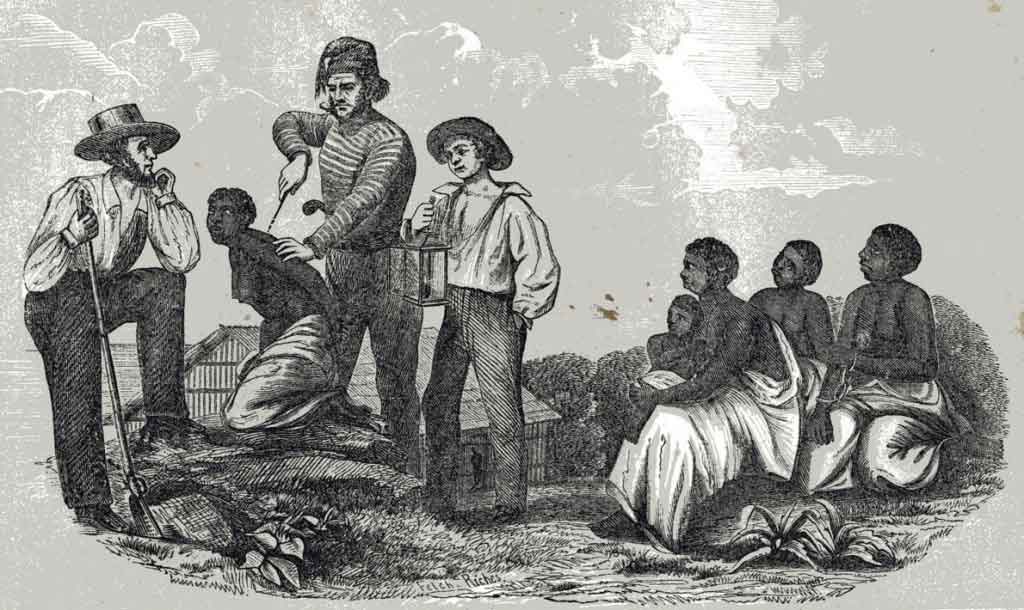
A closed stratification system, also known as a caste system, is a social hierarchy in which social status is determined by birth and remains fixed throughout an individual's lifetime. In a closed stratification system, mobility between social classes is limited or non-existent, meaning that an individual's position in society is largely predetermined by their parent's social status.
One of the most well-known examples of a closed stratification system is the caste system in India, which is a Hindu social hierarchy that has been in place for centuries. In the Indian caste system, there are four main castes: Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Sudras. Each caste has its own set of social, economic, and cultural practices and restrictions. For example, Brahmins, who are at the top of the hierarchy, are traditionally priests and scholars, while Sudras, who are at the bottom of the hierarchy, are traditionally manual laborers.
Another example of a closed stratification system is the feudal system that was present in medieval Europe. In this system, the nobility, or upper class, held land and power, while the peasants, or lower class, were bound to the land and worked for the nobility. Mobility between these two classes was extremely limited, and an individual's social status was largely determined by their family's social status.
Closed stratification systems can have negative consequences for individuals who are born into lower classes. These individuals may face discrimination and limited access to education, employment, and other opportunities that could allow them to improve their social status. Additionally, closed stratification systems can lead to social tensions and conflicts between different social classes, as individuals may feel resentful of their predetermined social status and the privileges or limitations that come with it.
In contrast, open stratification systems, also known as class systems, allow for mobility between social classes based on an individual's achievements, education, and other factors. In an open stratification system, an individual's social status may change throughout their lifetime, and they have the opportunity to improve their social standing based on their own actions and accomplishments.
Overall, a closed stratification system is a social hierarchy in which social status is fixed and mobility between social classes is limited or non-existent. This type of system can have negative consequences for individuals and can lead to social tensions and conflicts.