The pigeonhole principle, also known as the "boxes and pigeons" principle, is a simple but powerful concept in mathematics that states that if there are more objects than available spaces (or "pigeonholes"), then at least one space must contain more than one object. This principle has many applications in various fields, including computer science, economics, and even daily life.
One of the most common applications of the pigeonhole principle is in computer science, specifically in the field of data compression. In data compression, the goal is to represent a large amount of data using a smaller number of bits. One way to do this is by using a technique called "lossless compression," where the original data can be recovered exactly from the compressed version. The pigeonhole principle can be used to prove that certain lossless compression schemes are optimal, meaning that no other scheme can compress the data more efficiently. For example, suppose we have a set of data consisting of the letters A, B, C, and D. If we want to represent this data using only 2 bits per letter, we can use the pigeonhole principle to prove that at least one of the letters must be represented by two different combinations of 2 bits. This means that the data cannot be losslessly compressed using 2 bits per letter, and we must use a different method or a higher number of bits to achieve optimal compression.
Another application of the pigeonhole principle is in economics, specifically in the study of market equilibrium. Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service that is being supplied is equal to the quantity that is being demanded. The pigeonhole principle can be used to prove that under certain conditions, market equilibrium is always possible. For example, suppose we have a market for a certain type of good, and there are three sellers who each have a certain number of units of the good to sell. The pigeonhole principle states that if the sellers have a total of more than three units of the good, then at least one of them must have more than one unit to sell. This means that there must be at least one buyer who is willing to purchase more than one unit of the good, which is necessary for the market to reach equilibrium.
In daily life, the pigeonhole principle can also be used to solve practical problems. For example, suppose you have a group of friends who are going on a road trip, and you need to decide which car to take. You have three cars to choose from, each with a different number of seats. The pigeonhole principle states that if you have more friends than the total number of seats in the three cars, then at least one of the cars must have more than one person in it. This can help you decide which car to take, and also serve as a reminder to carpool to save space and reduce environmental impact.
In conclusion, the pigeonhole principle is a simple but powerful concept that has many applications in various fields, including computer science, economics, and daily life. Its versatility and simplicity make it a valuable tool for solving a wide range of problems.
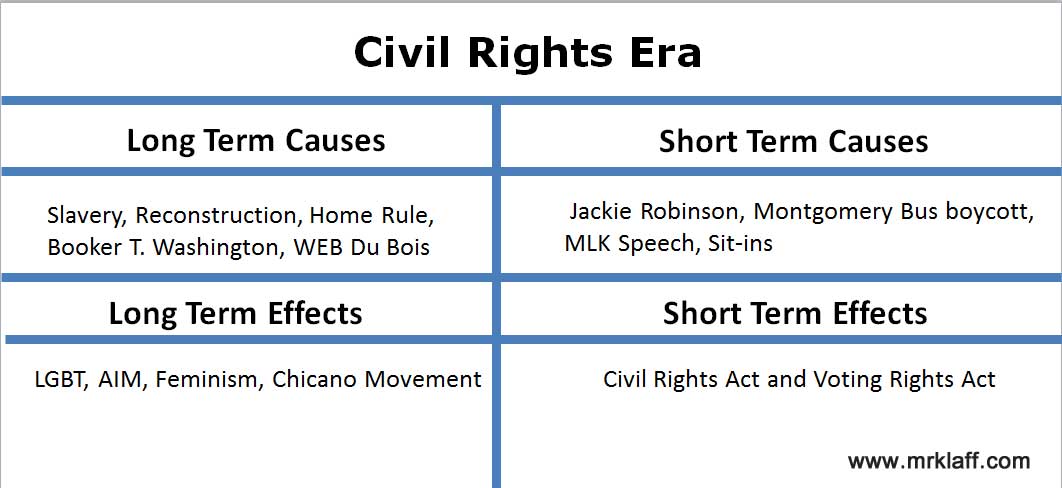
Cause and effect is a fundamental concept in history and is the basis for understanding how events and developments have shaped the world we live in today. When historians study the past, they often try to identify the causes of certain events and the effects they had on society. Understanding cause and effect can help us better understand how the world has changed over time and how different events and decisions have shaped the course of history.
One of the most significant examples of cause and effect in history is the Industrial Revolution. This period of rapid industrialization, which began in the 18th century and continued into the 19th century, had a number of causes, including advances in technology, the availability of raw materials, and changes in the way people worked and lived. The Industrial Revolution had a huge impact on society, transforming the way goods were produced and changing the way people lived and worked. It led to the growth of cities, the expansion of trade, and the development of new forms of transportation and communication.
Another example of cause and effect in history is the American Revolution. This event was caused by a number of factors, including colonial resentment of British rule, the influence of Enlightenment ideas, and the desire for independence and self-governance. The American Revolution had a significant impact on the world, as it led to the founding of the United States and the establishment of a new form of government based on the principles of democracy and liberty. It also inspired other movements for independence and self-determination, including the French Revolution and the liberation movements of the 19th and 20th centuries.
Cause and effect can also be seen in the rise and fall of empires. For example, the Roman Empire was one of the most powerful and influential empires in history. Its rise was due to a number of factors, including its military strength, its system of government, and its ability to assimilate conquered peoples into its culture. However, the Roman Empire eventually fell, due in part to internal conflicts, economic decline, and external threats. The fall of the Roman Empire had a significant impact on the world, as it led to the spread of Christianity and the development of feudalism in Europe.
In conclusion, cause and effect is a crucial concept in history, as it helps us understand how events and developments have shaped the world we live in today. By identifying the causes of historical events and the effects they had on society, we can better understand the complex forces that have shaped the course of human history.