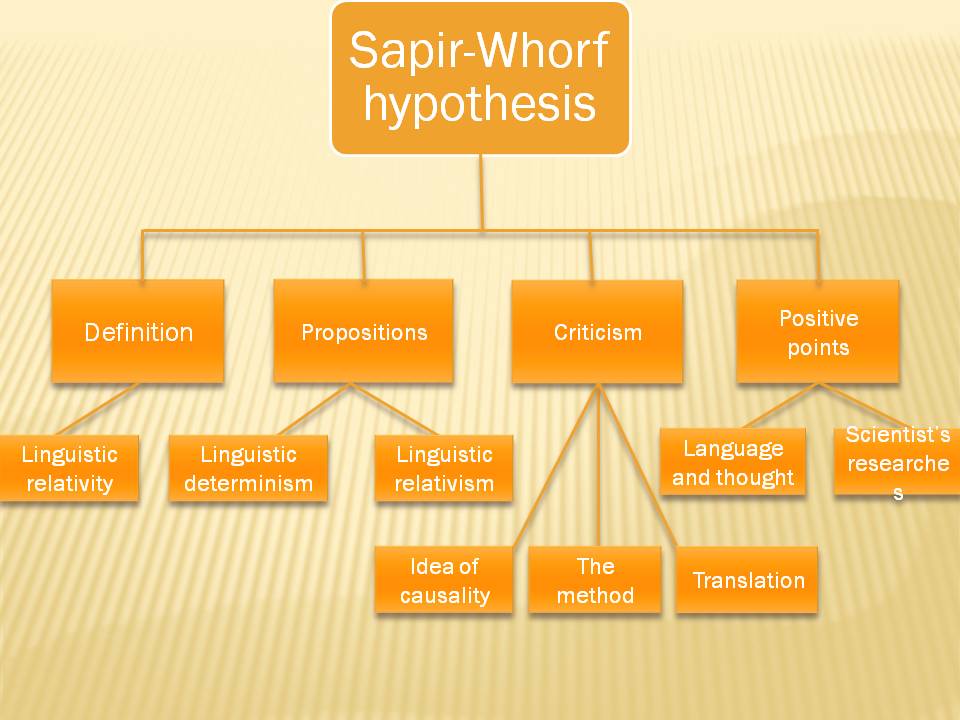
The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, also known as the theory of linguistic relativity, suggests that the language a person speaks influences their cognition and perception of the world. This hypothesis was developed by linguists Edward Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf in the early 20th century and has since been the subject of much discussion and debate in the fields of linguistics, psychology, and anthropology.
The basic premise of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis is that language shapes our thoughts and experiences. According to this theory, the structure and vocabulary of a language determines the way we think and the way we perceive the world around us. For example, if a language has no word for a particular concept, it is difficult for speakers of that language to think about or understand that concept. Similarly, if a language has multiple words for a concept, speakers of that language may be more attuned to the nuances of that concept.
One of the most famous examples of the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis is the concept of time. In English, we have a wide range of words and phrases to describe time, such as "past," "present," "future," "yesterday," "tomorrow," and so on. This allows us to think about and describe time in a detailed and nuanced way. In contrast, some languages, such as the Hopi language, do not have words for past, present, and future. Instead, they describe events in relation to other events, such as "before" or "after." This may make it more difficult for Hopi speakers to conceptualize time in the same way that English speakers do.
The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis has been widely debated and has received both support and criticism over the years. Some studies have found evidence to support the idea that language can influence perception and cognition, while other studies have found little or no effect. It is generally accepted that language does play some role in shaping our thoughts and experiences, but the extent to which it does so is still a matter of debate.
Despite the ongoing debate, the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis remains an important and influential theory in the fields of linguistics and psychology. It highlights the idea that language is not just a tool for communication, but also a powerful tool for shaping our thoughts, beliefs, and experiences. As such, it serves as a reminder of the importance of language and the role it plays in our lives.