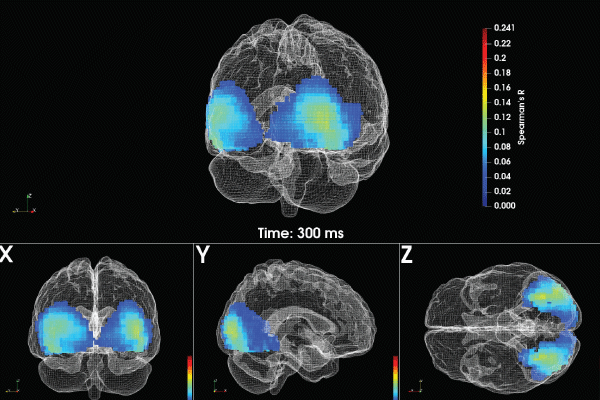
The constructivist theory of perception is a psychological theory that suggests that our perception of the world is not a direct reflection of reality, but rather a construct of our individual experiences, expectations, and interpretations. According to this theory, we do not simply observe and interpret stimuli in an objective manner; instead, we actively construct our own understanding of the world based on our prior knowledge, cultural and social influences, and personal beliefs.
One of the key proponents of the constructivist theory of perception was the psychologist Jean Piaget, who argued that our understanding of the world is shaped by our interactions with it. Piaget believed that we learn through our experiences, and that our perceptions are constantly adapting and changing as we gain new knowledge and insights.
Another influential figure in the development of the constructivist theory of perception was the philosopher and psychologist Ernst von Glasersfeld, who argued that our perceptions are influenced by our mental models and schemas. A mental model is a simplified representation of a complex system or process, while a schema is a mental framework that organizes and categorizes our knowledge and experiences. According to von Glasersfeld, we use these mental models and schemas to make sense of the world around us, and they shape our perceptions and interpretations of stimuli.
The constructivist theory of perception has important implications for education and learning. It suggests that we cannot simply impart knowledge to students in a one-size-fits-all manner, but must instead take into account their individual experiences, expectations, and mental models. This has led to the development of teaching approaches such as problem-based learning and experiential learning, which seek to engage students in actively constructing their own understanding of the world.
Overall, the constructivist theory of perception highlights the active role that our minds play in shaping our understanding of the world. It suggests that our perceptions are not simply passive reflections of reality, but rather are actively constructed based on our experiences, expectations, and mental models. This theory has had a significant impact on the fields of psychology and education, and continues to be an important perspective in the study of perception and learning.
Gibson's Theory of Direct Perception: Psychology

Gordon , 2004 It is important to set the scene surrounding visual perception theories as there are many different approaches to explaining visual perception and there are different levels of explanations Shiffman, 2001, Sternberg, 2006 Not one theory can be considered accurate however there are some have stronger evidence and provide a rational explanation. Constructivism is based on the idea that people actively construct or make their own knowledge and that reality is determined by our experiences as a learner Meaning of Constructivism Constructivism is the idea that learning does not just happen by the traditional methods of teachers standing in front of the class and lecturing. Direct, meaning sensations themselves are enough to create a complete representation of the world around us. The stimuli that was most relevant to the context, the baseball, was recognized quicker than those that were irrelevant, car and phone. Hunter-gatherers were not "fooled" by the illusion like Europeans and Americans were.
Evidence for the constructivist theory of visual perception

It cannot solely exist as the evidence by Brunswick and criticism against the radical constructivists suggests. However this explanation has been criticised and this is explained through a statistical relationship between images received through the retina in the eye and external sources Howe and Purves, 2004 However one could use this evidence to support the constructivist view as cognitive inferences i. Copy to Clipboard Reference Copied to Clipboard. When we are moving, objects near appear to move faster in relation to us, while objects far away appear to move slower. Perception is thought to be as a result of indirect, inferential processes. It cannot be argued that constructivism has not been immensely influential to the understanding of perception, it could be regarded that whilst ideologies existed hundreds of years prior to Helmholtz, and he pioneered valuable research that laid the foundations for future interpretations. Evaluation of Gregory's Constructivist Theory of Perception Let's consider the evidence for Gregory's Constructivist Theory of Perception and the contrasting theories.
gregory's constructivist theory of perception Flashcards

You can notice buildings or trees in the distance move significantly slower than the trees and objects that are right next to the road. Even though the elephant was far, it appeared between the hunter and the antelope. When individuals or learners come across something new, they have to merge it with their initial ideas and experiences, maybe to alter what they trust or conclude the new information is irrelevant. For instance, in learning, a student who has learned to write in the correct manner Therefore, constructivism learning is done in a manner in which the learners construct new knowledge based on their prior knowledge. As lighting conditions change, the color of objects, such as bananas or cherries, appear to remain constant. The Bartlett study provided relevant evidence to support that cognitive inference plays a role in repetiton and Sanford illustrated that a state of mind can influence interpretation of ambigious pictures.