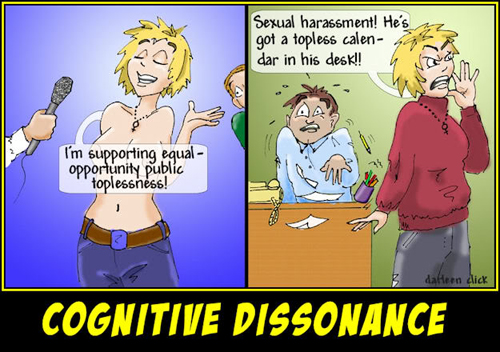
Cognitive dissonance is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when an individual holds two or more conflicting beliefs, values, or attitudes that are incompatible with each other. It can lead to discomfort, anxiety, and a sense of unease as the person struggles to reconcile these conflicting ideas. This type of psychological tension is an important concept to understand, as it can have significant impacts on our behavior, attitudes, and decision-making processes.
One common example of cognitive dissonance in everyday life occurs when an individual engages in behaviors that are inconsistent with their values or beliefs. For example, a person who values environmental conservation may feel cognitive dissonance when they drive a gas-guzzling vehicle or participate in activities that contribute to pollution. To reduce this discomfort, the person may try to justify their actions by telling themselves that they need the car for their job, or that the environmental impact of their actions is minimal.
Another example of cognitive dissonance can occur when an individual holds two conflicting beliefs about the same subject. For example, a person may believe that smoking is harmful to their health, but they continue to smoke cigarettes. In this case, the person may feel cognitive dissonance as they try to reconcile their belief that smoking is harmful with their behavior of continuing to smoke. To reduce this tension, the person may try to minimize the risks of smoking by telling themselves that they only smoke a few cigarettes a day, or that they will quit soon.
Cognitive dissonance can also occur when an individual is presented with new information that contradicts their existing beliefs or attitudes. For example, a person who has always believed that vaccinations are safe and effective may feel cognitive dissonance when they come across information suggesting that vaccines may cause harm. To reduce this tension, the person may try to discredit the new information or find ways to justify their existing beliefs.
There are a number of strategies that people use to reduce cognitive dissonance and the discomfort it causes. One common strategy is to change one's beliefs or attitudes to align with their behaviors or actions. For example, a person who values environmental conservation may choose to purchase a more fuel-efficient vehicle in order to reduce the cognitive dissonance caused by driving a gas-guzzling car. Another strategy is to change one's behavior to align with their beliefs or attitudes. For example, a person who believes that smoking is harmful may choose to quit smoking in order to reduce the cognitive dissonance caused by continuing to smoke.
In conclusion, cognitive dissonance is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when an individual holds two or more conflicting beliefs, values, or attitudes. It can lead to discomfort and a sense of unease as the person struggles to reconcile these conflicting ideas. Understanding and recognizing cognitive dissonance can be useful in helping us to identify and resolve conflicts within ourselves and make more informed decisions.