Carl Gustav Jung was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded the school of analytical psychology. Jung is best known for his theories on the collective unconscious, archetypes, and the process of individuation, which he saw as the psychological process of integrating the unconscious with the conscious self.
Jung was born in 1875 in Switzerland and was the son of a pastor. He studied medicine at the University of Basel and later trained as a psychiatrist at the Burghölzli Psychiatric Clinic in Zurich. In 1913, he met Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, and the two men developed a close friendship and professional collaboration. However, Jung eventually broke away from Freud's theories, particularly his emphasis on sexual repression as the root of all psychological problems, and developed his own ideas about the human psyche.
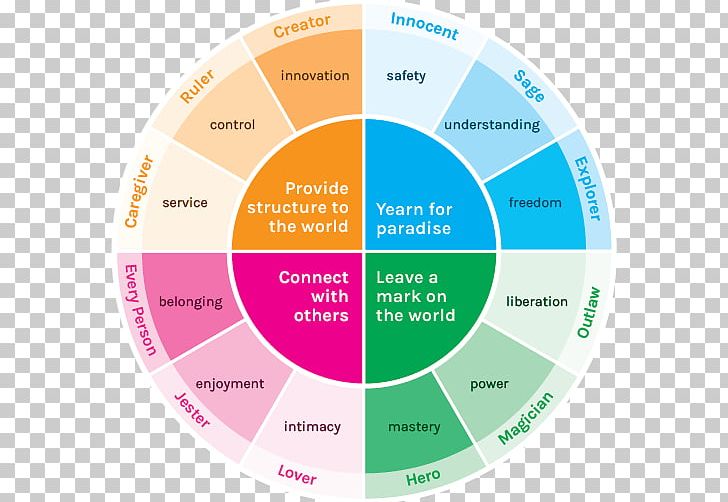
One of Jung's most influential concepts is the idea of the collective unconscious, which he saw as a reservoir of the experiences and memories of the human race. According to Jung, the collective unconscious is made up of archetypes, which are universal patterns or themes that are present in the mythology, literature, and religion of all cultures. These archetypes include the mother, the father, the hero, the trickster, and the anima and animus (the feminine and masculine aspects of the psyche). Jung believed that these archetypes influenced the way people perceive and experience the world, and that understanding them was essential for psychological growth and development.
Jung's theory of individuation, which he saw as the process of becoming a fully-fledged individual, was also central to his analytical psychology. Jung believed that in order to achieve individuation, an individual must integrate their unconscious with their conscious self, and this process involves exploring and coming to terms with one's own personal archetypes and the collective unconscious. This process requires a journey into the unconscious and a confrontation with one's own shadow, which Jung saw as the unconscious part of the psyche that contains all of the repressed thoughts, feelings, and impulses that an individual is not aware of. By facing and accepting the shadow, an individual can achieve greater self-awareness and wholeness.
Jung's ideas had a significant impact on the field of psychology and continue to be influential today. His theories on the collective unconscious, archetypes, and individuation have inspired numerous psychologists, therapists, and writers, and have been applied in a variety of fields, including literature, art, and film. Despite his many contributions to psychology, Jung was a controversial figure and his theories were often met with criticism and skepticism. However, his ideas about the human psyche and the importance of self-exploration remain a valuable and enduring legacy in the field of psychology.