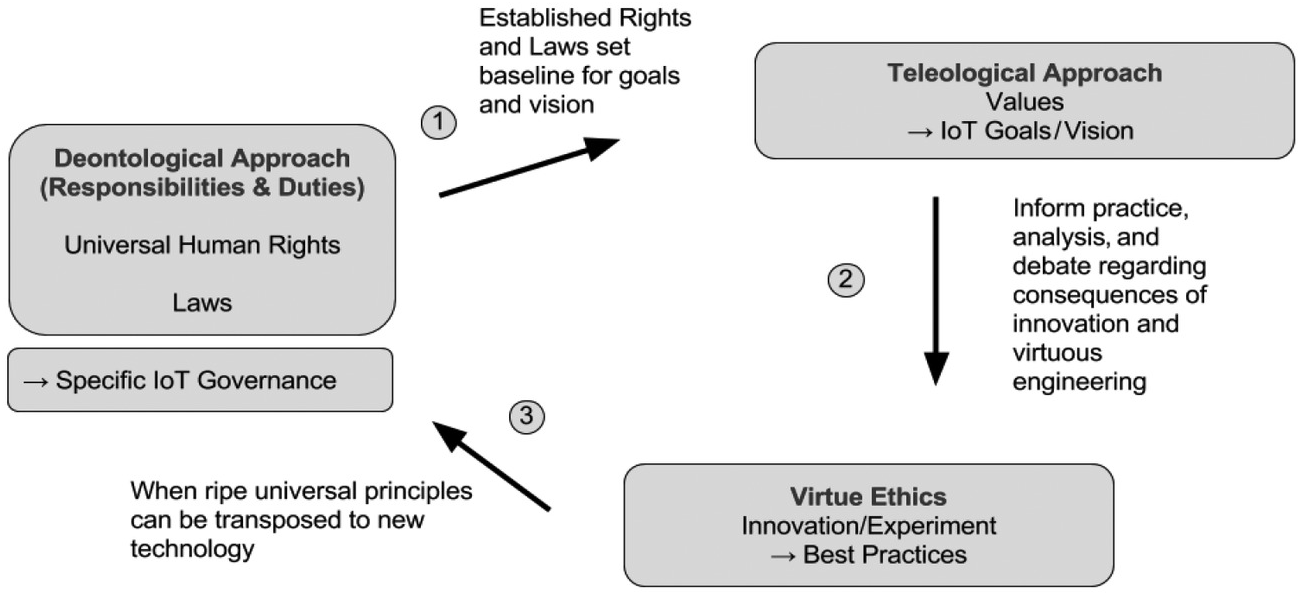
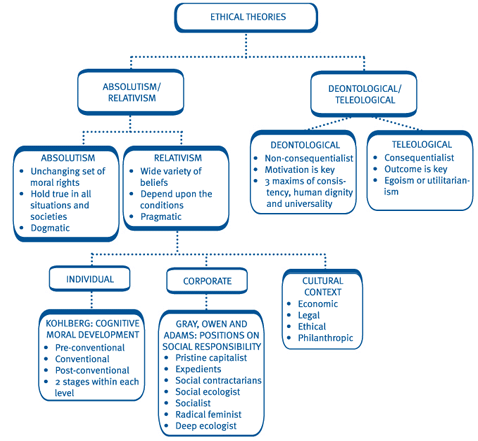
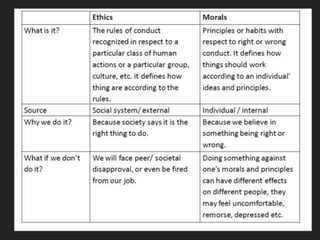
Deontological and teleological approaches to ethics are two distinct ethical frameworks that can be used to evaluate the morality of actions and decisions. Deontological ethics, also known as duty ethics or deontology, is a moral theory that asserts that the moral worth of an action is determined by whether it conforms to a set of rules or duties. These duties are considered to be fundamental and absolute, and they may be based on principles such as the respect for the autonomy of others or the promotion of the common good.
On the other hand, teleological ethics, also known as consequentialist ethics, is a moral theory that holds that the moral worth of an action is determined by its consequences. According to teleological ethics, the right action is the one that leads to the best overall consequences, regardless of whether it conforms to any particular set of rules or duties. Teleological ethics is often associated with utilitarianism, a moral theory that holds that the right action is the one that maximizes happiness or well-being for the greatest number of people.
Both deontological and teleological approaches to ethics have their own strengths and weaknesses. Deontological ethics is often praised for its emphasis on the inherent value of human beings and the importance of respecting their autonomy. It also provides clear and objective guidelines for moral decision-making, which can be helpful in situations where the consequences of an action are uncertain or difficult to predict.
However, deontological ethics can also be criticized for being inflexible and for failing to take into account the specific circumstances of a situation. For example, a deontological approach might require an individual to follow a certain duty or rule even if doing so leads to negative consequences for others.
Teleological ethics, on the other hand, is often praised for its focus on maximizing the overall well-being of individuals and society. It allows for flexibility and takes into account the specific circumstances of a situation, allowing individuals to weigh the pros and cons of different actions and choose the one that leads to the best overall consequences.
However, teleological ethics can also be criticized for its focus on the ends rather than the means, which can lead to immoral or unethical actions being justified if they lead to desirable outcomes. Additionally, it can be difficult to predict and measure the consequences of an action, leading to subjectivity and disagreement about what is considered the "best" outcome.
In conclusion, deontological and teleological approaches to ethics are two distinct frameworks that can be used to evaluate the morality of actions and decisions. While each has its own strengths and weaknesses, both can be useful in different situations and it is important for individuals to consider both when making moral decisions.