The Chinese Civil War was a conflict that took place in China between 1927 and 1950, following the collapse of the Qing dynasty in 1911 and the subsequent warlord era. The conflict was primarily fought between the Nationalist Party, led by Chiang Kai-shek, and the Communist Party, led by Mao Zedong.
The origins of the Chinese Civil War can be traced back to the 1920s, when the Nationalist Party and the Communist Party were both working towards the goal of overthrowing the warlord government and establishing a unified, democratic China. However, the two parties had different ideologies and methods for achieving this goal. The Nationalists, who were supported by the Western powers, believed in a gradualist approach that focused on building a strong, centralized government and modernizing the economy. The Communists, on the other hand, believed in a more radical approach that involved land reform and the establishment of a socialist state.
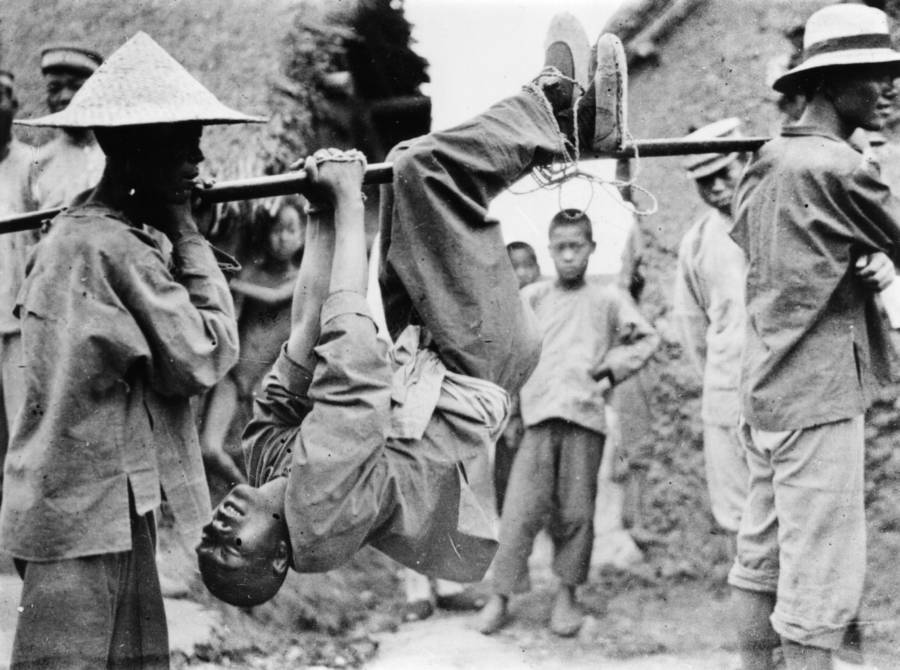
The tensions between the Nationalists and the Communists came to a head in 1927, when Chiang Kai-shek, the leader of the Nationalists, launched a campaign to suppress the Communists. This campaign, known as the "White Terror," led to the execution and imprisonment of many Communist Party leaders and members. In response, the Communists launched a series of uprisings, including the famous "Autumn Harvest Uprising," which was led by Mao Zedong.
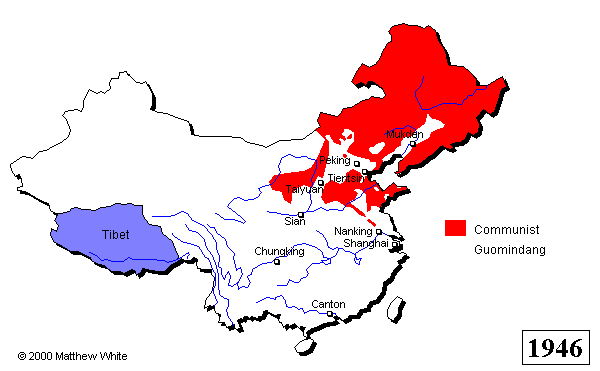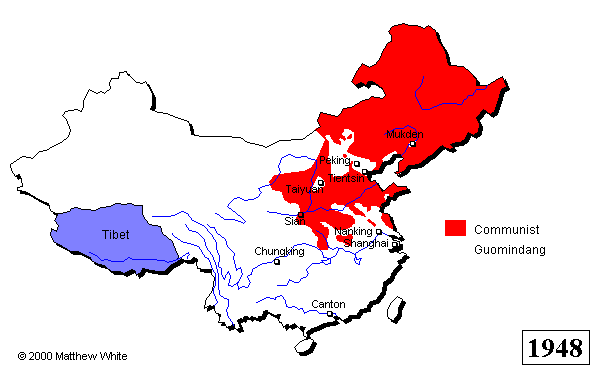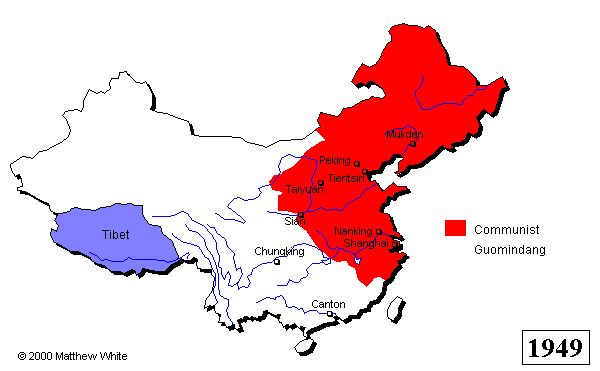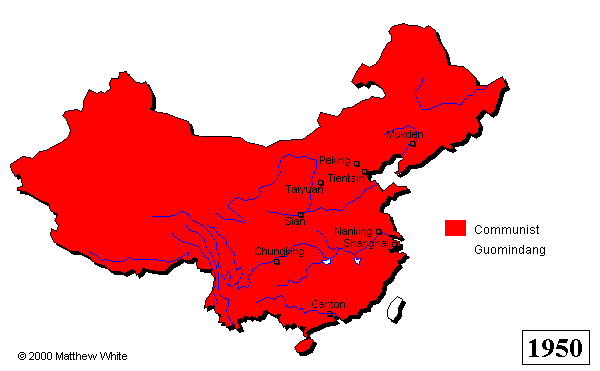
The Chinese Civil War continued for more than two decades, with both sides experiencing victories and setbacks. In 1937, the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out, and the Nationalists and the Communists temporarily set aside their differences to fight against the Japanese invasion. After World War II ended in 1945, the Chinese Civil War resumed, and in 1949, the Communist Party emerged victorious. The Nationalist government fled to Taiwan, where it continued to rule until the late 1970s.
The Chinese Civil War had a significant impact on the course of Chinese history. It led to the establishment of the People's Republic of China, which remains in power to this day, and it also had a lasting impact on the relationship between China and the United States, as the US supported the Nationalist government during the conflict. The Chinese Civil War also had a profound effect on the lives of ordinary Chinese citizens, as it was a time of great turmoil and violence, with many people losing their homes, families, and livelihoods as a result of the conflict.