Classical demand theory is a fundamental concept in economics that explains how consumers make purchasing decisions based on their preferences and the prices of goods and services. It is a key component of microeconomic analysis and is used to understand how changes in prices and incomes affect the demand for different goods and services.
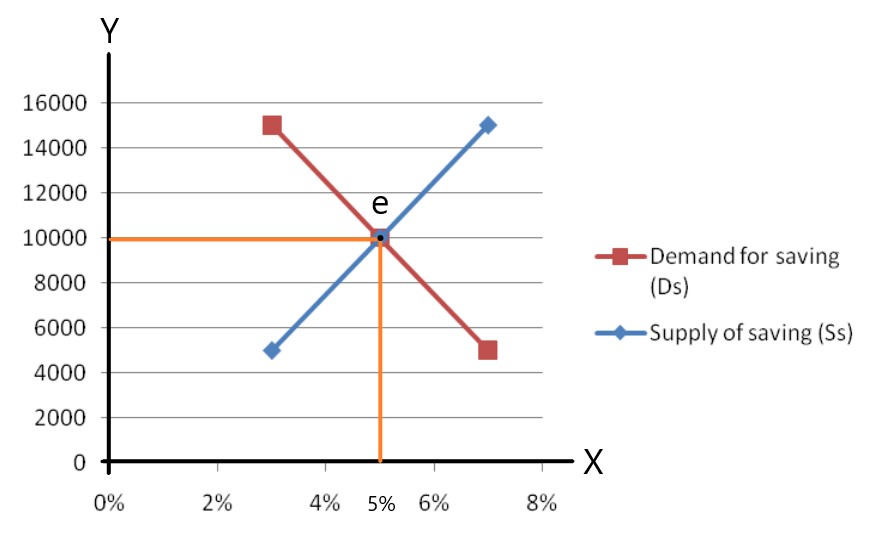
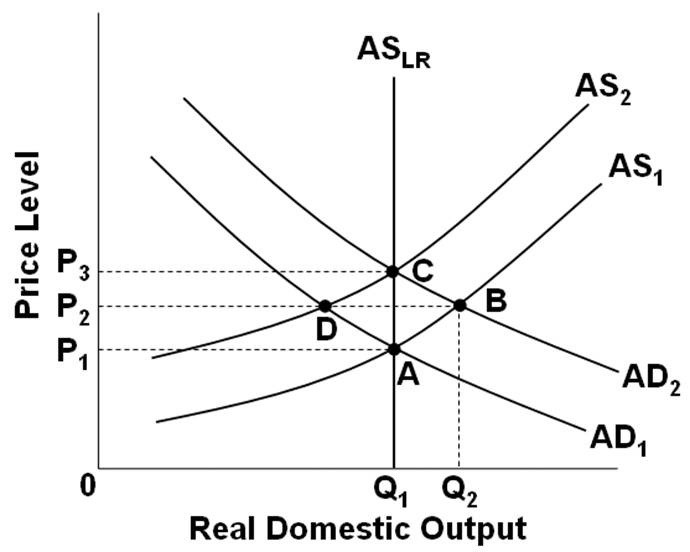
The basic principles of classical demand theory can be explained through the concept of demand curves. A demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity of that good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase. It is typically depicted as a downward-sloping curve, which reflects the fact that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded by consumers decreases. This is known as the law of demand.
There are several factors that can influence the shape and slope of a demand curve. One of these is the price of related goods or substitutes. If the price of a good increases, consumers may switch to a substitute that is cheaper or less expensive. This is known as the substitution effect and can lead to a shift in the demand curve to the left, as consumers are willing to purchase less of the good at a higher price.
Another factor that can affect the demand curve is the income of consumers. If consumers have a higher income, they may be willing and able to purchase more of a good or service, even if the price increases. This is known as the income effect and can lead to a shift in the demand curve to the right, as consumers are willing to purchase more of the good at a higher price.
In addition to these factors, the demand for a good or service can also be influenced by changes in the price of complementary goods or the availability of credit. Complementary goods are goods that are used in conjunction with each other, such as gasoline and cars. If the price of a complementary good increases, the demand for the other good may decrease, leading to a shift in the demand curve to the left. Similarly, if credit becomes more readily available, consumers may be able to finance larger purchases, leading to an increase in demand and a shift in the demand curve to the right.
Classical demand theory is an important tool for understanding how consumers make purchasing decisions and how changes in the economy can affect the demand for different goods and services. It is a fundamental concept in economics and is used by policymakers, businesses, and economists to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and resource allocation.