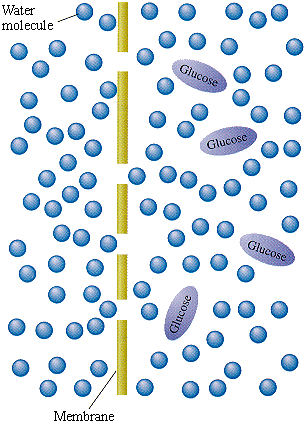
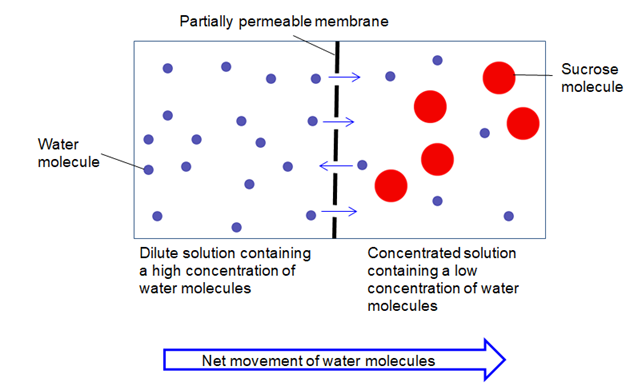
Osmosis is the movement of a solvent, such as water, across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. It is an important process that occurs in cells and helps to maintain homeostasis, or balance, within the cell.
The process of osmosis begins with a solution that contains a solvent and solute, such as salt dissolved in water. When this solution is separated from a pure solvent, such as water, by a semi-permeable membrane, the solvent will begin to move across the membrane in order to equalize the solute concentration on both sides.
The movement of the solvent across the membrane is driven by a concentration gradient, or a difference in solute concentration between the two sides of the membrane. If the concentration of solute is higher on one side of the membrane, the solvent will move from the side with a lower concentration of solute to the side with a higher concentration. This movement will continue until the concentration of solute is equal on both sides of the membrane.
The rate of osmosis can be affected by several factors, including the size of the solute molecules, the surface area of the membrane, and the pressure applied to the solution. Smaller solute molecules are able to pass through the membrane more easily, while larger solute molecules may be restricted. Increasing the surface area of the membrane also increases the rate of osmosis, as there is more space for the solvent to pass through. Finally, applying pressure to the solution can also affect the rate of osmosis, as it can push the solvent across the membrane.
In cells, osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. For example, if a cell is placed in a solution with a higher concentration of solute, water will move out of the cell in order to equalize the solute concentration. This can cause the cell to shrink, a process known as crenation. Conversely, if the cell is placed in a solution with a lower concentration of solute, water will move into the cell, causing it to swell. This can be dangerous for the cell if it swells too much, as the cell membrane may burst.
Overall, osmosis is a fundamental process that occurs in cells and helps to maintain balance within the cell. It is driven by the concentration gradient of solute across a semi-permeable membrane and is affected by several factors, including the size of the solute molecules, the surface area of the membrane, and the pressure applied to the solution. Understanding osmosis is important for a variety of fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine.