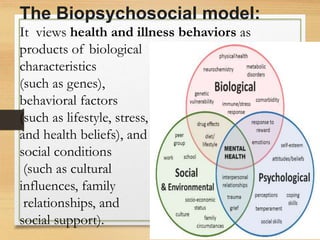
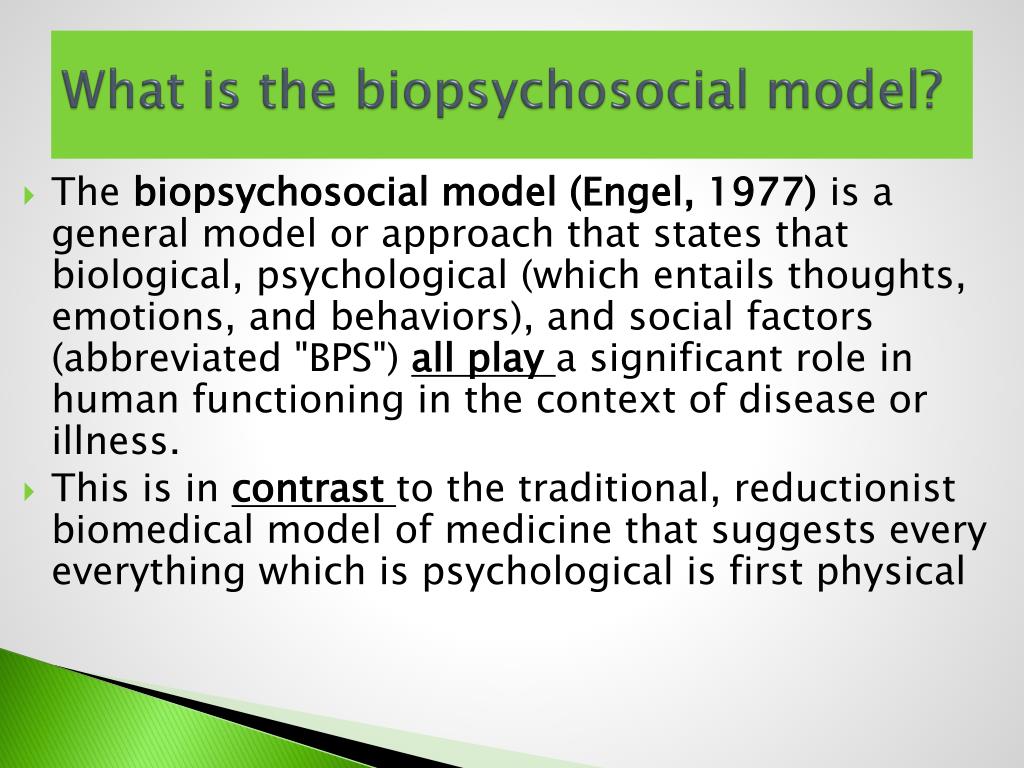
The biopsychosocial model of depression is a comprehensive approach to understanding and treating depression that acknowledges the interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors. This model recognizes that depression is not simply a result of a chemical imbalance in the brain, but rather is influenced by a complex interaction of multiple factors.
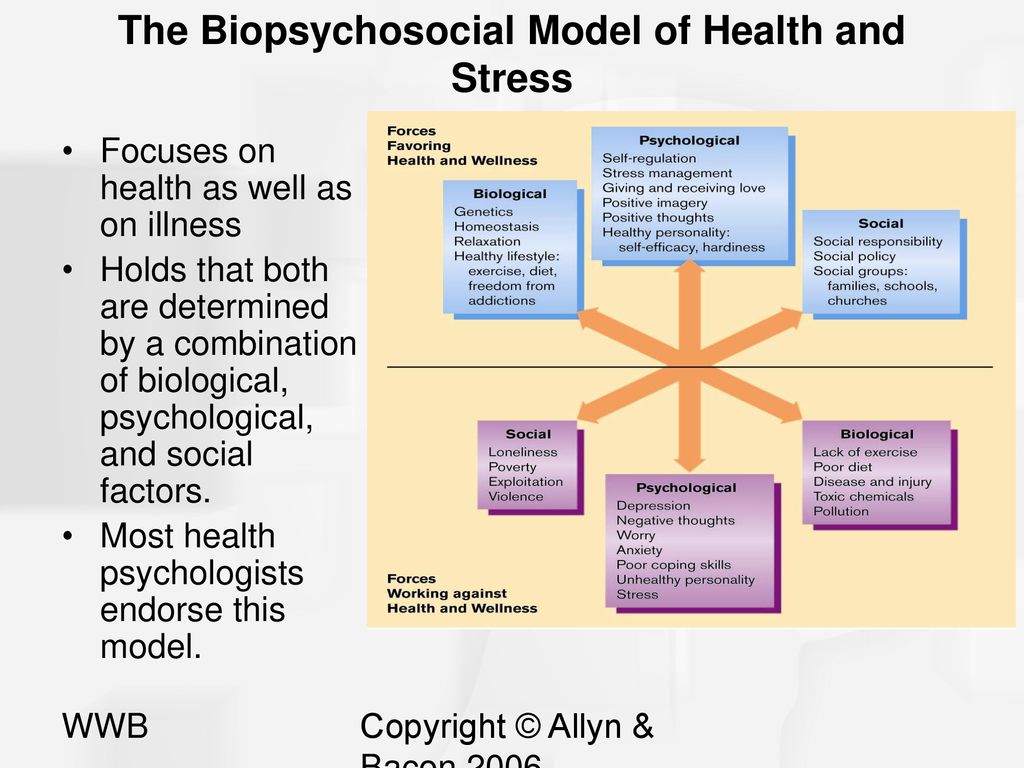
Biological factors that can contribute to depression include genetics, neurotransmitter imbalances, and hormonal imbalances. For example, research has shown that people with a family history of depression are more likely to experience depression themselves, suggesting that genetics may play a role in the development of the disorder. Neurotransmitter imbalances, such as low levels of serotonin, can also contribute to the development of depression. Hormonal imbalances, such as those related to thyroid function or the menstrual cycle, can also be contributing factors.
Psychological factors that can contribute to depression include negative thinking patterns, low self-esteem, and a lack of social support. Negative thinking patterns, such as rumination, can lead to a cycle of negative thoughts that can exacerbate feelings of sadness and hopelessness. Low self-esteem can lead to a negative self-image and a lack of confidence in one's abilities, which can contribute to feelings of worthlessness and helplessness. A lack of social support can leave individuals feeling isolated and disconnected, which can also contribute to the development of depression.
Social factors that can contribute to depression include stress, trauma, and social isolation. Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one or financial strain, can trigger a bout of depression. Trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, can also lead to the development of depression. Social isolation, whether due to a lack of social connections or a lack of social support, can also be a risk factor for depression.
The biopsychosocial model of depression highlights the importance of considering all of these factors when seeking treatment for depression. Treatment approaches that take a holistic approach, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can be effective in addressing the multiple factors that contribute to the disorder. Additionally, medication, such as antidepressants, can be helpful in addressing the biological factors that contribute to depression.
In conclusion, the biopsychosocial model of depression recognizes the complex interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors in the development and treatment of depression. This model highlights the importance of considering all of these factors in order to effectively treat the disorder and improve the overall well-being of individuals struggling with depression.