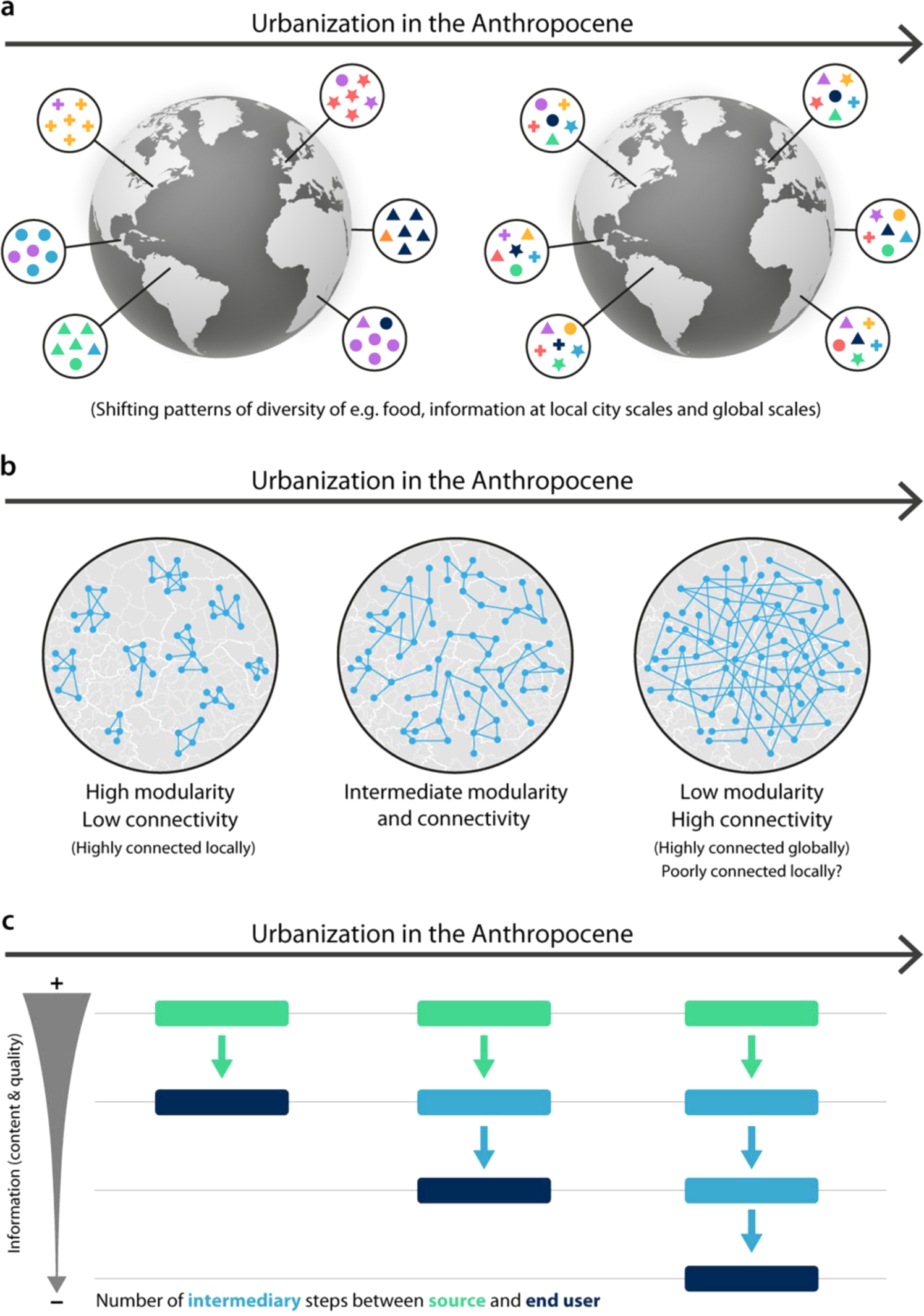
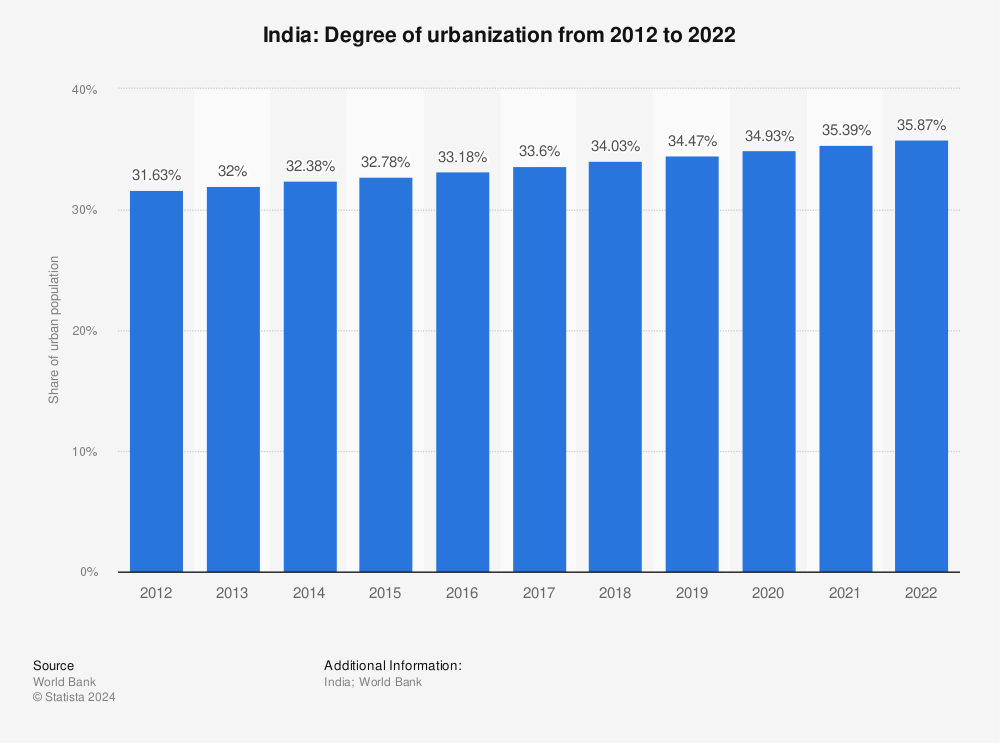
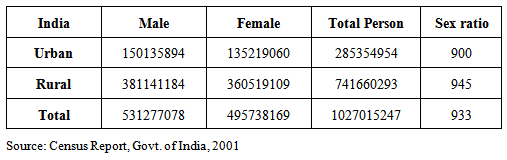
Urbanization in India refers to the process of population shift from rural areas to urban centers, resulting in the growth and development of cities and towns. India is undergoing rapid urbanization, with the proportion of its urban population increasing from 27.8% in 2001 to 34.5% in 2011, and it is expected to reach 50% by 2031.
One of the main characteristics of urbanization in India is the rapid growth of its cities. The country has several megacities, including Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Bengaluru, and Chennai, which have populations of over 10 million. These cities are attracting large numbers of migrants from rural areas due to the availability of jobs and higher living standards. The rapid growth of these cities has led to overcrowding and inadequate infrastructure, which has resulted in problems such as traffic congestion, pollution, and lack of housing.
Another characteristic of urbanization in India is the significant economic transformation that it has brought about. The growth of cities has led to the development of industries, services, and trade, which has contributed to the country's economic growth. However, this economic transformation has also led to social and economic inequalities, with the urban areas experiencing higher levels of prosperity compared to the rural areas.
The process of urbanization in India has also been accompanied by the emergence of slums and informal settlements. These settlements, which are often characterized by poor living conditions, have emerged as a result of the large influx of migrants to the cities. The lack of affordable housing has forced many of these migrants to live in slums, which lack basic amenities such as electricity, clean water, and sanitation.
Another characteristic of urbanization in India is the changing demographics of its cities. The cities are becoming more diverse, with people from different regions, cultures, and backgrounds living together. This has led to the emergence of multicultural and cosmopolitan cities, which have a unique blend of traditional and modern values.
In conclusion, urbanization in India is characterized by the rapid growth of its cities, the economic transformation it has brought about, the emergence of slums and informal settlements, and the changing demographics of its cities. While it has contributed to the country's economic growth, it has also resulted in social and economic inequalities and has created several challenges for the country to address.