Community service is an integral part of my life and has always been an important way for me to give back to my community. I have been fortunate enough to be able to volunteer my time and energy to a variety of organizations, and each experience has been incredibly rewarding. From helping to feed the homeless and collect donations for those in need, to tutoring disadvantaged children and cleaning up local parks, I have always been committed to making a positive impact on those around me.
I believe that community service is not only a way to help others, but also a way to learn and grow as an individual. Through my experiences volunteering, I have gained valuable skills such as leadership, teamwork, and communication. I have also had the opportunity to learn about different cultures and ways of life, as well as develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for the diversity within my community.
One of the most memorable experiences I had while volunteering was when I worked at a local animal shelter. Not only did I get to spend time with and care for the animals, but I also learned about the importance of responsible pet ownership and the role that shelters play in our community. I was able to make a small difference in the lives of those animals and it was an incredibly fulfilling experience.
In addition to the personal growth and satisfaction that comes with community service, I also believe that it is important to give back to the community in which we live. We are all a part of a larger whole and by volunteering our time and resources, we can make a meaningful difference in the lives of others.
For these reasons, I am grateful for the opportunity to apply for a community service scholarship. Receiving this scholarship would not only recognize my dedication to community service, but also allow me to continue to make a positive impact in my community. I am committed to using this scholarship to continue to volunteer my time and energy to organizations that are making a difference in the lives of others. Thank you for considering my application.
Cell Transport Mechanisms and Permeability Worksheet...
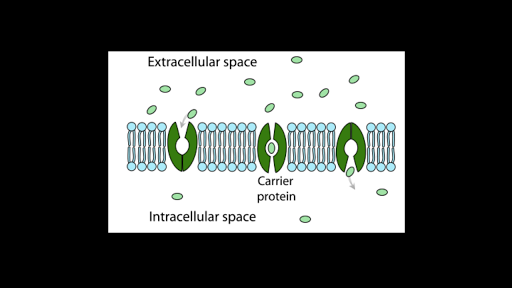
In this experiment NaCl, albumin, and glucose will be used to help show the movement of water across a membrane. If the hydrostatic pressure is high enough then all the solutes and water will able to pass through the membrane. Why or why not? How did the surface area affect the diffusion of the cube? Each process has similar variables that will affect the rate or capability to diffuse, but some require more work, energy or other substances needed to allow diffusion to occur. State whether each of the following will a move into the sac, b move out of the sac, or c not move Both hydrochloric acid HCl with a molecular weight of about 36. In this experiment it represented the sodium potassium pump which the solutes presences directly affects whether or not the process will occur, because without one or the other the process would not be able to occur at all. What about the surface area to volume ration? Urea was able to pass through two out of four membranes, and also once through it had an average rate of.
Cell Transport Mechanisms and Permeability: Computer...
Filtration is a process that You correctly answered: c. Second, to gain a better understanding of the role of selectively permeable membranes in osmosis, and to learn about the significance of hypotonic, isotonic, or…. With out the different specific types of processes some solutes would never be able to pass through a membrane or there would be no control of how much or when a solute is allowed to cross over. The first type of cell transport is passive processes which are driven by concentration or pressure differences in the interior and exterior of the cell. These pores let only tiny molecules to go through them.
Cell Transport Mechanisms and Permeability: Computer Simulation (400 Words)
To further explain if there is a low water concentration, high amounts of solutes will be present. What happens to the urea concentration in the left beaker the patient? Permeability, concentration gradients, plasmolysis, water potential, and equilibrium were also concepts that were delved into in this lab. Meaning the pressure on either side of the membrane is what pushes or decides whether or not the water and solutes will be able to pass through. Activity 2: Simulating Dialysis 6. It will always move to the solution with the highest concentration of solutes. Which solute s were able to pass through the 20 MWCO membrane? Diffusion, osmosis, and passive and active transport are all fundamental concepts of Biology. Small pores in the semi selectively permeable membranes, which flow only towards one way, allow the process of osmosis to continue.
Computer Simulation of Cell Transport Mechanisms and...

Albumin was added to the solution, but was not able to pass through any of the membranes since the solute was too large, but the pressure was constant through every size membrane. Active transport, the only active process, uses cellular energy ATP to help move solutes across the membrane. In this experiment NaCl, urea, albumin and glucose will be used to show how different substances move differently across the membrane. In this experiment we will demonstrate a sodium potassium pump to illustrate how ATP is needed to get both NaCl and K across the membrane. This was evident in the results when we decided to run an experiment with the same starting concentration and same size membrane, but different pressures. .
Exercise 5 The Cell: Transport Mechanisms and Cell Permeability Flashcards

The following refer to Activity 1: Simulating Dialysis Simple Diffusion. In the chart labeled filtration it shows the size of the membrane, pressure, the rate of filtration, if residue was present in the membrane, the starting concentration and the filter concentration. In the final experiment where we tested active transport we only half way supported our hypothesis. Results The results and data from the experiments are presented in several charts attached to the lab report. Molecules cross cell membrane by diffusion. In both runs no solutes were able to pass even though the pressure behind it had increased by 50, the pressure did not affect the solution enough to pass through the membrane since the solutes were to large to pass through membrane in the first place.








