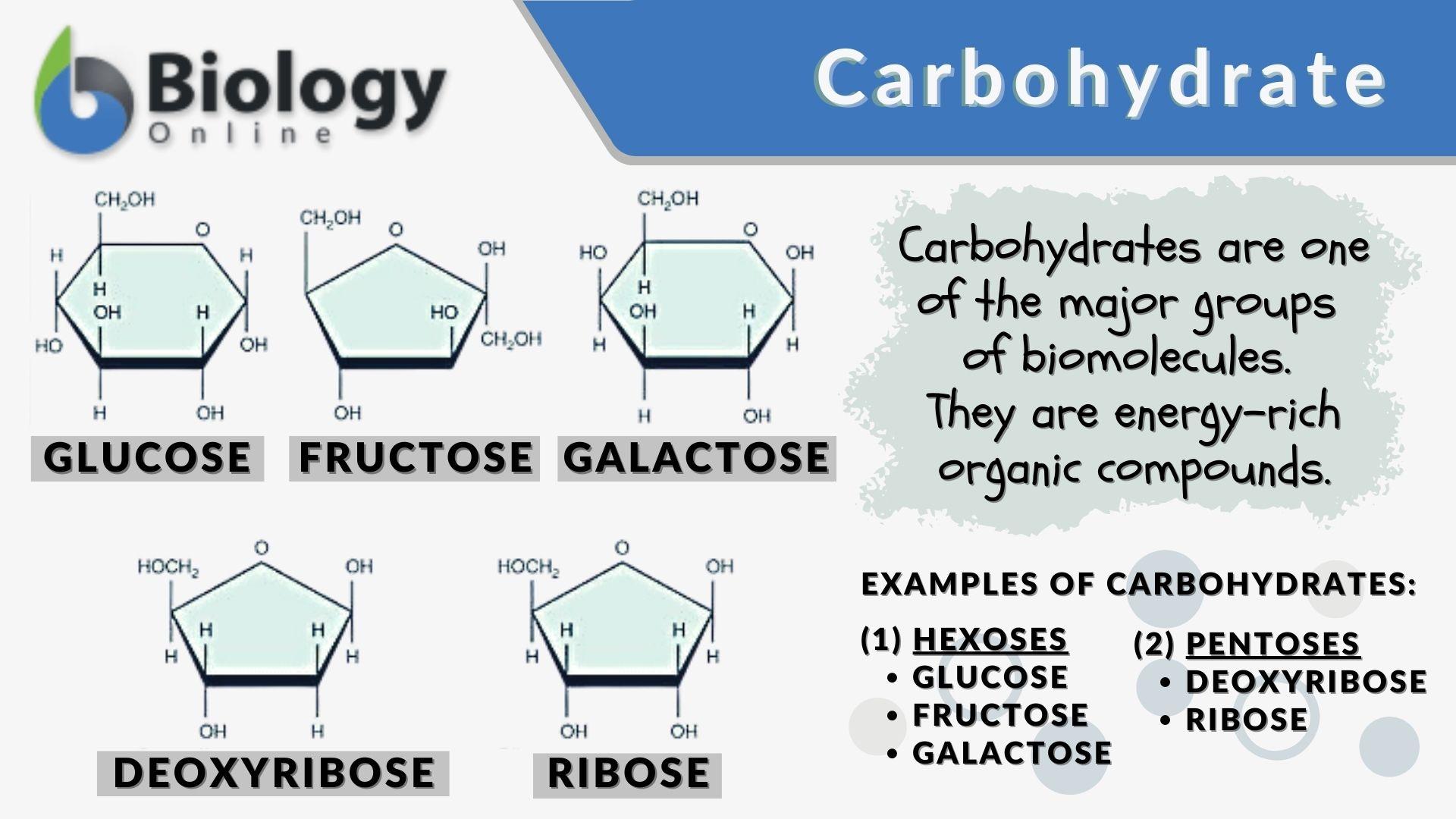
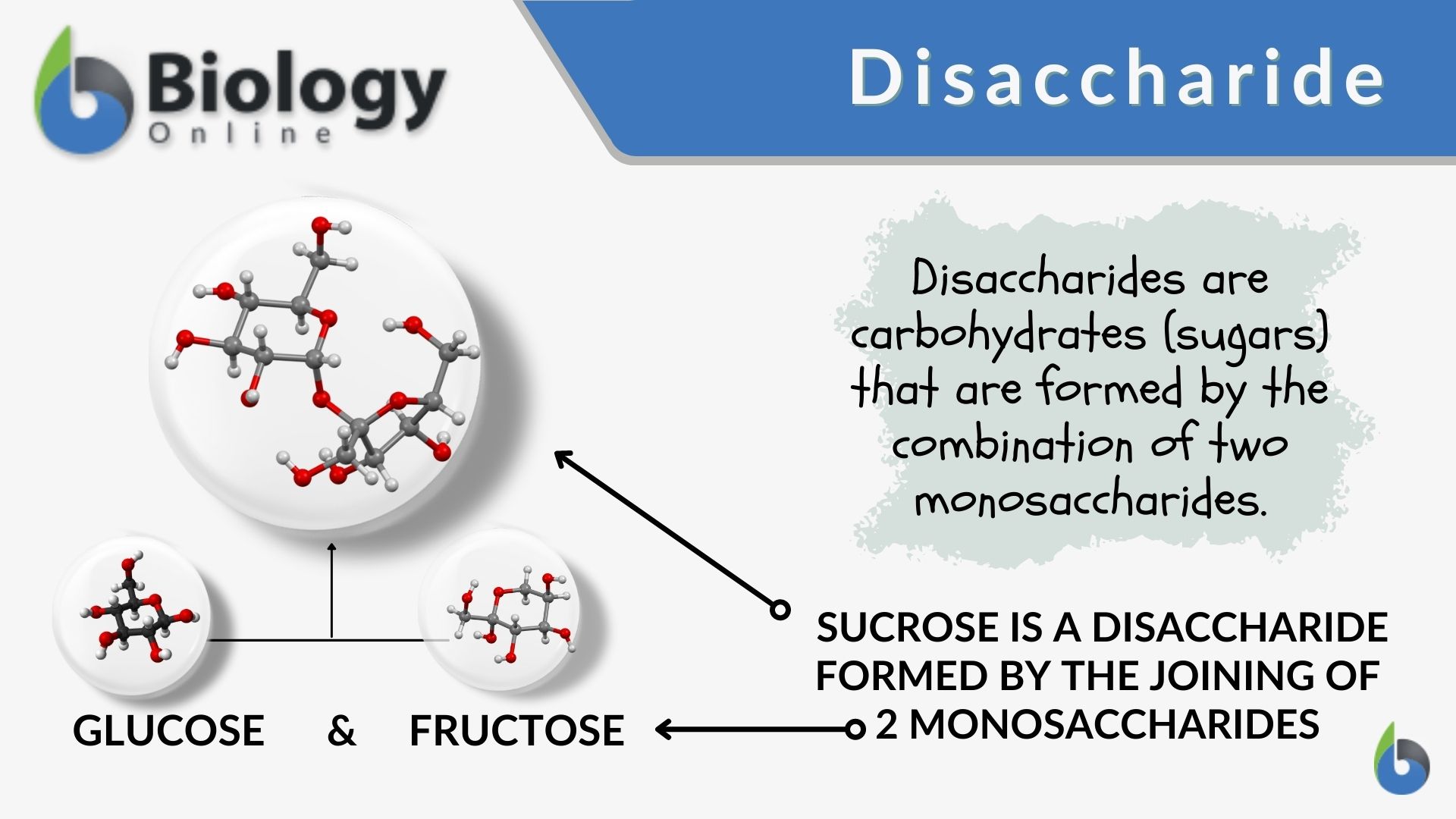
Carbohydrates are molecules that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are an important source of energy for living organisms, and they also play a structural role in plants, providing support and protection. Examples of carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, and cellulose.
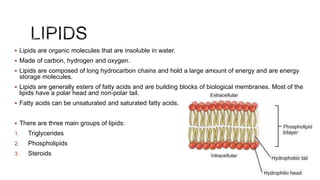
Lipids are biomolecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, but in a different ratio than carbohydrates. They are known for their role in energy storage, insulation, and cell membrane formation. Examples of lipids include fats, oils, and waxes.
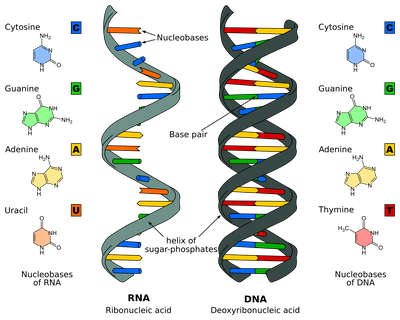
Nucleic acids are biomolecules that are made up of long chains of nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are two types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the synthesis of proteins, while RNA plays a role in the translation of these instructions into proteins.
Proteins are biomolecules that are made up of long chains of amino acids. They play a variety of roles in the body, including catalyzing chemical reactions, transporting molecules, and providing structural support. Proteins are also involved in the immune system, as antibodies help to protect the body against foreign invaders.
In conclusion, biomolecules are a vital component of living organisms and play a variety of important roles in the proper functioning of the body. They are classified into four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Each of these biomolecules has unique properties and functions that contribute to the overall health and well-being of the organism.
Biomolecule Definition & Meaning
Non-essential Amino acids— The amino acids, which can be synthesised in the body itself, are known as non-essential amino acids. Based on the structure and shape of proteins, globular proteins can be studied as under: I. Starch is a polysaccharide that is stored in plants as a form of energy. Structurally based on glyceride units, they are divided as monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides. Cane sugar, glucose, starch, etc. Proteins are the major constituents of all living organisms. Nucleic acids enable a cell to grow, maintain and divide by directing the synthesis of structural proteins.
Biomolecule

. They are also classified as: a. There are 20 different types of amino acids, and the sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its specific function. The nitrogenous bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine in DNA, and adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil in RNA. We hope this detailed article on Biomolecules helps you in your preparation.
Biomolecules: Meaning, Types of Biomolecules, Function

Tripeptide— If a third amino acid is attached to a dipeptide through another peptide bond, then the product formed is called a tripeptide. Molecular Insights into the Living Process. Proteins are essential for the body to build and maintain tissues, enzymes, and other proteins. For example, vegetable oils, sunflower oil, walnuts, fish oil, etc. Can you name some organic and inorganic substances which are present inside the cell? They are the major component of cell membranes and important for energy storage. Nucleic acids are used to store genetic information in the cell.
Proteins
Structure and Functions of Proteins As we know that proteins are the polymers of α-amino acids and are connected to each other by peptide bonds. For example, keratin present in hair, wool, silk and myosin fibres present in muscles , and many more. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the simplest form of organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. RNA is a polymer of ribose, which is a pentose sugar. Read this article to explore the different types of biomolecules and their importance in the body of living organisms. Ultimately, the biomolecules pdf gives a great overview covering some of the most important points in the field of biology.