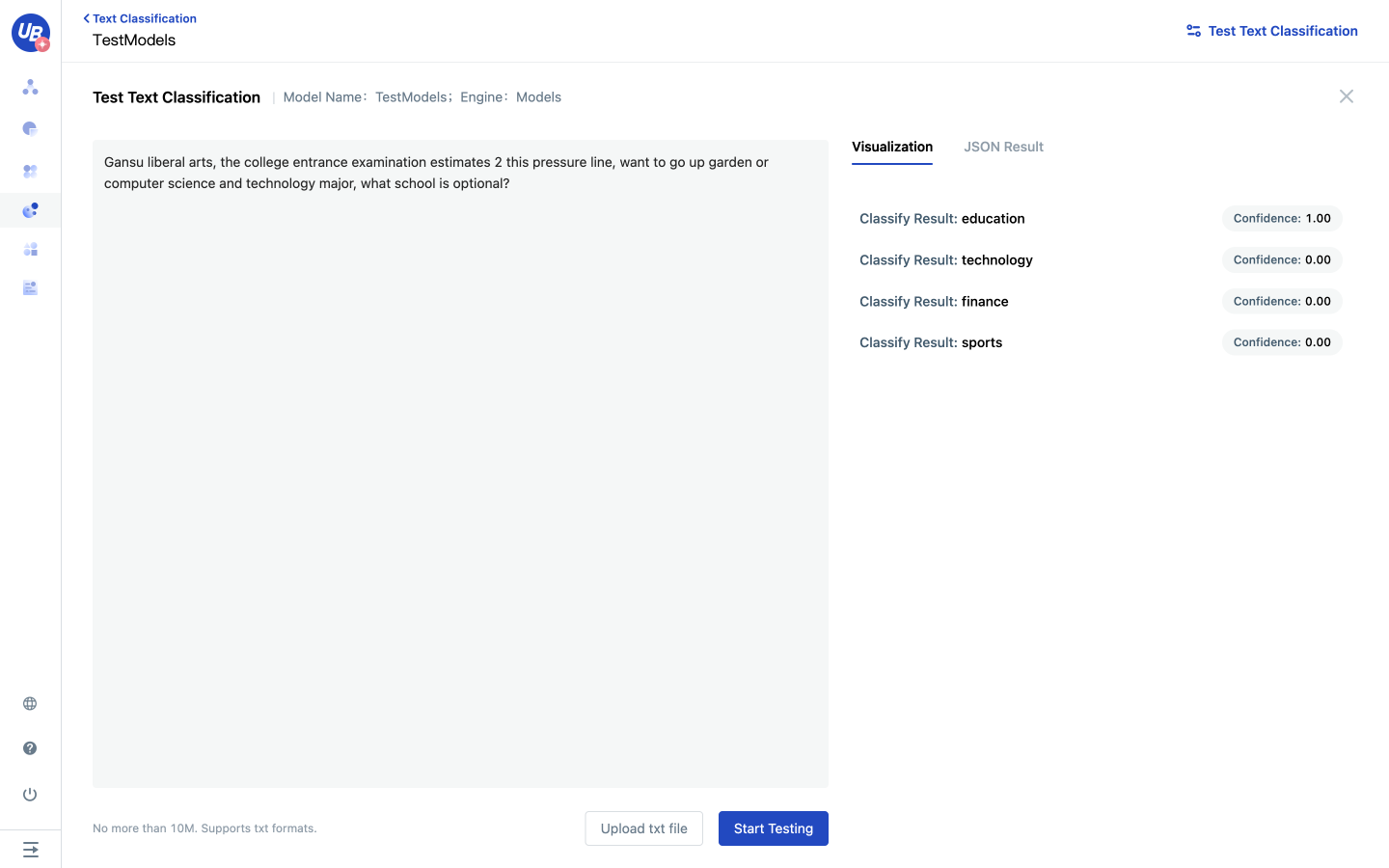
In education, tests are a common method of assessing student learning and progress. Tests can be classified in several ways, including the purpose of the test, the format of the test, and the length of the test.
One way to classify tests is by their purpose. Some tests are used to diagnose student weaknesses and strengths, while others are used to evaluate student progress. Diagnostic tests are typically administered at the beginning of a course or unit and are used to identify areas where the student may need extra help. These tests may be more open-ended and allow students to demonstrate their knowledge in a variety of ways. On the other hand, evaluative tests are typically administered at the end of a course or unit and are used to determine how well a student has learned the material. These tests may be more structured and focus on specific content or skills.
Another way to classify tests is by their format. Some tests are written, while others are oral or practical. Written tests may include multiple choice, short answer, or essay questions. Oral tests may involve students giving presentations or participating in class discussions. Practical tests may involve hands-on activities, such as conducting experiments or solving problems.
Finally, tests can also be classified by their length. Some tests are relatively short, lasting only a few minutes or hours, while others may take several days or weeks to complete. Short tests may focus on a narrow range of content or skills, while longer tests may cover a broader range of material.
In conclusion, tests in education can be classified in several ways, including their purpose, format, and length. Understanding these different types of tests can help educators choose the most appropriate assessment method for their students.