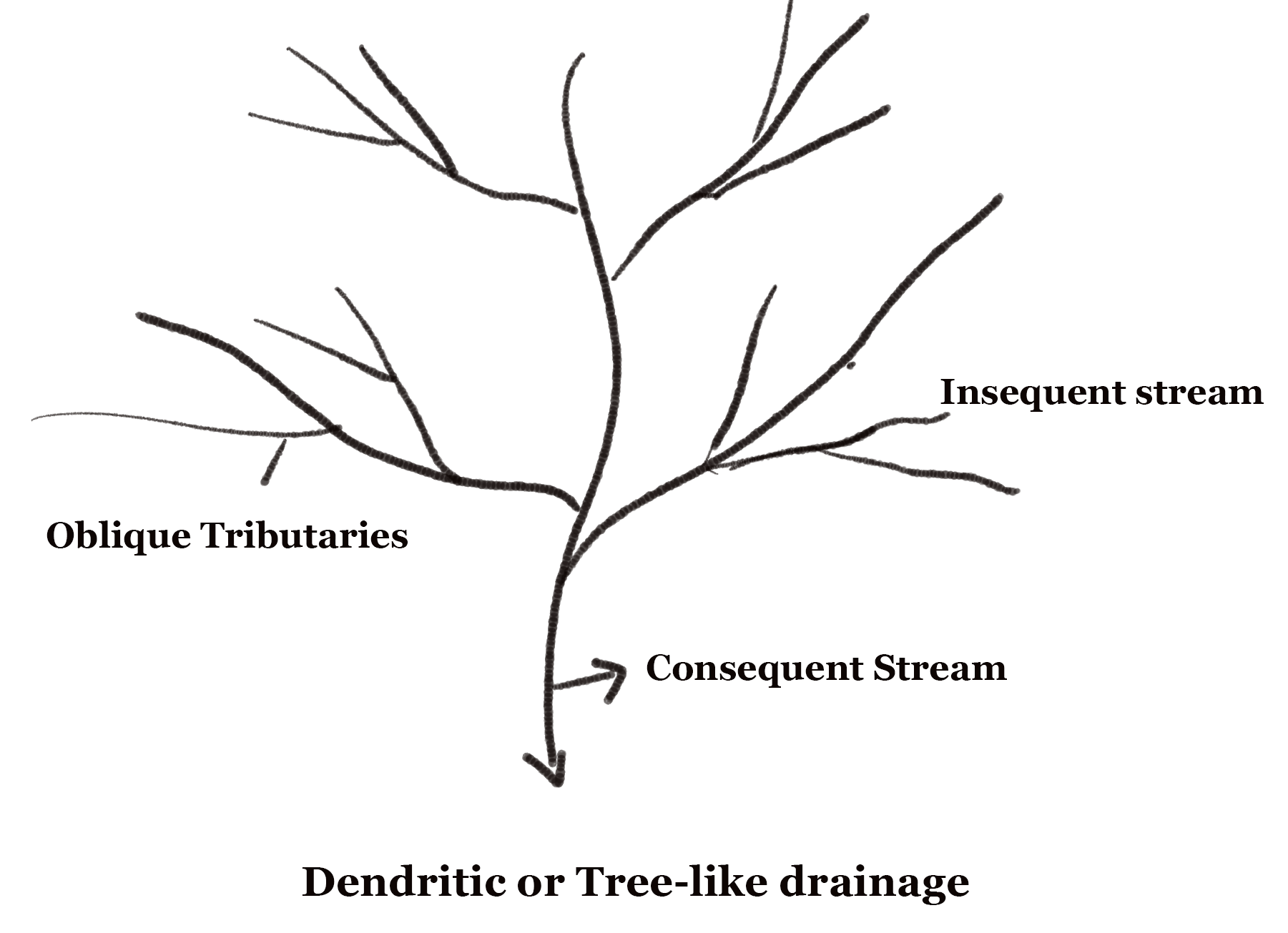
Dendritic drainage is a type of drainage pattern that occurs in landscapes where the underlying rock is relatively homogeneous and permeable. It is characterized by a network of branching channels that resemble the branches of a tree, hence the name "dendritic," which comes from the Greek word for tree, "dendron."
In dendritic drainage systems, water flows from high elevations to low elevations, following the path of least resistance through the landscape. As the water flows downhill, it cuts channels into the rock or soil, creating a network of streams and rivers that branch out from their sources in the mountains or hills. These channels follow the contours of the landscape, winding around obstacles and flowing towards the lowest point in the area.
Dendritic drainage systems are common in regions where the rock is composed of sedimentary or metamorphic materials that are relatively soft and easily eroded. They can also occur in areas with a gently sloping topography, where the gradient is not steep enough to create a more linear drainage pattern.
One of the defining features of dendritic drainage systems is their relatively low energy and low erosion rates. This is because the water flows slowly and smoothly through the network of channels, rather than rushing downhill in a more concentrated flow. As a result, the channels are typically shallow and wide, with gently sloping sides.
Dendritic drainage systems are often found in regions with a humid climate, where there is a high amount of rainfall and the water table is close to the surface. They are also common in areas with a well-developed network of underground aquifers, which can help to recharge the water supply and keep the streams and rivers flowing.
Overall, dendritic drainage is a important aspect of the hydrological cycle, influencing the distribution of water and nutrients in the landscape and shaping the physical characteristics of the land. It plays a vital role in the health and functioning of ecosystems, and is an important factor to consider in the management and conservation of natural resources.




].jpg)