Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite (most notably as limestone, which is a type of sedimentary rock consisting mainly of calcite) and is the main component of pearls and the shells of marine organisms, snails, and eggs.
Hydrochloric acid, on the other hand, is a strong acid with the chemical formula HCl. It is a corrosive, colorless liquid that has a strong, pungent smell. It is commonly used in the production of chemicals, in the pickling of steel, and as a laboratory reagent.
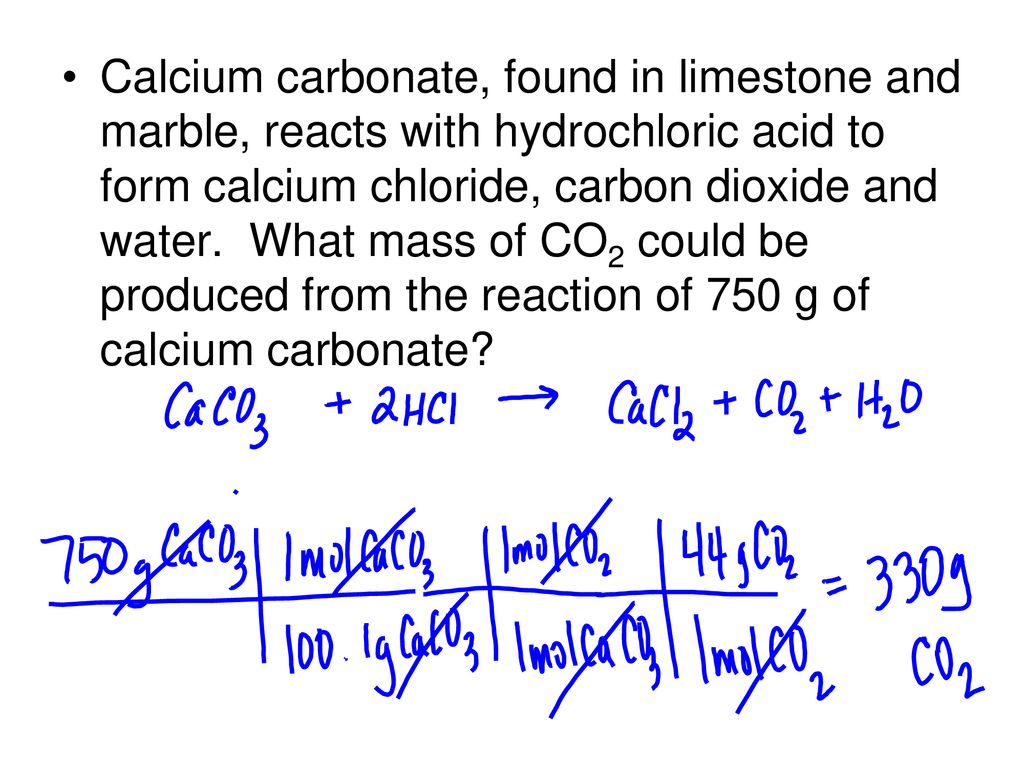
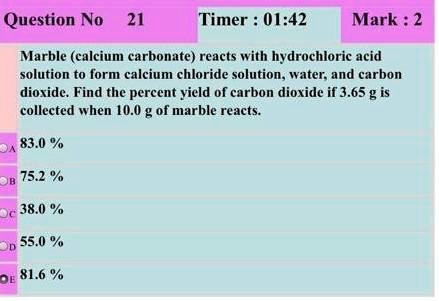
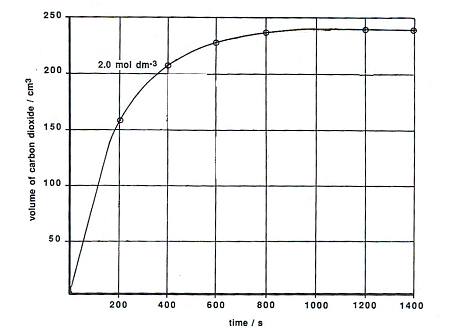
When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, a chemical reaction takes place that produces water, carbon dioxide, and calcium chloride. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
CaCO3 + 2 HCl -> CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
In this equation, the reactants (calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid) are written on the left side of the arrow, while the products (calcium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide) are written on the right side. The coefficients in front of each compound indicate the number of molecules involved in the reaction.
During the reaction, the hydrochloric acid donates its hydrogen ions (H+) to the calcium carbonate, causing the calcium carbonate to break down into its component ions: calcium ions (Ca2+) and carbonate ions (CO32-). The calcium ions then react with the chloride ions (Cl-) from the hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride, while the carbonate ions react with the hydrogen ions to form water and carbon dioxide.
Overall, the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is a classic example of an acid-base reaction, in which the hydrochloric acid acts as the acid and the calcium carbonate acts as the base. It is a exothermic reaction, meaning that it releases heat as it occurs.
In conclusion, the chemical reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid results in the production of water, carbon dioxide, and calcium chloride. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is CaCO3 + 2 HCl -> CaCl2 + H2O + CO2. This reaction is a classic example of an acid-base reaction and is exothermic in nature.