The Cold War was a period of political and military tension between the Western powers, led by the United States, and the Eastern powers, led by the Soviet Union, that lasted from the end of World War II until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The causes of the Cold War can be traced back to the ideologies and actions of the two superpowers, as well as the events and circumstances of the post-World War II world.
One of the primary causes of the Cold War was the fundamental differences in ideology between the United States and the Soviet Union. The United States was a capitalist democracy, while the Soviet Union was a communist state. These differences in ideology led to deep mistrust and hostility between the two countries, as each saw the other's system as a threat to its own.
Another cause of the Cold War was the actions of the two superpowers in the aftermath of World War II. The United States and the Soviet Union emerged as the dominant powers in Europe after the war, and each sought to spread its influence and ideology throughout the continent. This led to a series of proxy wars and conflicts, as the two sides supported different sides in various conflicts around the world.
The development of nuclear weapons was also a major factor in the Cold War. The United States was the first to develop nuclear weapons, and used them to drop atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan during World War II. The Soviet Union soon followed suit, and the two sides engaged in an arms race that lasted for decades, as each side sought to develop more and more powerful weapons.
In addition to these factors, the Cold War was also shaped by the events of the time, including the decolonization of Africa and Asia, the rise of nationalism and anti-colonial movements, and the emergence of new states in the post-World War II world. These events often pitted the United States and the Soviet Union against each other, as each sought to gain influence and support in these regions.
Overall, the causes of the Cold War were complex and multifaceted, involving deep ideological differences, actions taken by the two superpowers, and the events and circumstances of the post-World War II world. While the Cold War eventually came to an end with the collapse of the Soviet Union, its legacy continues to shape international relations and global politics to this day.
Causes Of The Cold War

Here Kennan pleaded for a stronger attitude toward the Soviet Union. After the surrender, Germany was divided into four zones each under the control of USA, USSR, France and England. Also missed, has been the profound difference in British and American conceptions of international relations that would arguably later surface in the Suez Crisis, and in American commitments of force, including ground troops, to areas of realtively minimal material interest to the United States. The West Asian conflict is the last remaining major legacy of half a century of the cold war, in whose solution lies the complete and of the cold war. Still, this situation changed quickly as the Soviet Union became a force to be reckoned with. They wanted global charge and other nations to follow the same economic and political systems.
Cold War: Origin and Causes
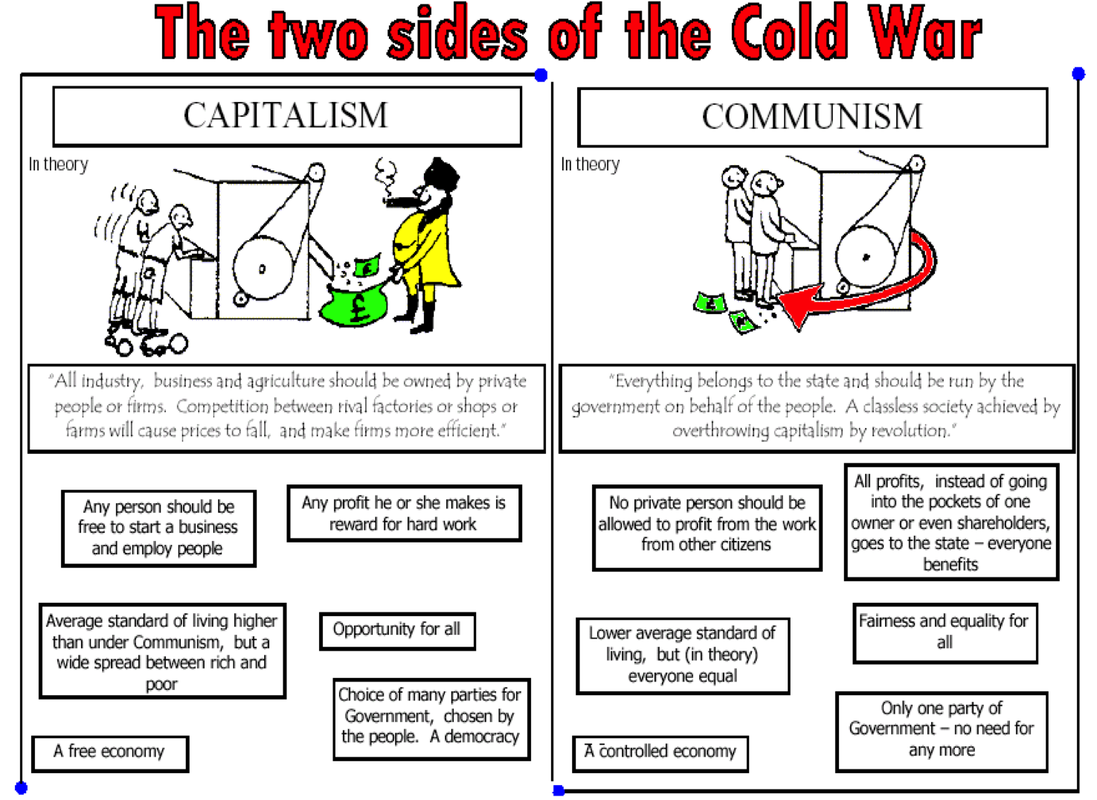
Ideological Differences The United States of America follows a democratic approach while the Soviet Union followed a communist approach to government and a way of life. The climax of the Berlin crisis came, when on August 13, 196La 25 miles long Berlin Partition Wall was erected to check refugees fleeing from East Berlin to West Berlin. Instead of sitting at the UN to think of ways and means to help humanity, there had been going on wordy duels. The American refusal to inform the Soviets of the Manhattan Project to develop the atomic bomb, the delay in sending the Soviets promised Lend-Lease supplies, the delay in opening up the second front causing Stalin to doubt that American policy was to let the Russians and Germans destroy each other so that the United States could then pick up the pieces from among the rubble the American failure to inform the Soviets of wartime strategy to the extent that it informed Great Britain and the use of the atomic bomb against Japan, perhaps misunderstood as a ploy to prevent Russian involvement in Pacific peace settlement. This changed in 1949, when the USSR tested its first atomic bomb, leading to a wrestle between the countries to have the most powerful nuclear weapons with the most effective delivery mechanisms. Likewise, in communist countries, capitalism was painted as a pure devil.
Causes Of Cold War

After the war, the West felt threatened by the continued expansionist policy of the Soviet Union, and the traditional Russian fear of incursion from the West continued. The Cold War encompasses a period from the end of the Second World War WWII , in 1945, to the fall of the Soviet Union, in 1989. Bibliography Alfred von Tirpitz and Bernhard von Bülow. Containing growing Soviet trim and communism in the Balkans in the post-war years triggered the cold war. During the second world war, Britain, France, USA and the Soviet Union had all been allies, fighting against Germany.
(PDF) Analysis of the Causes of the Cold War

With its Asian allies, the US organized CENTO and SEATO, and with Australia and New Zealand formed ANZUS. In short, it can be defined as a state of intense diplomatic, political, economic, and ideological struggle short of armed belligerency and clash. The Cold War was a time of suspicion and rivalry between America and the Soviet Union. The United States president Harry S. The United States is a capitalist country. Resemblances of the Cold War were seen in Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Americas. This bi polarization had led to a situation of the cold war.









