A cross cheque, also known as a crossed check, is a type of check that has two parallel lines drawn across the face of the check, usually with the words "and company" written between the lines. This feature is used to prevent the check from being cashed at a bank or financial institution. Instead, the check must be deposited directly into the payee's account or presented to the payee for payment.
The purpose of a cross cheque is to increase the security and traceability of the check. By requiring the check to be deposited directly into the payee's account, it becomes much harder for the check to be stolen or misused. Additionally, the fact that the check is deposited directly into the payee's account allows for easier tracking and reconciliation of the transaction.
There are two types of cross cheques: general and special. A general cross cheque can be deposited into any account at any bank, whereas a special cross cheque can only be deposited into a specific account at a specific bank. Special cross cheques are often used when the payee does not have an account at the issuing bank, or when the payee wishes to ensure that the funds are deposited into a specific account.
Cross cheques are commonly used in business transactions, as they offer a higher level of security and traceability than regular checks. They are also often used in real estate transactions, as they offer a way for buyers to transfer large sums of money securely and without the risk of the funds being misused.
In summary, a cross cheque is a type of check that is marked with two parallel lines and the words "and company" written between the lines. It is used to increase the security and traceability of the check and is often used in business and real estate transactions.
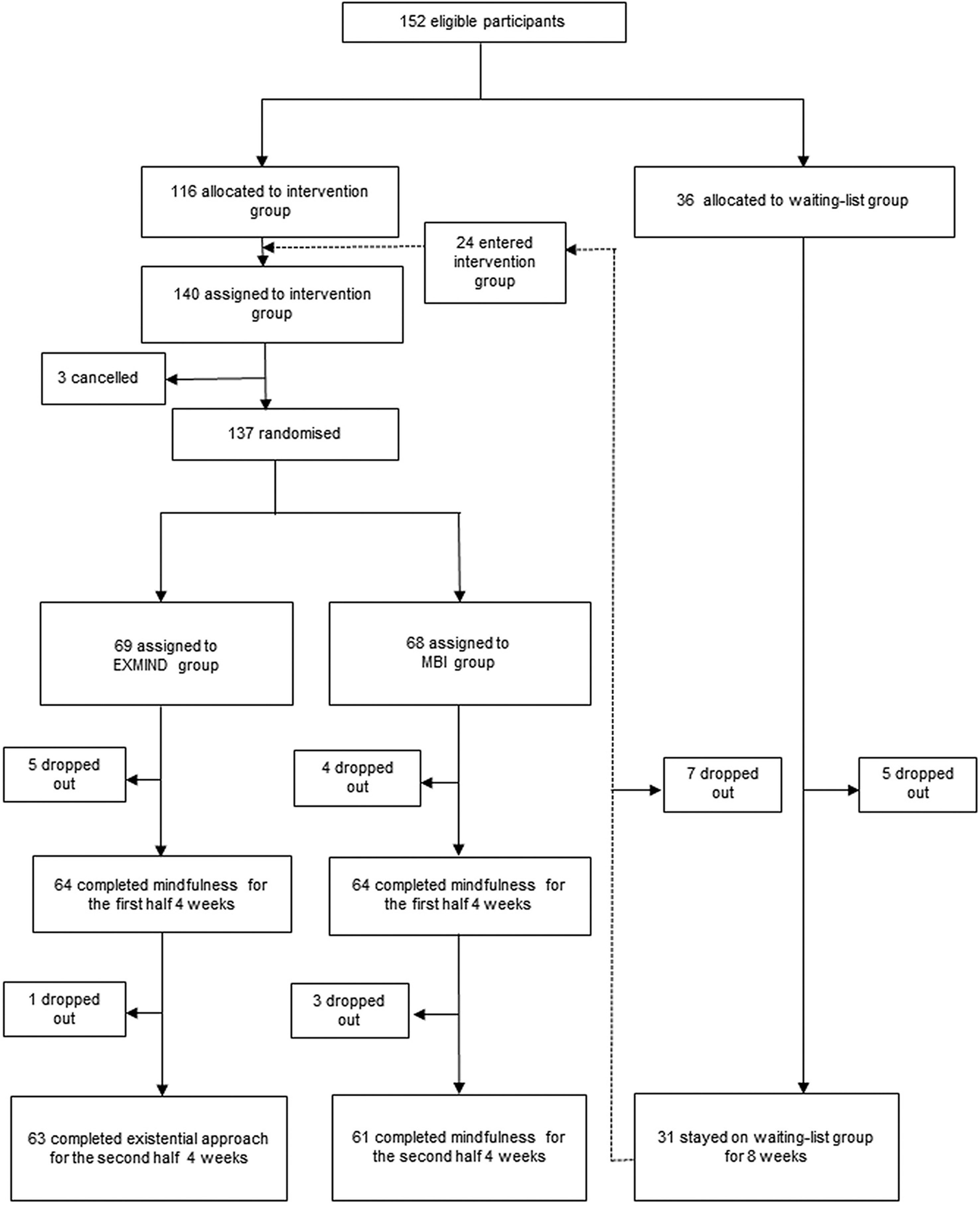
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and existential therapy are both forms of psychotherapy that can be effective in helping individuals address psychological challenges and improve their overall well-being. However, these two approaches differ in their focus, assumptions, and techniques.
CBT is a goal-oriented, action-based therapy that aims to help individuals identify and modify negative or distorted thought patterns that contribute to their emotional and behavioral problems. It is based on the premise that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and that by changing our thoughts, we can change our emotions and behaviors. CBT techniques include cognitive restructuring, in which the therapist helps the client identify and challenge negative thoughts, and exposure therapy, in which the client is gradually exposed to a fear-provoking situation in order to reduce anxiety.
Existential therapy, on the other hand, is a more philosophical and introspective approach that focuses on helping individuals find meaning and purpose in their lives. It is based on the belief that we all have an inherent desire to find meaning in our lives and that psychological problems can arise when we are unable to do so. Existential therapists often use techniques such as self-exploration and reflection to help clients understand and come to terms with the fundamental human issues of death, freedom, isolation, and meaninglessness.
One key difference between CBT and existential therapy is their focus. CBT is focused on identifying and changing specific thoughts and behaviors, while existential therapy is focused on helping individuals understand and come to terms with the larger, more abstract issues of life. CBT is often used to treat specific problems such as anxiety, depression, and phobias, while existential therapy is more suitable for individuals who are struggling with a sense of meaning and purpose in their lives.
Another difference between these two approaches is their assumptions about human nature. CBT assumes that individuals are rational and that their problems can be solved through logical thought and behavior modification. Existential therapy, on the other hand, assumes that individuals are irrational and that their problems stem from a lack of meaning and purpose in their lives.
In terms of techniques, CBT and existential therapy also differ significantly. CBT techniques are focused on helping individuals identify and change specific thoughts and behaviors, while existential therapy techniques are more focused on self-exploration and reflection. CBT techniques are often structured and goal-oriented, while existential therapy techniques are more open-ended and exploratory.
In conclusion, while both CBT and existential therapy can be effective in helping individuals address psychological challenges and improve their overall well-being, they differ in their focus, assumptions, and techniques. CBT is a goal-oriented, action-based therapy that aims to help individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns, while existential therapy is a more philosophical and introspective approach that focuses on helping individuals find meaning and purpose in their lives.