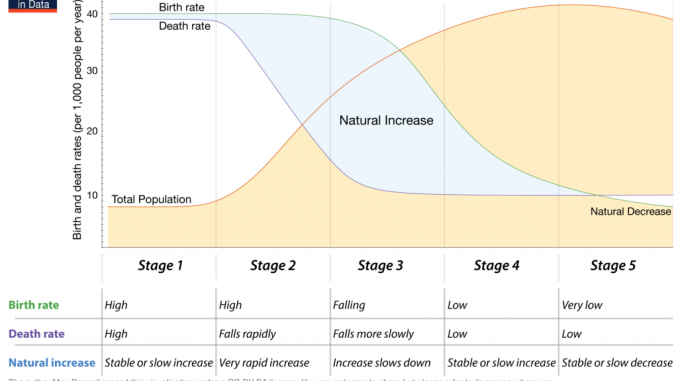
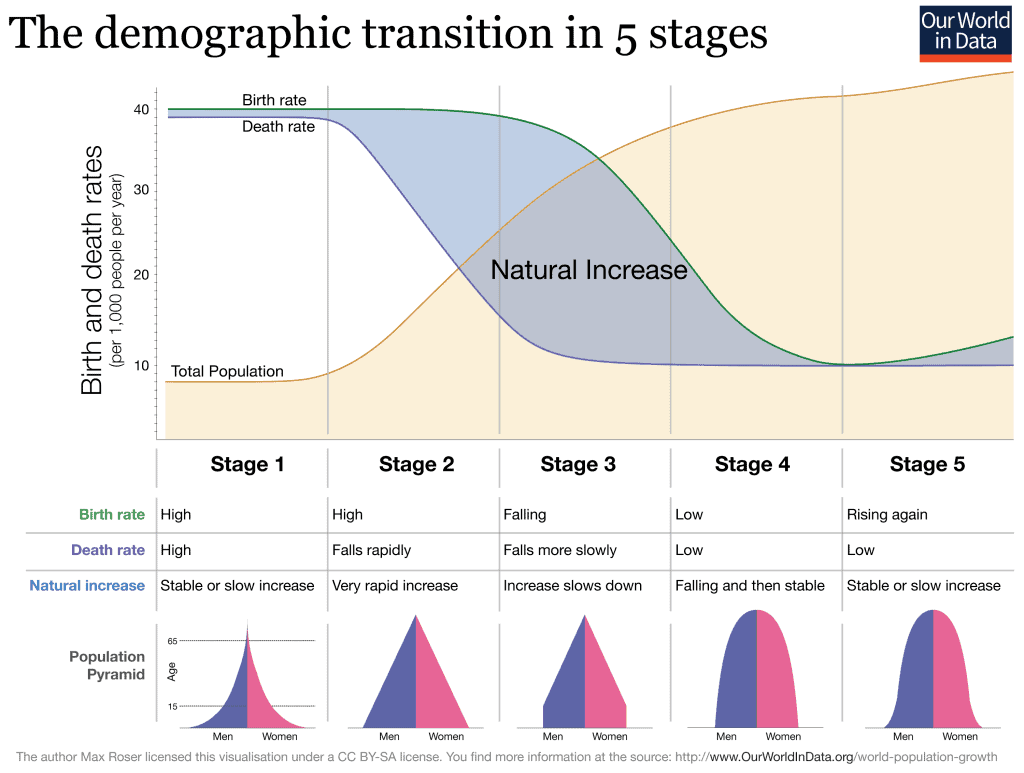
The demographic transition model (DTM) is a theoretical model that explains the relationship between a population's birth and death rates, and the resulting changes in population size over time. It has been widely used to understand and predict population growth patterns in various countries and regions, and has been influential in shaping policy and decision-making related to population and development.
One of the main strengths of the DTM is that it provides a clear and concise framework for understanding the complex interactions between population growth and social, economic, and technological factors. The model outlines a series of stages through which societies typically pass as they transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates, and it allows researchers to track the progress of a society through these stages and make predictions about future population trends.
Another strength of the DTM is that it is based on extensive data and empirical evidence from a wide range of countries and regions. The model has been tested and refined over time, and has proven to be a reliable tool for understanding and predicting population growth patterns in many different contexts.
However, the DTM also has a number of weaknesses that should be taken into account when using it to analyze population trends. One weakness is that the model is based on broad generalizations and may not accurately reflect the specific circumstances of individual countries or regions. The model assumes that all societies follow a similar trajectory as they transition from high to low birth and death rates, but in reality, the pace and pattern of this transition can vary significantly depending on a wide range of factors.
Another weakness of the DTM is that it does not adequately account for the role of migration in shaping population trends. The model assumes that population size is determined primarily by birth and death rates, but in many cases, migration can have a significant impact on population size and structure. For example, if a country experiences a large influx of immigrants, its population may grow more quickly than would be predicted based on its birth and death rates alone.
Despite these weaknesses, the demographic transition model remains a valuable tool for understanding and predicting population trends, and it has played a key role in shaping policy and decision-making related to population and development. However, it is important to recognize the limitations of the model and to consider other factors that may influence population trends when using it to analyze population growth patterns.