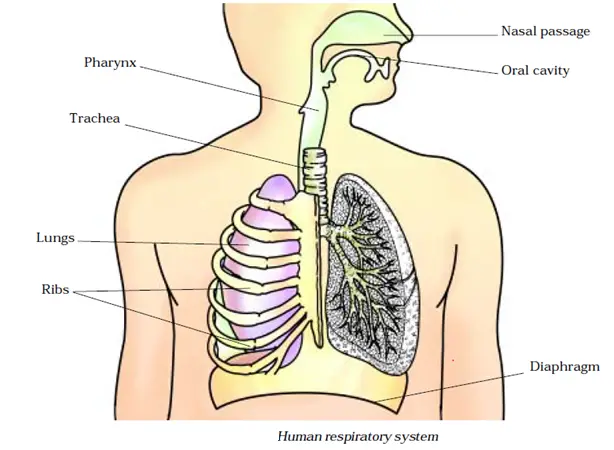
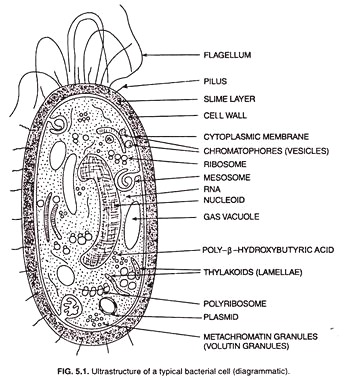
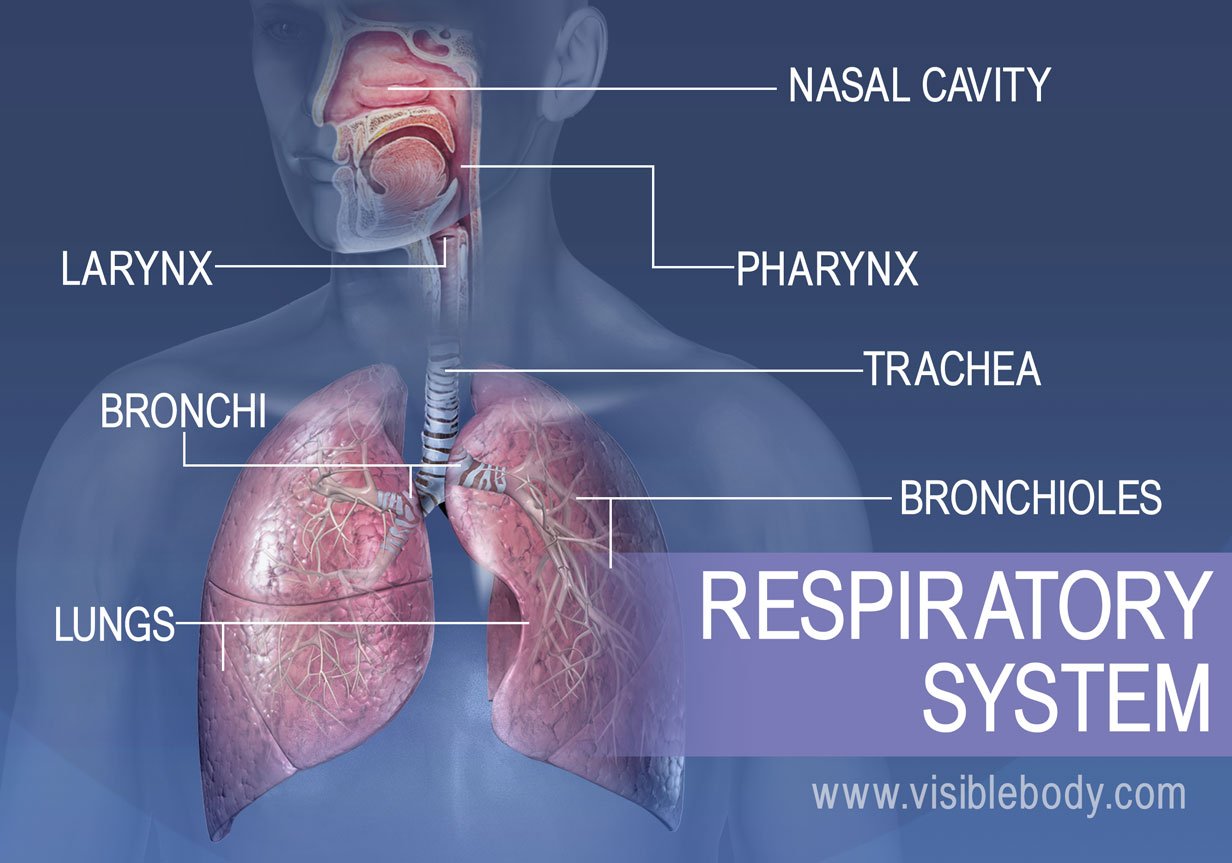
Respiration is the process by which living organisms produce energy from the nutrients they consume. It involves a series of chemical reactions that convert nutrients into a form that can be used by cells to power their various functions.
The most common type of respiration in animals and humans is aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell.
The first step of aerobic respiration is glycolysis, which breaks down glucose (a simple sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate. This process releases a small amount of energy and produces a molecule called NADH, which will be used later in the process to produce more energy.
The pyruvate is then transported into the mitochondria, where it is further broken down through a process called the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle. This process releases even more energy and produces additional NADH molecules.
The final step of aerobic respiration is the electron transport chain, which uses the energy from the NADH molecules to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell and is used to power all the cell's functions.
In the absence of oxygen, cells can use anaerobic respiration, which does not require oxygen but is less efficient at producing energy. One example of anaerobic respiration is fermentation, which is used by yeast and some bacteria to produce energy.
Overall, respiration is a vital process that allows living organisms to produce the energy they need to survive and thrive. It is a complex process that involves multiple steps and relies on the efficient functioning of various cellular structures and chemical reactions.