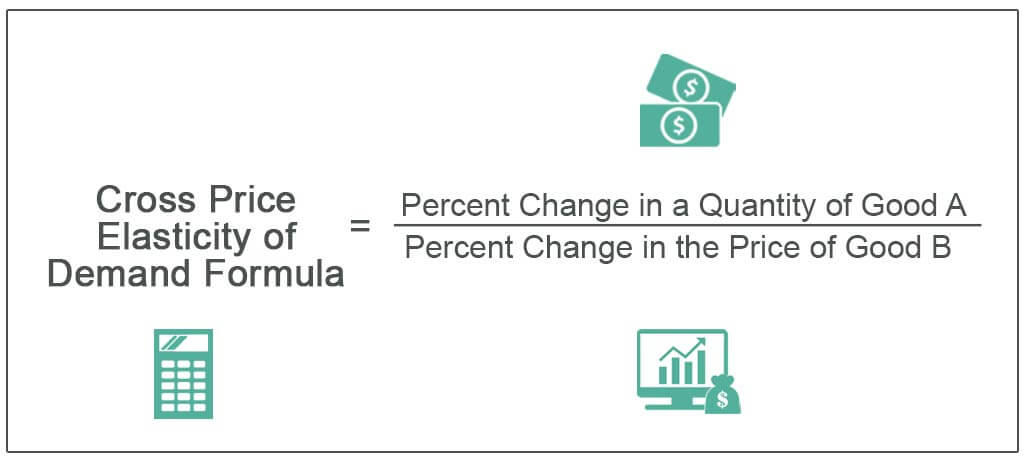
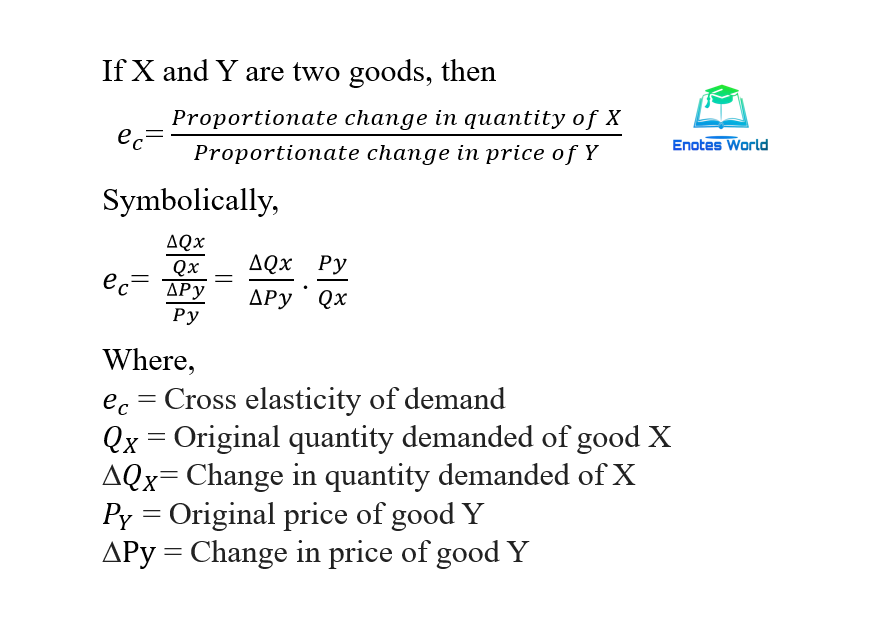
Cross elasticity of demand (XED) is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in the price of another good, or in a non-price determinant of demand for the other good. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good divided by the percentage change in the price of another good, or in a non-price determinant of demand for the other good.
The cross elasticity of demand curve shows the relationship between the quantity demanded of one good and the price of another good, or a non-price determinant of demand for the other good. It is typically represented graphically as a curve, with the quantity demanded of one good on the y-axis and the price of the other good, or a non-price determinant of demand for the other good, on the x-axis.
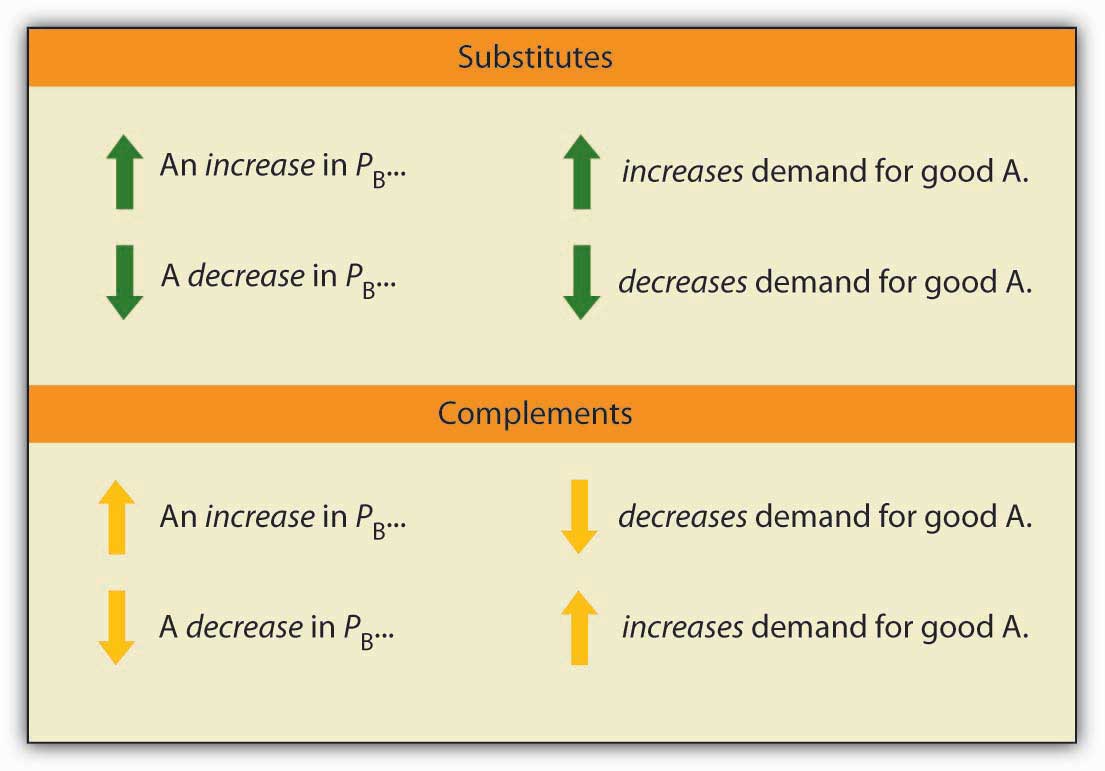
There are several types of cross elasticity of demand, depending on the nature of the relationship between the two goods. If the two goods are substitutes, then an increase in the price of one good will lead to an increase in the demand for the other good, resulting in a positive cross elasticity of demand. For example, if the price of coffee increases, then the demand for tea as a substitute for coffee will also increase.
If the two goods are complements, then an increase in the price of one good will lead to a decrease in the demand for the other good, resulting in a negative cross elasticity of demand. For example, if the price of automobiles increases, then the demand for gasoline as a complement to automobiles will decrease.
If the two goods are unrelated, then a change in the price of one good will not affect the demand for the other good, resulting in a zero cross elasticity of demand. For example, a change in the price of coffee will not affect the demand for bicycles.
In addition to the price of another good, cross elasticity of demand can also be affected by other non-price determinants of demand, such as income, population, and tastes and preferences. For example, if income increases, the demand for luxury goods may increase, resulting in a positive cross elasticity of demand between luxury goods and income.
Understanding cross elasticity of demand is important for businesses and policymakers as it can help them to predict the impact of changes in the prices of goods or non-price determinants of demand on the demand for other goods. It can also help businesses to identify potential substitutes or complements for their products and to anticipate changes in demand for their products due to changes in the prices or non-price determinants of demand for other goods.