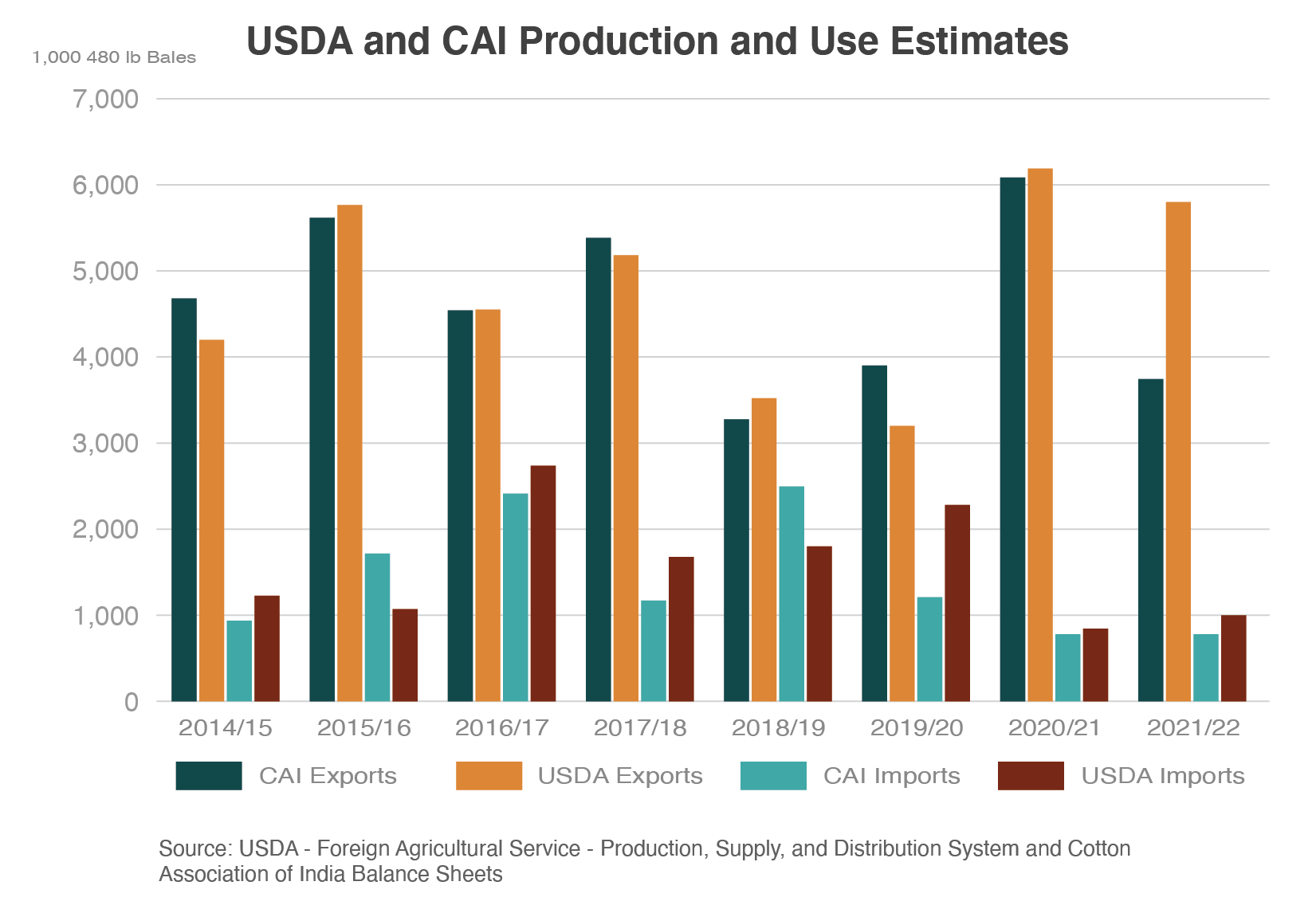
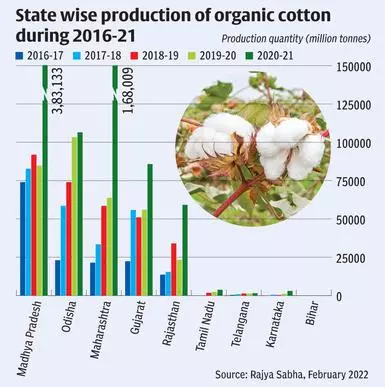
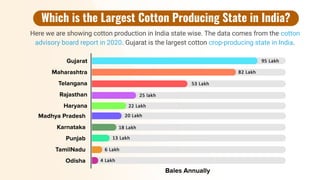
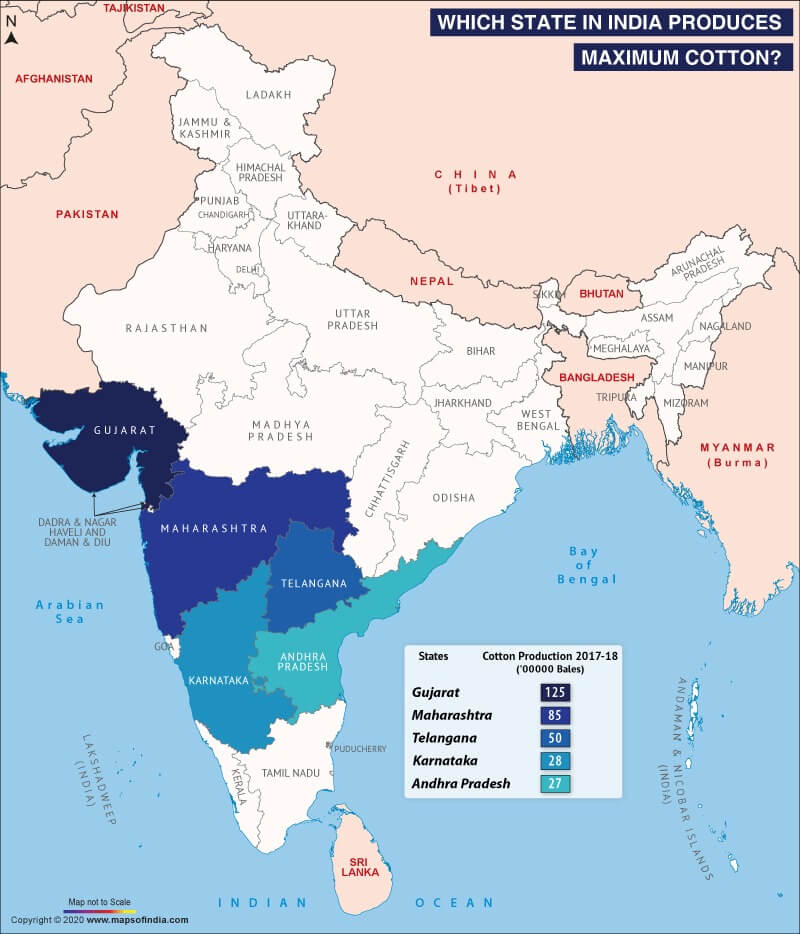
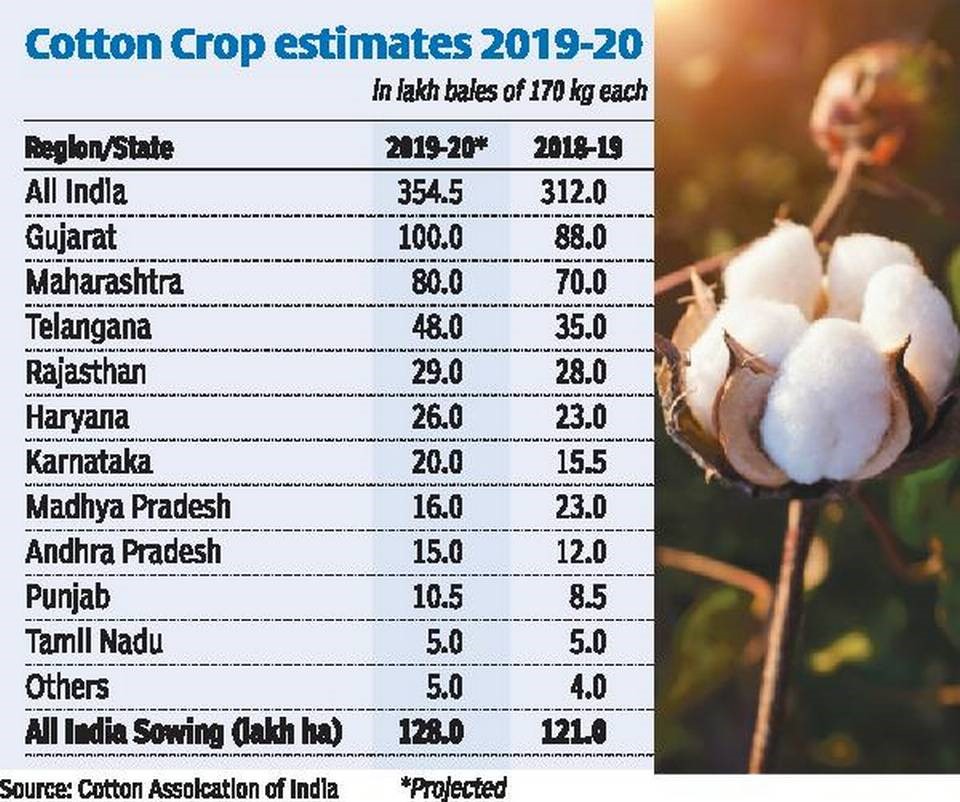
Cotton production is a major contributor to India's economy and plays a significant role in the country's agricultural sector. India is one of the largest producers and exporters of cotton in the world, with the majority of production concentrated in the states of Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh.
The history of cotton production in India dates back to ancient times, with the country being one of the earliest centers of cotton cultivation and trade. Today, India is home to a wide variety of cotton cultivars, including both indigenous and hybrid varieties, which are grown under diverse climatic and soil conditions.
Cotton production in India is primarily rainfed, with only a small percentage of production being irrigated. The country has a long growing season, with the main cotton-growing regions receiving sufficient rainfall during the monsoon season. In recent years, the adoption of modern irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation, has helped to improve the efficiency of water usage in cotton production and reduce the reliance on monsoon rains.
One of the major challenges facing cotton production in India is the issue of pest and disease management. Cotton plants are prone to attack by a range of insects and fungi, which can significantly reduce yields and quality. To address this issue, farmers in India commonly use a combination of chemical pesticides and biological control methods, such as the use of natural predators to control pests.
In addition to pest and disease management, the use of genetically modified (GM) cotton has become increasingly common in India in recent years. GM cotton varieties have been developed to be resistant to certain pests and diseases, which has helped to improve yields and reduce the need for chemical pesticides. However, the use of GM cotton remains controversial, with some people expressing concerns about the potential risks and impacts on the environment.
Despite the challenges, cotton production in India remains a vital part of the country's economy, providing employment and income for millions of people. In recent years, the government has implemented a range of policies and programs aimed at supporting the cotton sector, including initiatives to improve the availability of quality seeds, promote the use of modern technologies, and provide financial support to farmers.
In conclusion, cotton production is an important economic activity in India, with the country being one of the largest producers and exporters of cotton in the world. While there are challenges facing the sector, such as the need to effectively manage pests and diseases and the controversy surrounding the use of GM cotton, the government is taking steps to support the cotton industry and help it continue to thrive.