Departmentation is the process of grouping activities into departments. It is a fundamental aspect of management that helps to organize and coordinate the activities of a business or organization. There are several types of departmentation that can be used, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. In this essay, we will explore the different types of departmentation and the role that it plays in management.
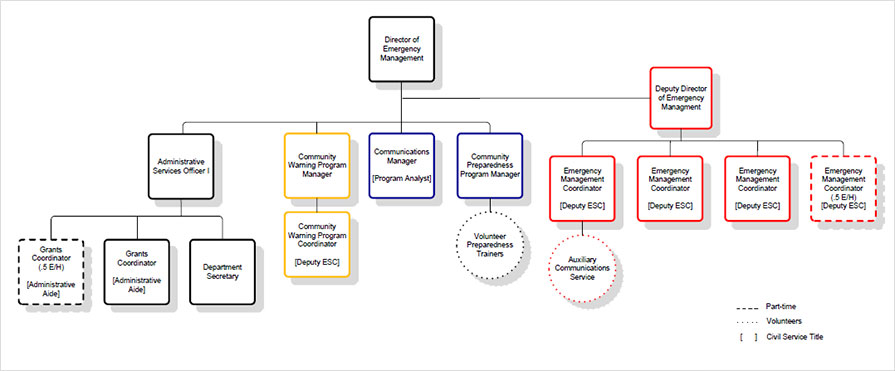
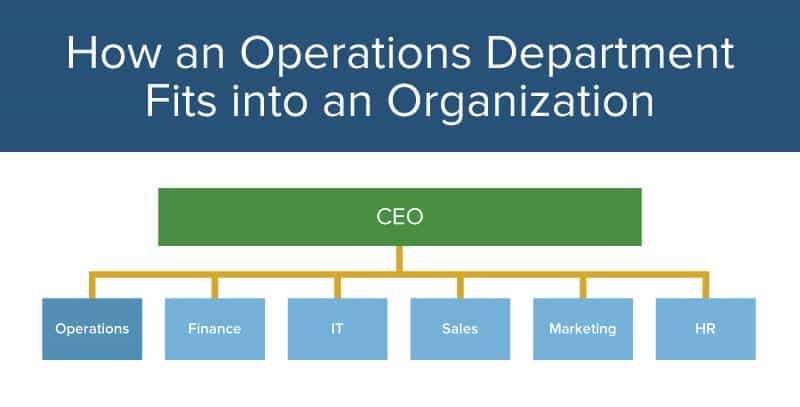
The most common type of departmentation is functional departmentation. This involves grouping activities based on the function or specialization of the work being done. For example, in a manufacturing company, there may be a production department, a marketing department, and a finance department. Each department is responsible for a specific set of activities and functions within the organization.
Functional departmentation has several advantages. It allows for specialization of knowledge and skills, as employees within a department are typically experts in their field. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity. It also allows for clear lines of authority and responsibility, as each department is headed by a manager who is responsible for the performance of the department.
However, functional departmentation can also have some limitations. It can lead to silos within the organization, as departments may become isolated and focused on their own goals and objectives. This can lead to a lack of coordination and communication between departments, which can hinder the overall performance of the organization.
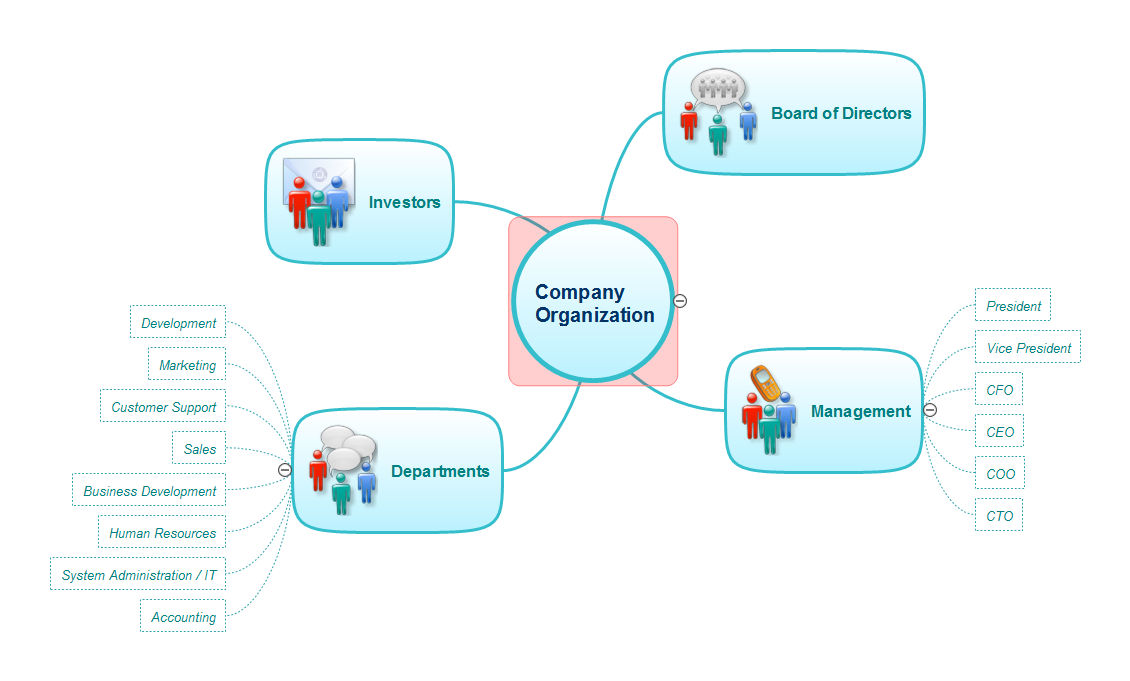
Another type of departmentation is divisional departmentation. This involves grouping activities based on the product or service being offered. For example, a company that manufactures both automobiles and airplanes may have separate divisions for each product line. Each division is responsible for its own sales, production, and finance activities.
Divisional departmentation allows for greater autonomy and decision-making authority within each division. It also allows for customization of products and services to meet the needs of specific markets or customer groups. However, it can also lead to duplication of resources and increased costs, as each division may have its own support functions such as finance or HR.
A third type of departmentation is matrix departmentation. This involves combining functional and divisional departmentation, creating a matrix structure where employees report to both a functional manager and a divisional manager. This can allow for increased coordination and communication between departments, as well as flexibility in the allocation of resources. However, it can also lead to confusion and conflict as employees may have conflicting goals and priorities.
In conclusion, departmentation is a key aspect of management that helps to organize and coordinate the activities of an organization. Different types of departmentation have their own benefits and limitations, and the best approach will depend on the specific needs and goals of the organization. It is important for managers to carefully consider the pros and cons of each approach and to choose the one that best fits the needs of the organization.