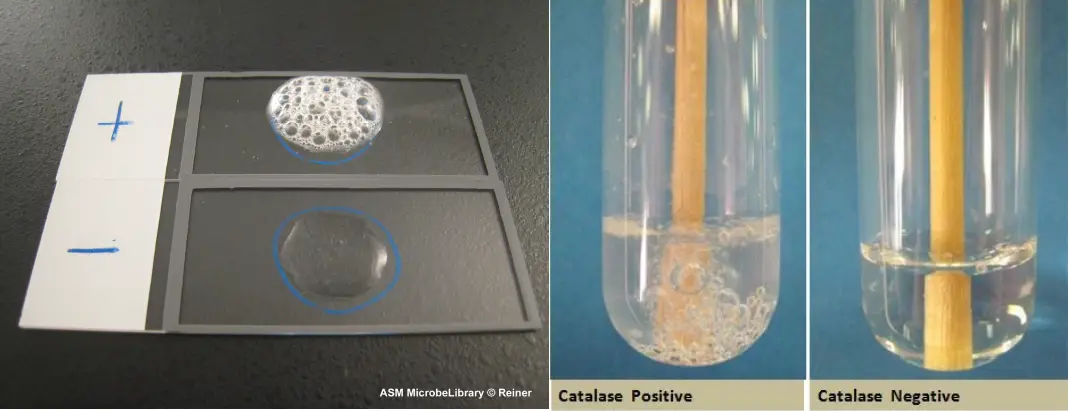
Catalase is an enzyme that is found in the cells of many organisms, including plants and animals. It is responsible for catalyzing the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide, a toxic compound that can damage cells, into water and oxygen. This process is important for maintaining the health of cells and preventing oxidative stress, which can lead to cell death.
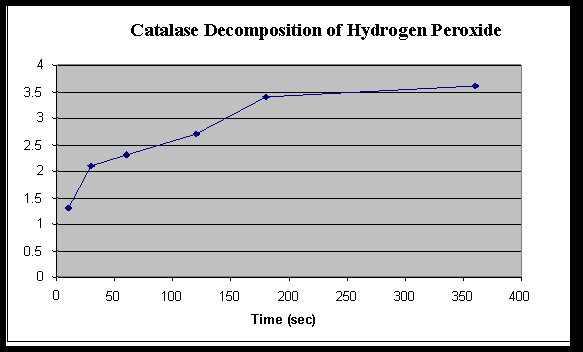
One way to study the activity of catalase is through an enzyme experiment. In this type of experiment, the rate of catalase activity can be measured by observing the production of oxygen gas as hydrogen peroxide is broken down. This can be done by adding a small amount of catalase to a solution of hydrogen peroxide and then measuring the rate at which oxygen is produced.
There are several variables that can affect the activity of catalase in this type of experiment. One important variable is the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, which can influence the rate of catalase activity. Higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide can result in faster rates of oxygen production, while lower concentrations may result in slower rates.
Temperature is also an important variable in catalase experiments. Enzymes, including catalase, are sensitive to temperature and their activity can be influenced by changes in temperature. In general, higher temperatures tend to increase the activity of enzymes, while lower temperatures can decrease their activity.
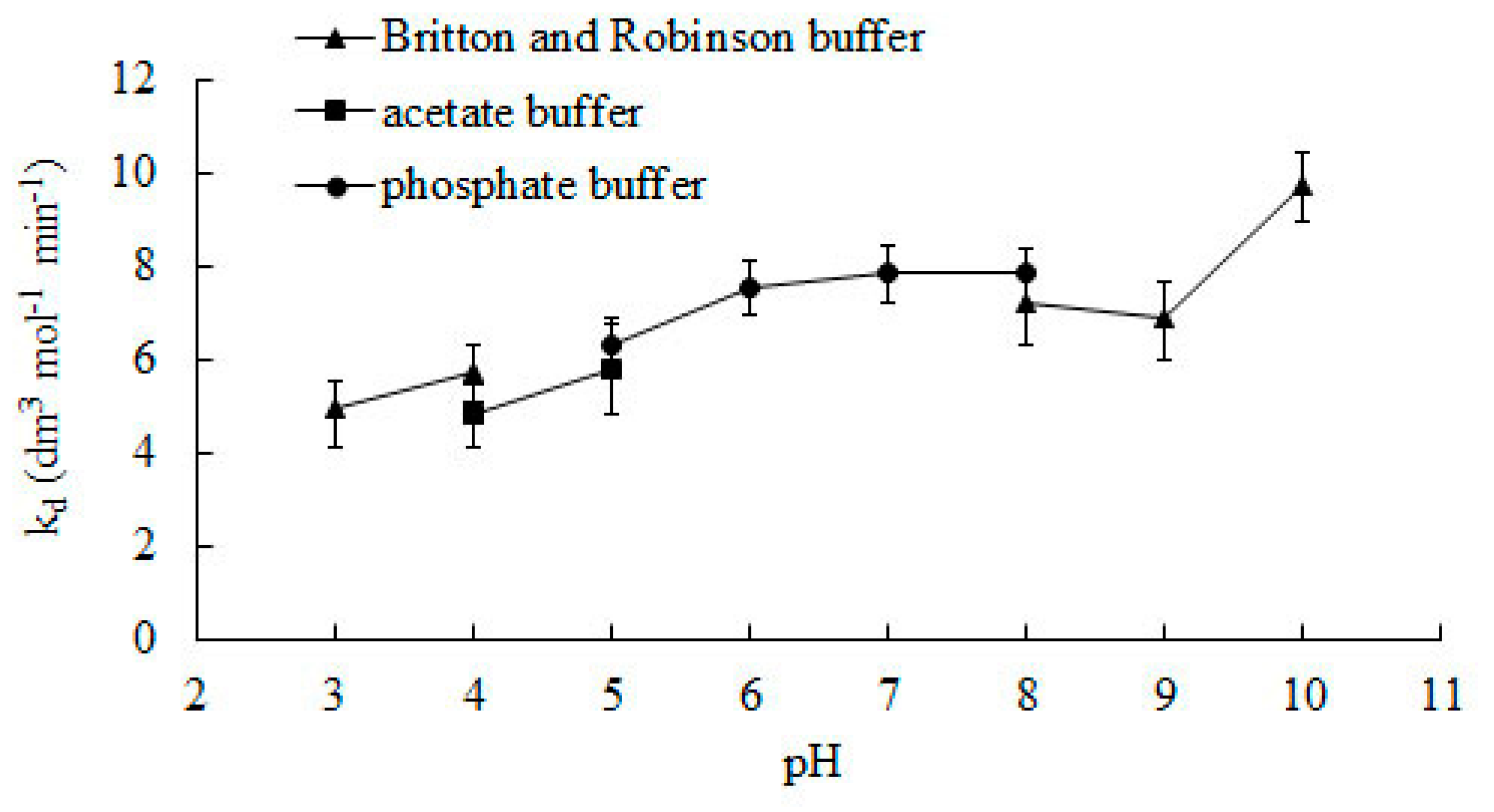
pH is another important variable that can affect the activity of catalase. The pH of the solution in which the enzyme is placed can influence the ionization state of the enzyme, which can in turn affect its activity. In general, enzymes tend to work best at a specific pH, known as their optimal pH, and their activity can decrease outside of this range.
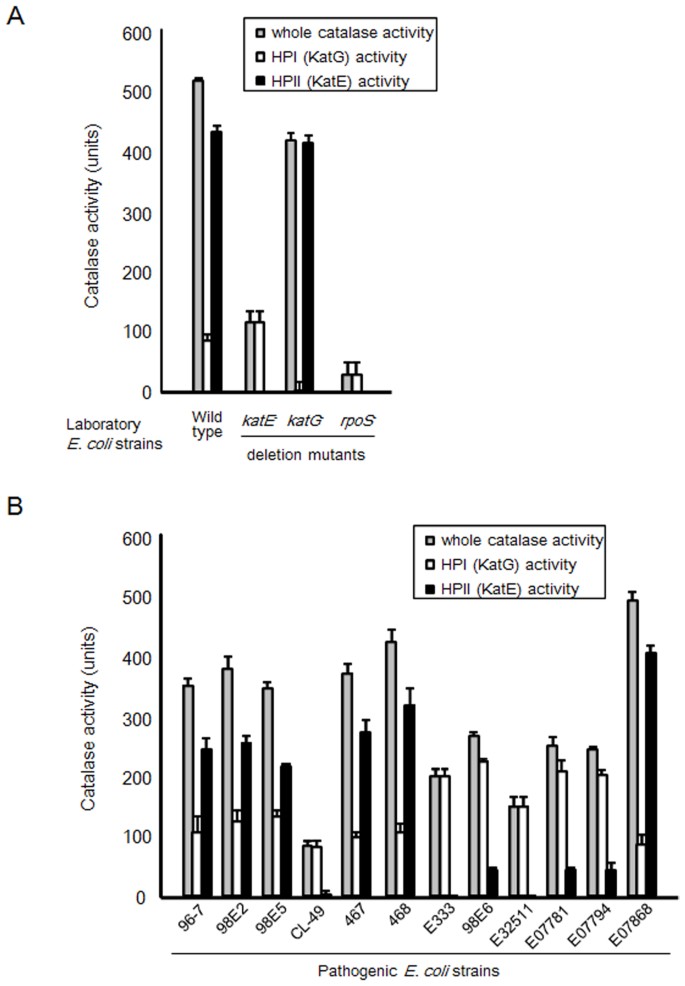
Finally, the presence of inhibitors can also affect the activity of catalase. Inhibitors are substances that can bind to the enzyme and block its activity, either by preventing the substrate from binding to the enzyme or by altering the structure of the enzyme. The presence of inhibitors can significantly decrease the activity of catalase in an experiment.
In conclusion, the activity of catalase can be studied through an enzyme experiment in which the production of oxygen gas is measured as hydrogen peroxide is broken down. There are several variables that can affect the activity of catalase in this type of experiment, including the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the temperature of the solution, the pH of the solution, and the presence of inhibitors. Understanding the factors that influence the activity of catalase can help researchers to better understand the role of this enzyme in cells and how it contributes to maintaining the health of organisms.