Christaller. Walter Christaller 2022-12-10
Christaller
Rating:
8,8/10
755
reviews
Christaller is a German geographer and economist who is known for his central place theory, which is a model that explains the patterns of settlement in urban systems. According to Christaller, people tend to settle in certain locations in order to access certain goods and services. This is because people are willing to travel a certain distance to access these goods and services, but not too much further.
The central place theory is based on the idea that people will travel to central places to access a range of goods and services, rather than having to travel to multiple locations to access them. This is because central places are more efficient for people to access the goods and services they need.
Christaller's central place theory suggests that there are three types of central places:
Market centers: These are places that have a wide range of goods and services, and are typically located in large cities.
Service centers: These are places that offer specialized services, such as healthcare or education, and are typically located in smaller towns or villages.
Industrial centers: These are places that are focused on manufacturing and other types of industry, and are typically located in even smaller towns or rural areas.
According to Christaller's theory, these central places are interconnected and form a hierarchy. For example, a small town may have a service center that serves the local community, while a larger city nearby may have a market center that serves a wider region.
One of the key insights of Christaller's theory is that central places are not randomly distributed, but rather follow a pattern based on the needs of the population and the accessibility of the location. This means that central places are typically located in areas that are easy to reach, such as along major transportation routes.
Christaller's central place theory has had a significant influence on the study of urban geography and planning, and is still widely used today to understand the patterns of settlement in urban systems. It is a useful tool for planners and policymakers who are looking to create efficient and effective urban systems that meet the needs of the population.
What does Christaller mean?

When central places are arranged according to transport principle, the lower order centres are located at the midpoint of each side of the hexagon rather than at the corner. Examples of regional capitals—which are not necessarily political capitals—would include Paris or Los Angeles. Thus to make it functional as per actual scenario various modifications are required in the basic theory. Retrieved 21 October 2018. He decided that the countryside in the areas he was studying would be flat, so no barriers would exist to impede people's movement across it. In addition to this, there is no preference for a particular shop.
Next
Johann Gottlieb Christaller
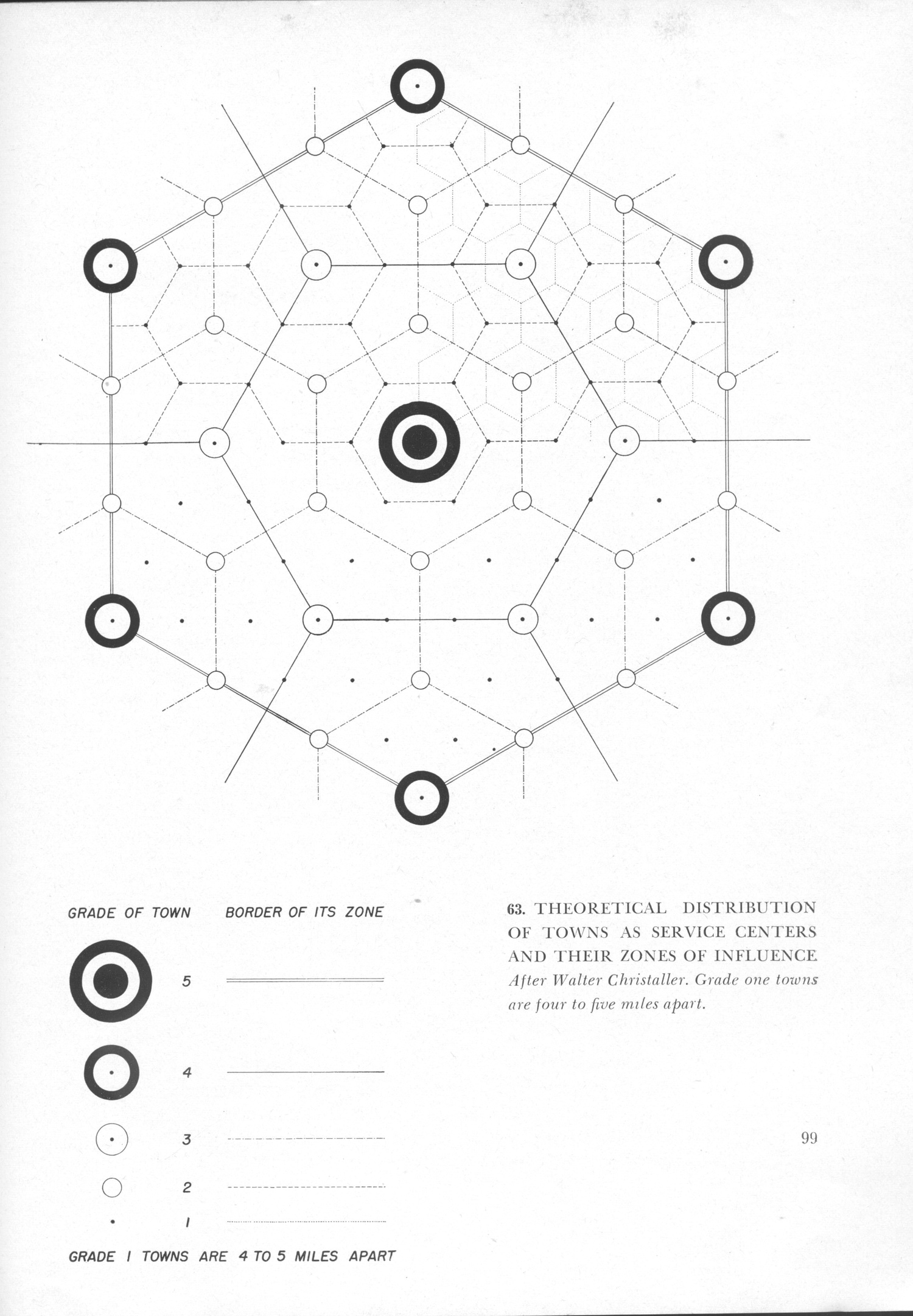
During his retirement in Basel, Christaller became editor of a journal entitled The Christian Messenger. The low order centres, position themselves on the boundaries of market areas of middle order centres. First, the higher-order central places will provide all goods and services that are found at the lower-order centers. Annals of the Association of American Geographers 103 3 , 669—687. Midwest or Alaska with the many small communities that are served by larger towns, cities, and regional capitals. No real world settlement system can be expected to conform to all the propositions of the Central Place.
Next
Difference between Christaller and Losch on central place theory UPSC ~ Geography Notes for UPSC , State PCS Exam, and NCERT Classes

The aim of the journal was to encourage African scholars to write in Twi and Ga This publication is not to be confused with The Christian Messenger and Examiner, founded in Cape Coast in 1859 by Revs. In India, ratio of districts to state is almost 1:19, where gram panchayat per community development block may reach up to 40 in number. History of the Gold Coast and Asante 2nd edition. Nowhere in the world, the central-place system remains static. Filed Under: Tagged With: Primary Sidebar. Higher order centres have bigger hexagonal market areas, and low order centres have smaller hexagons. Here again, the spacing of tehsil and district level centres confirms to the theory.
Next
Christaller's Model of Central Place

But circles do not use space efficiently and leave un-served space, and overlapping areas Figure 11. Further, In an isotropic surface, the complementary area is always a circle with the central place at the centre of this circle. The criterion of telephone of determine centrality of a place has been questioned by many people on the ground that it may have been true of southern Germany when Christaller did his work; but for all times and all places it cannot be held valid. Central Place Theory Today Though Losch's central place theory looks at the ideal environment for the consumer, both his and Christaller's ideas are essential to studying the location of retail in urban areas today. Wiase abasem mu nsemma-nsemma wo Twi-kasa mu "Stories from general history translated from German into Twi" , 2nd revised and augmented edition edited by J. Shapes of Complementary Areas: ADVERTISEMENTS: On an entirely uniform plain having a purely agricultural economy, ideal complementary area for each central place should approximate a circle with radial traffic routes converging at the centre. In order to serve the unserved customers, suppliers or entrepreneurs come closer together causing the circular areas to overlap.
Next
Christaller, Johannes Gottlieb (A)

This followed from works by economists His field survey in southern Germany, which at that time stretched from the Alsace region to Christaller developed the idea of a space that is supposed to be isotropic, homogenous, and functioning in self-sufficiency in perfect conditions of competition from economic agents, producers, and consumers. The more unimportant places may not be taken into cognizance. For example, a minimum varyingpopulation is needed to retain a doctor, bank or a post office. It is the standard Twi dictionary, and was revised in 1933. These also take into account the economic growth and development of towns, human behaviour, human geography, economic theory and fundamentals of economics.
Next
An Overview of Christaller's Central Place Theory
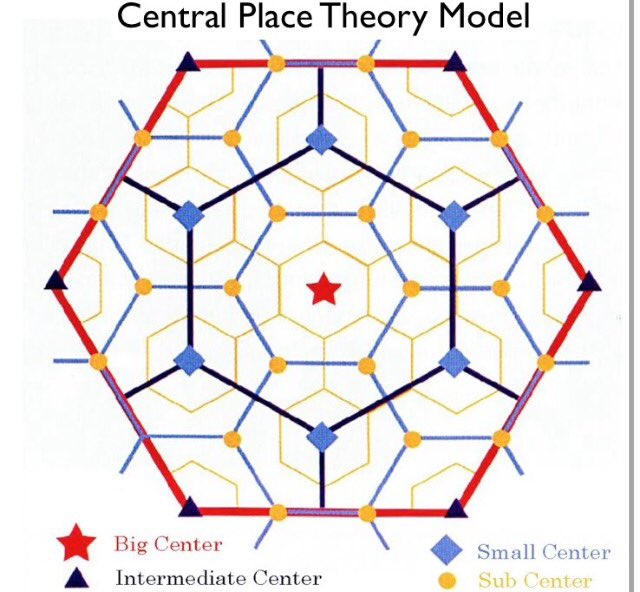
The lower size nodes 6 in numbers and 2nd larger circles are located at the corner of the largest hexagon around the high-order settlement. He instead focused on maximizing consumer welfare and creating an ideal consumer landscape where the need to travel for any good was minimized, and profits remained relatively equal, regardless of the location where goods are sold. The first issue was dated March 1, 1883. In addition, central place theory has three orders or principles. Zimmerman A Dictionary, English, Tshi Asante , Akra; Tshi Chwee Comprising as Dialects: Akan and Fante; Accra connected with Adangme; Gold Coast, West Africa, Basel, 1874, A Grammar of the Asante and Fantu Language Called Tschi Chwee, Twi Based on the Akuapem Dicalect, With Reference to Other Akan and Fante Dialects, Basel, 1875 Co, Twi mmebusem mpensa-ahansia mmoaano. However, an administrative hierarchy of places doe exists, though the number and spacing of different hierarchical levels of places is far from ideal.
Next
Christaller's Central Place Theory
Well, we will let it know as we proceed further. Christaller's work followed several theoretical works that started in the 19th century and aimed to determine the optimal location of an economic or a geographic entity in a given environment. The transport principle states that the distribution of central places is most favorable when as many places of concern or importance lie on one traffic route between two important towns, the route being established as straight and as cheap as possible. The highest order centers, those with the greatest centrality index were Frankfurt, Nuremberg, Stuttgart, Strasbourg, Zurich, and Munich. Debrunner, A History of Christianity in Ghana, Accra, 1967; C.
Next
Emilie Christaller

Geschichte der Basler Mission, 1815-1915. The larger the city, the greater the likelihood of very specialized goods and services. This study included analysing the relationships between settlements of different sizes and related their economic activities market with the population. And when more than forty millions of Germans enjoy a common book-language, half a million Fantes may more easily be brought to a common medium of communication by writing. A Bibliography and Vocabulary of the Akan Twi-Fante Language of Ghana.
Next







