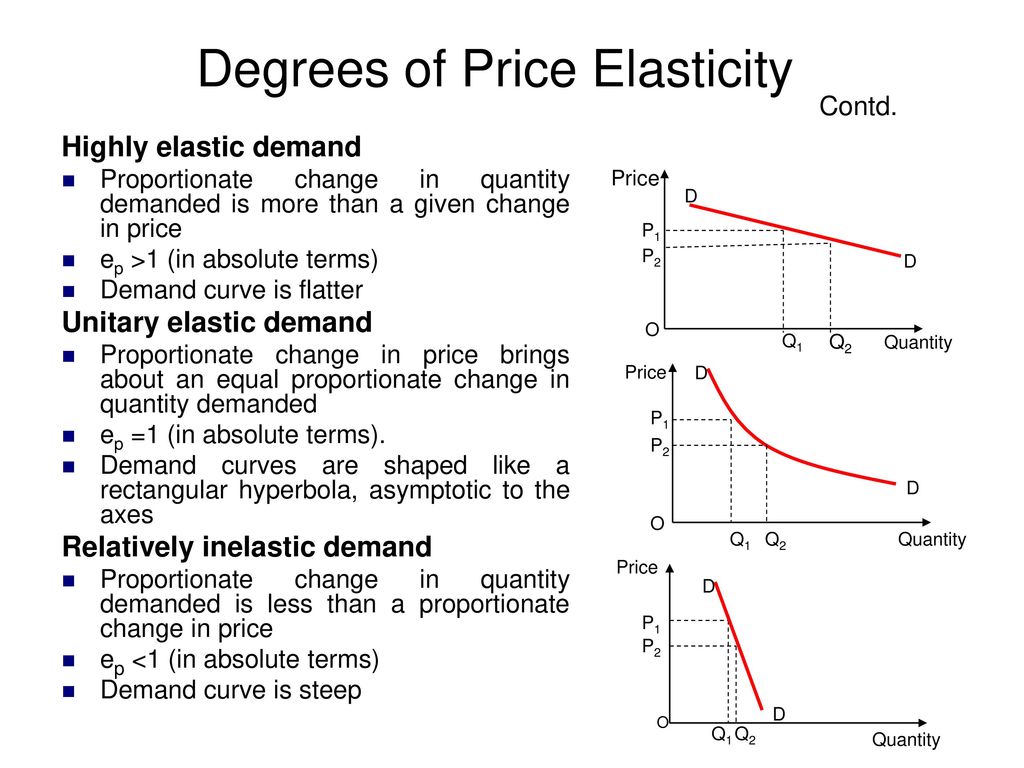
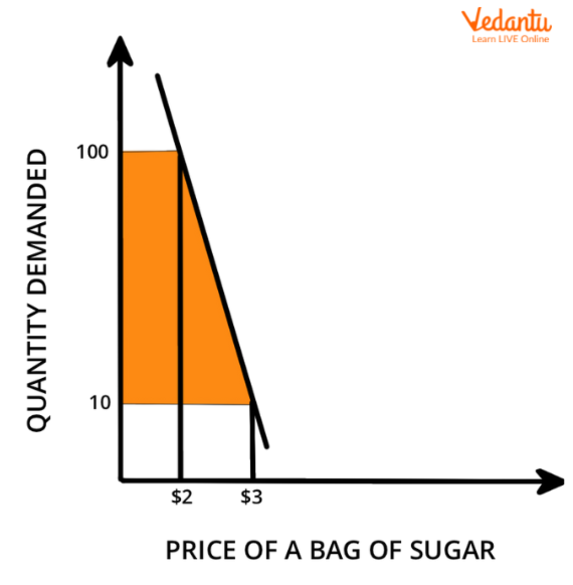
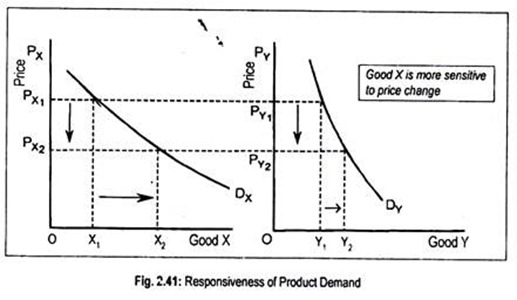
The degree of elasticity of demand refers to the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. In other words, it measures how sensitive consumers are to changes in the price of a good or service. Elasticity of demand is an important concept in economics because it helps to determine the impact that changes in price will have on the overall quantity of a good or service that is consumed.
There are several factors that can affect the elasticity of demand for a good or service. One of the most important factors is the availability of substitutes. If a good or service has many substitutes, then the demand for it will be more elastic, as consumers can easily switch to a substitute if the price of the original good or service increases. On the other hand, if a good or service has few substitutes, then the demand for it will be less elastic, as consumers have fewer options if the price increases.
Another factor that can affect the elasticity of demand is the proportion of a consumer's budget that is spent on a particular good or service. If a good or service represents a small portion of a consumer's budget, then the demand for it will be more elastic, as the price increase will have a relatively small impact on the consumer's overall budget. However, if a good or service represents a large portion of a consumer's budget, then the demand for it will be less elastic, as the price increase will have a larger impact on the consumer's overall budget.
The time frame in which the demand for a good or service is considered can also affect its elasticity. In the short run, the demand for a good or service may be more inelastic, as consumers may not have the time or resources to switch to substitutes if the price increases. However, in the long run, the demand for a good or service may be more elastic, as consumers have more time to adjust their consumption patterns and find substitutes.
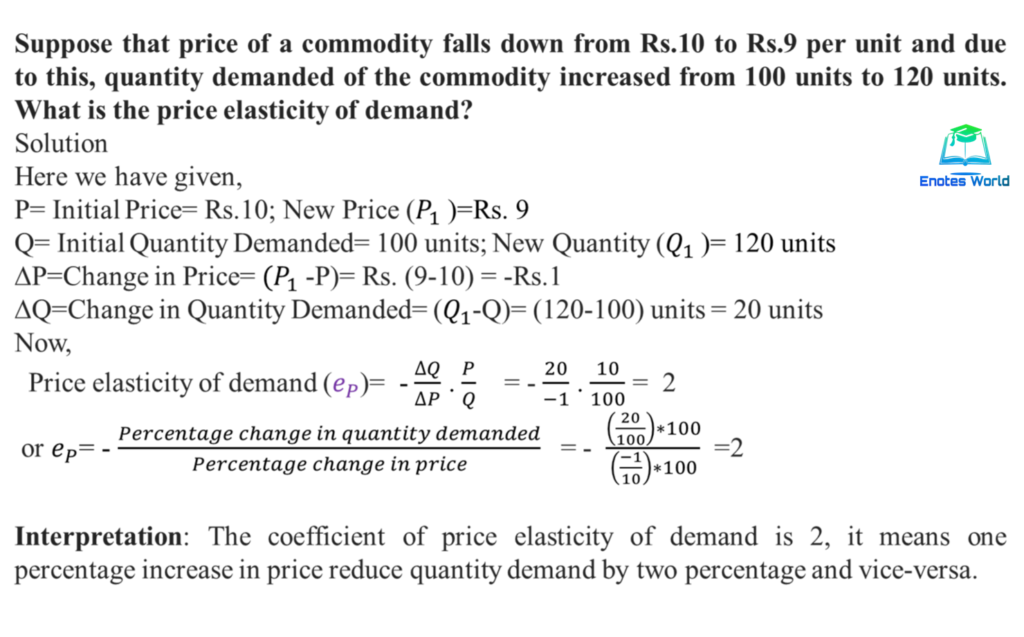
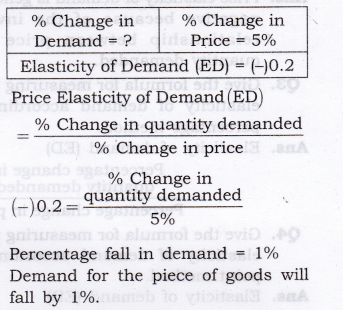
There are several methods that can be used to measure the elasticity of demand for a good or service. The most common method is to calculate the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service in response to a percentage change in its price. This can be done using the following formula:
Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Price)
A demand curve that is perfectly elastic will have an elasticity of demand equal to infinity, as the quantity demanded will change by an infinite amount in response to a small change in price. A demand curve that is perfectly inelastic will have an elasticity of demand equal to zero, as the quantity demanded will not change in response to a change in price. Most demand curves fall somewhere between these two extremes, with some being more elastic and others being more inelastic.
Understanding the degree of elasticity of demand is important for businesses and policymakers because it helps them to determine the impact that changes in price will have on the quantity of a good or service that is consumed. It also helps them to predict how consumers will respond to changes in the price of a good or service, which can be useful in making pricing and marketing decisions.