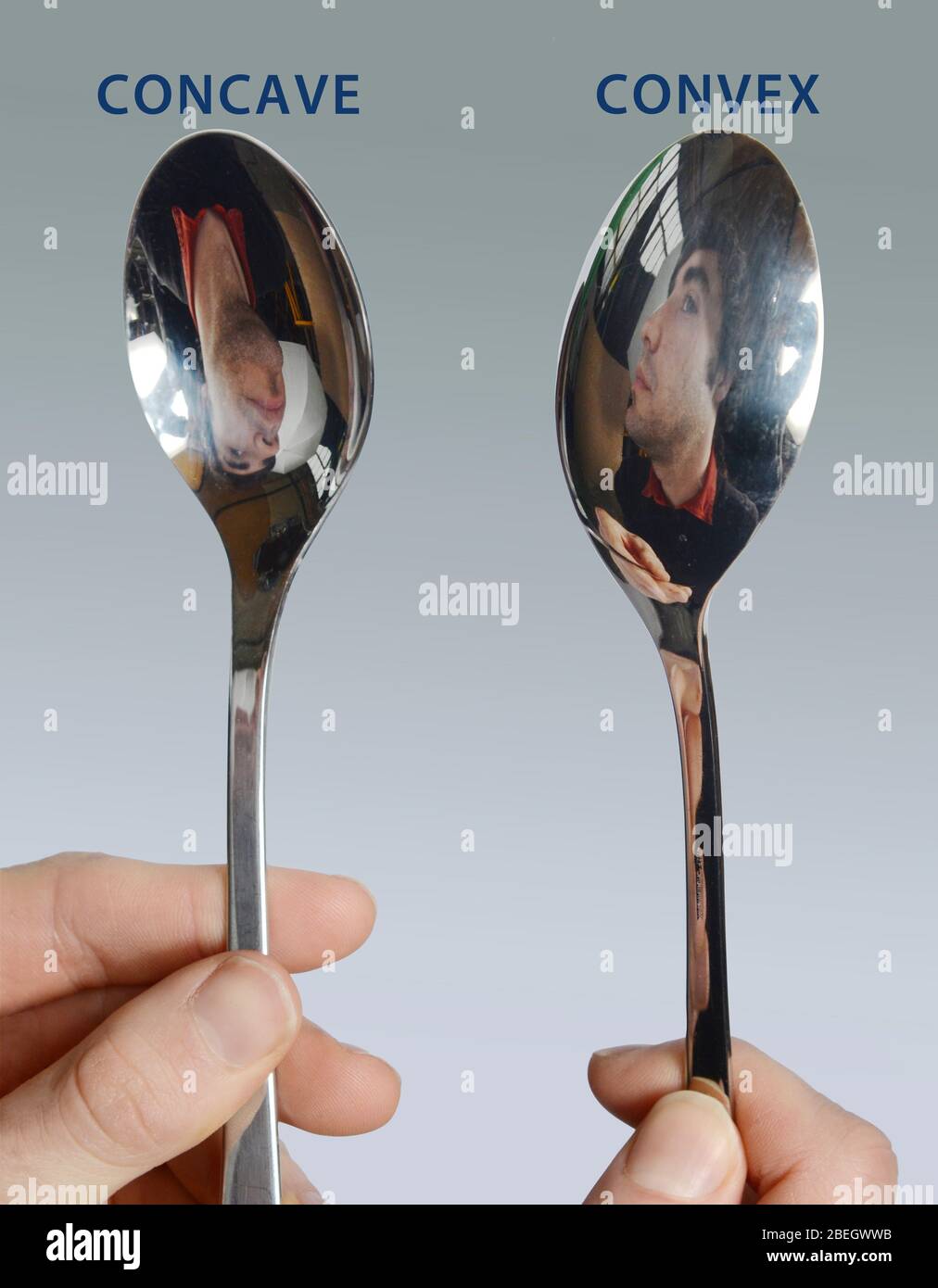
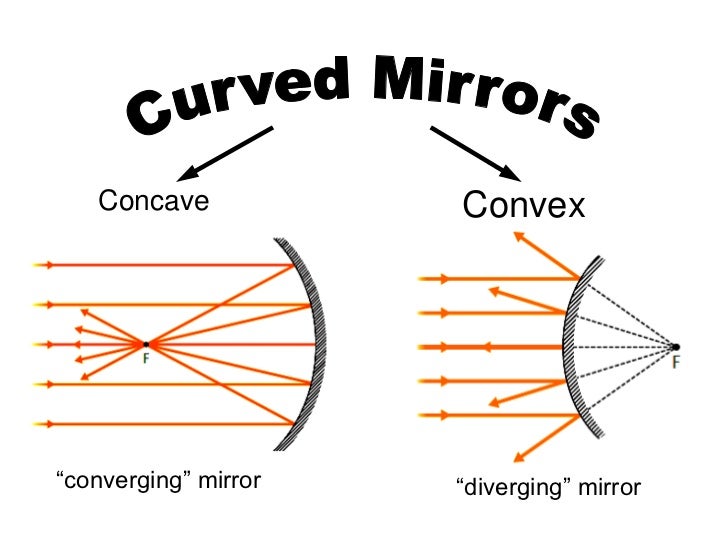
A concave mirror is a curved mirror that bulges inward, like the inside of a bowl. The mirror has a smaller radius of curvature, meaning that the curve of the mirror is more pronounced. As a result, concave mirrors are able to focus light rays that are parallel to the axis of the mirror. This makes them useful for a variety of applications, including telescopes, makeup mirrors, and rearview mirrors in vehicles.
Concave mirrors are able to focus light because of the way that they reflect rays of light. When a ray of light hits a concave mirror, it is reflected in such a way that it appears to come from a single point, known as the focal point. The distance from the mirror to the focal point is called the focal length.
The size and shape of the image produced by a concave mirror depends on the distance of the object from the mirror and the position of the mirror relative to the object. When the object is located at a distance that is equal to the focal length of the mirror, the image is located at the center of curvature of the mirror, which is twice the distance of the focal length from the mirror. When the object is located at a distance that is greater than the focal length, the image is located behind the mirror, and it is inverted. When the object is located at a distance that is less than the focal length, the image is located in front of the mirror, and it is upright.
A convex mirror is a curved mirror that bulges outward, like the outside of a bowl. Convex mirrors are commonly used in places where a wide field of view is needed, such as in parking lots or on the side of vehicles. Unlike concave mirrors, convex mirrors do not focus light, and they produce a smaller, distorted image of the object.
Convex mirrors are useful in certain situations because they provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors. This makes them useful for seeing around corners or for monitoring large areas, such as parking lots or warehouses. However, because the image produced by a convex mirror is distorted, it is not always accurate for judging distance or size.
In conclusion, concave and convex mirrors are both useful for different purposes. Concave mirrors are able to focus light and produce a clear, focused image, while convex mirrors provide a wider field of view but produce a distorted image. Understanding the characteristics and uses of these two types of mirrors can help us make informed decisions about which type of mirror is best suited for a particular application.