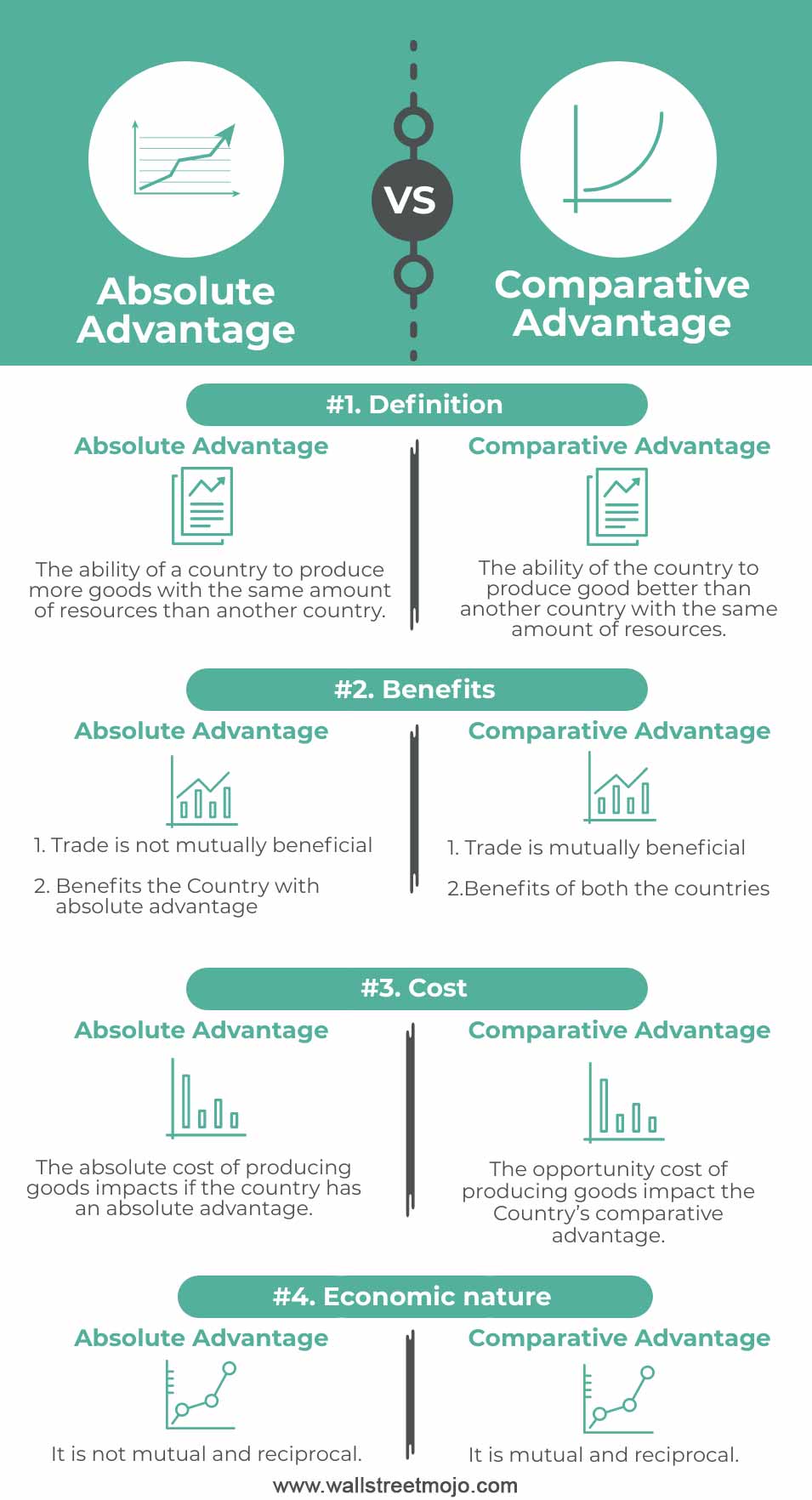
Comparative cost advantage is a concept in international trade theory that refers to the ability of a country to produce a particular good or service at a lower cost than its trading partners. This advantage can be the result of various factors, including the availability of natural resources, the level of technology and infrastructure, and the efficiency of the country's production processes.
There are several ways in which a country can gain a comparative cost advantage. One is by having access to abundant natural resources, such as oil, timber, or minerals. These resources can be used as inputs in the production process, helping to lower the overall cost of production. Another way a country can gain a comparative cost advantage is by investing in technology and infrastructure. This includes investing in transportation networks, communication systems, and other types of infrastructure that can make production more efficient.
In addition to these factors, a country's labor market also plays a role in its comparative cost advantage. For example, a country with a well-educated and skilled workforce may be able to produce goods and services more efficiently than a country with a less skilled workforce. This is because workers with higher levels of education and training are typically more productive and able to use advanced technologies more effectively.
However, it is important to note that comparative cost advantages can change over time. For example, if a country experiences a decline in its natural resource base, or if its infrastructure deteriorates, it may lose its comparative cost advantage in the production of certain goods or services. Similarly, if another country invests in technology and education, it may be able to catch up and eventually surpass the original country in terms of production efficiency.
In conclusion, comparative cost advantage is an important concept in international trade theory that refers to a country's ability to produce goods or services at a lower cost than its trading partners. This advantage can be the result of various factors, including access to natural resources, investments in technology and infrastructure, and the efficiency of the country's labor market. However, comparative cost advantages can change over time, and countries must be prepared to adapt to shifts in the global economic landscape.